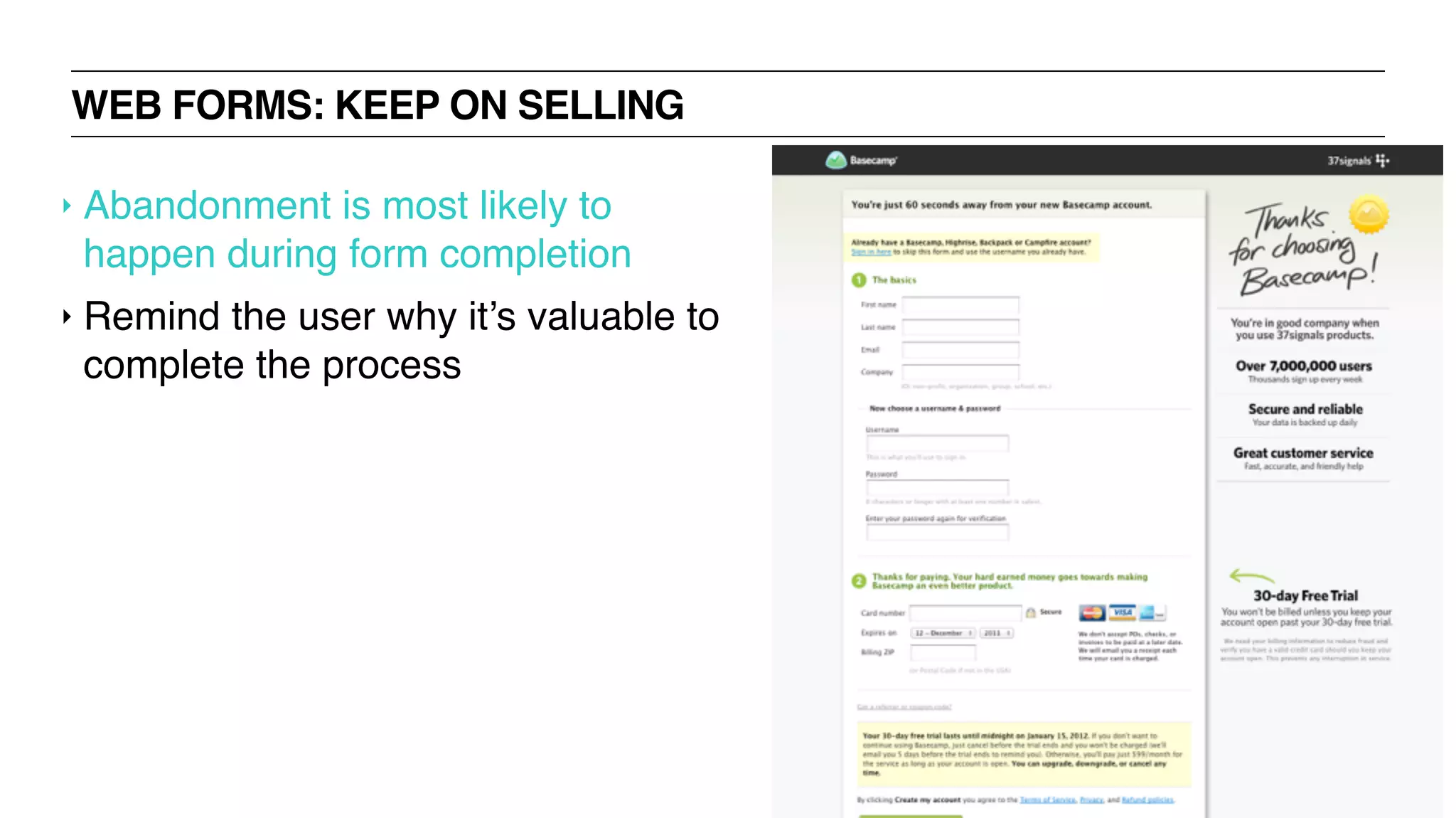
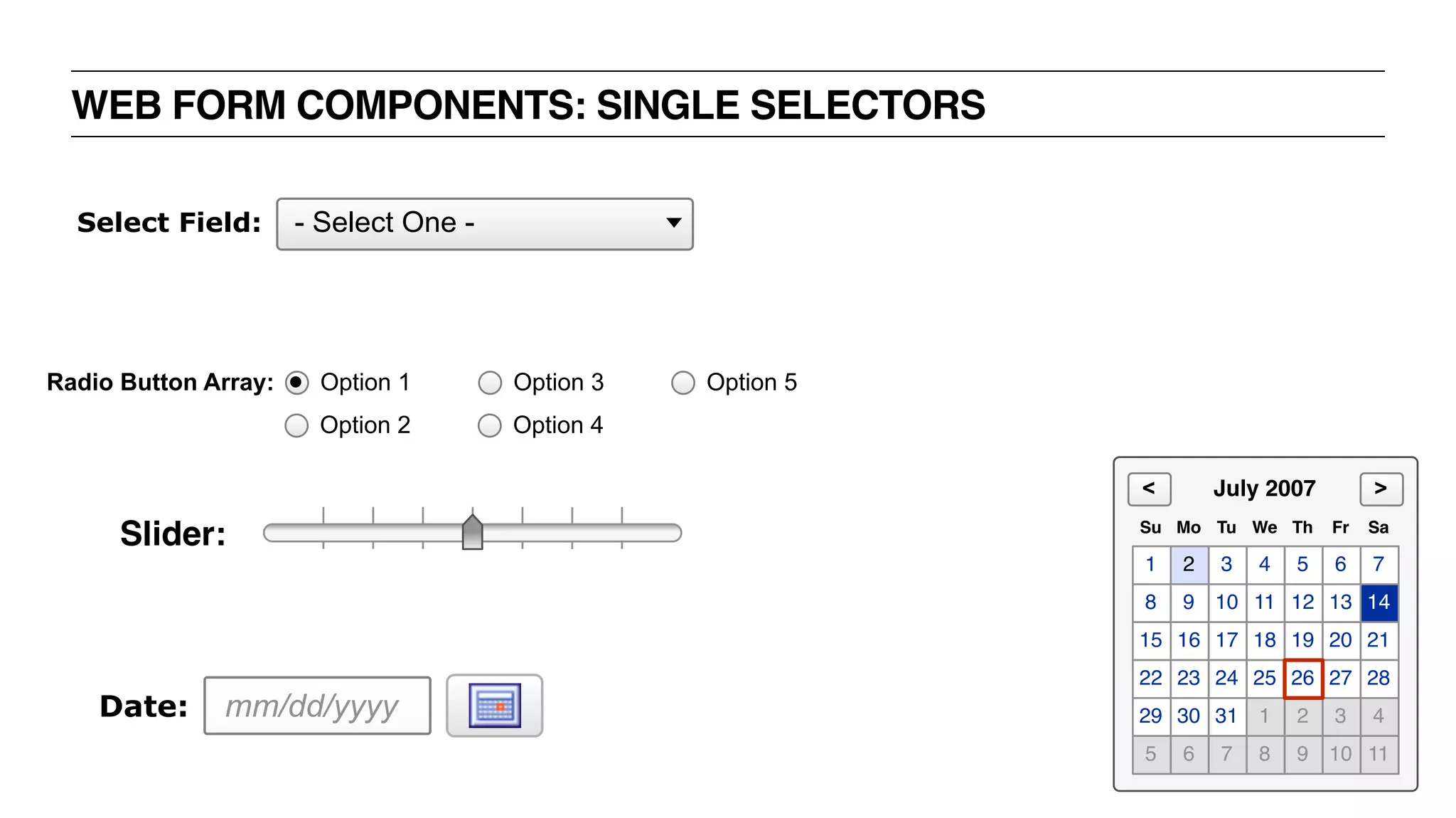
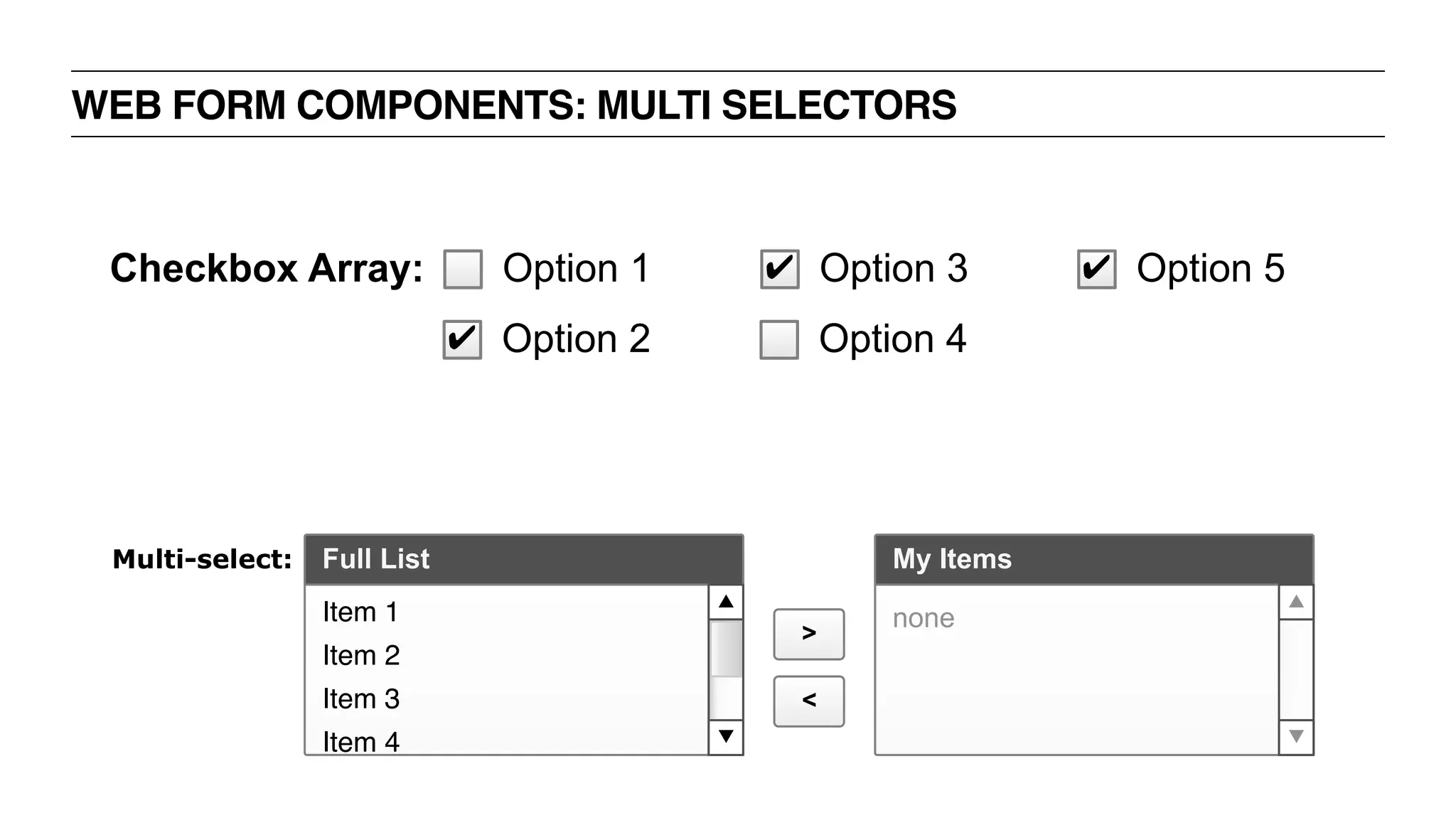
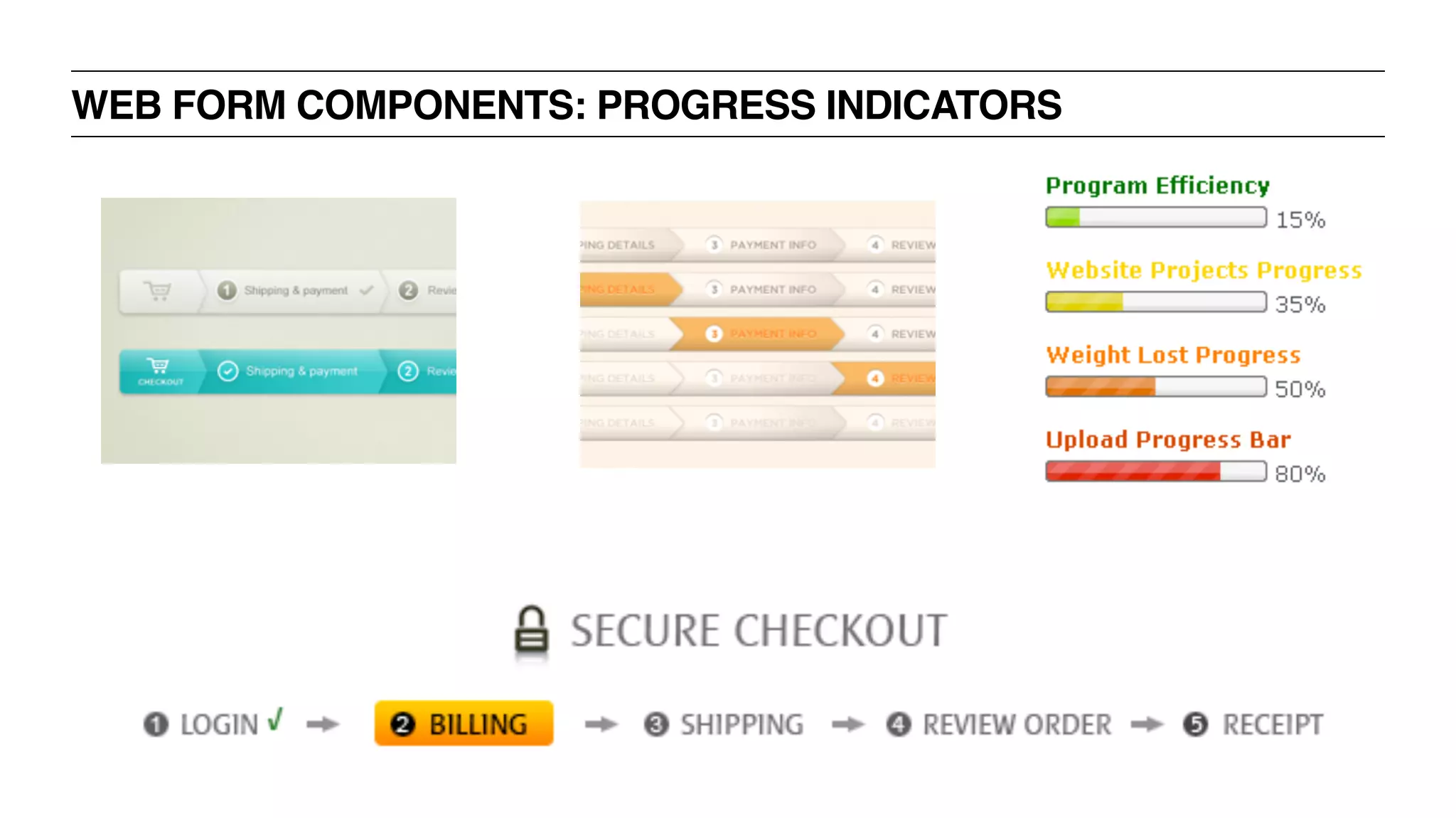
The document outlines the content and structure of a UX bootcamp led by Jacklyn Burgan, covering user experience design, usability, and various roles within the UX field. It discusses the UX process, research methods, user interviewing techniques, and the importance of understanding user needs, as well as creating personas and employing various methodologies for UX design. The bootcamp aims to equip participants with essential knowledge and skills for effective user experience practices.





![‣ Describe the field of UX + how it relates to other disciplines
‣ Identify the different roles within UX + the responsibilities of each
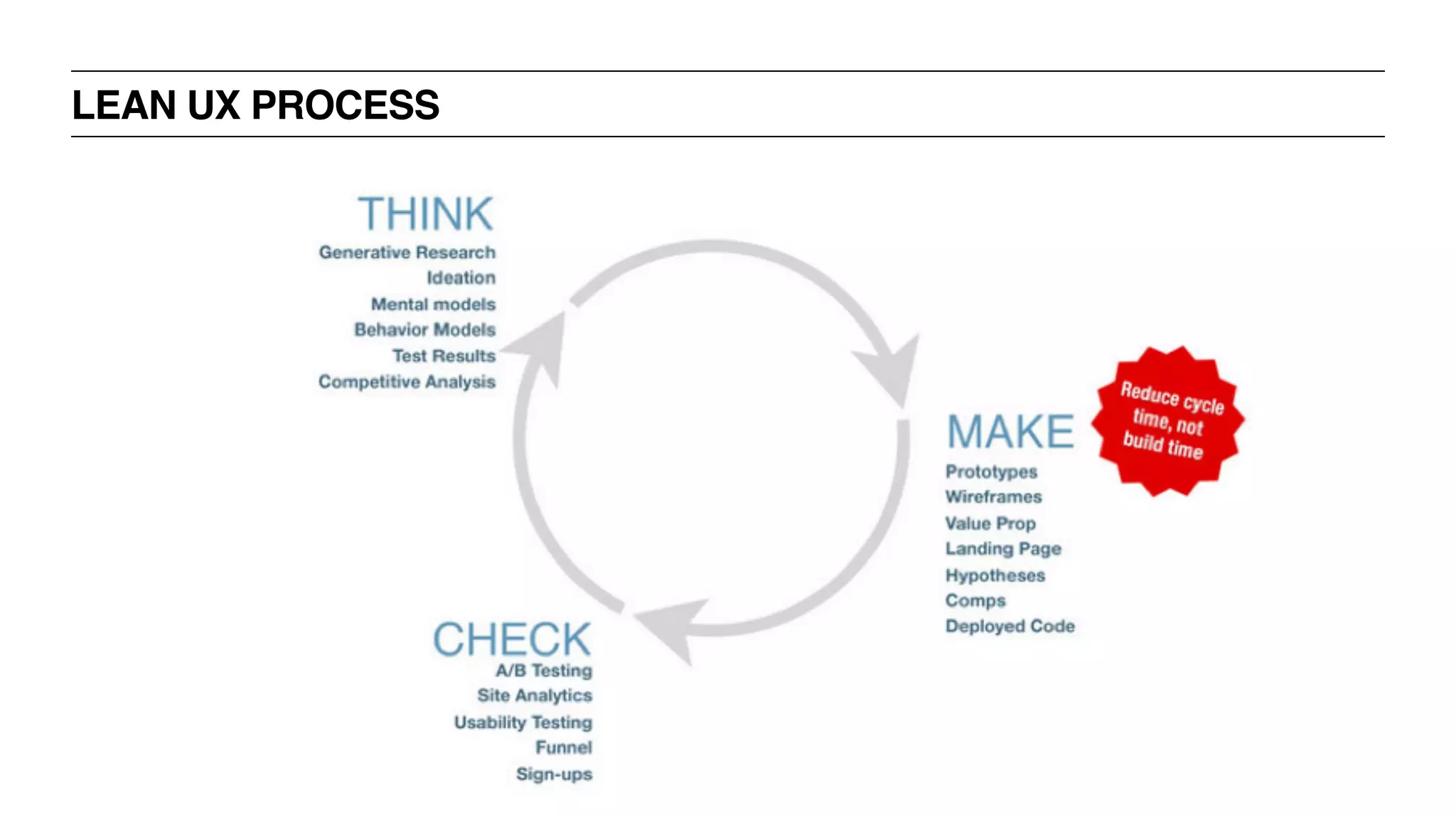
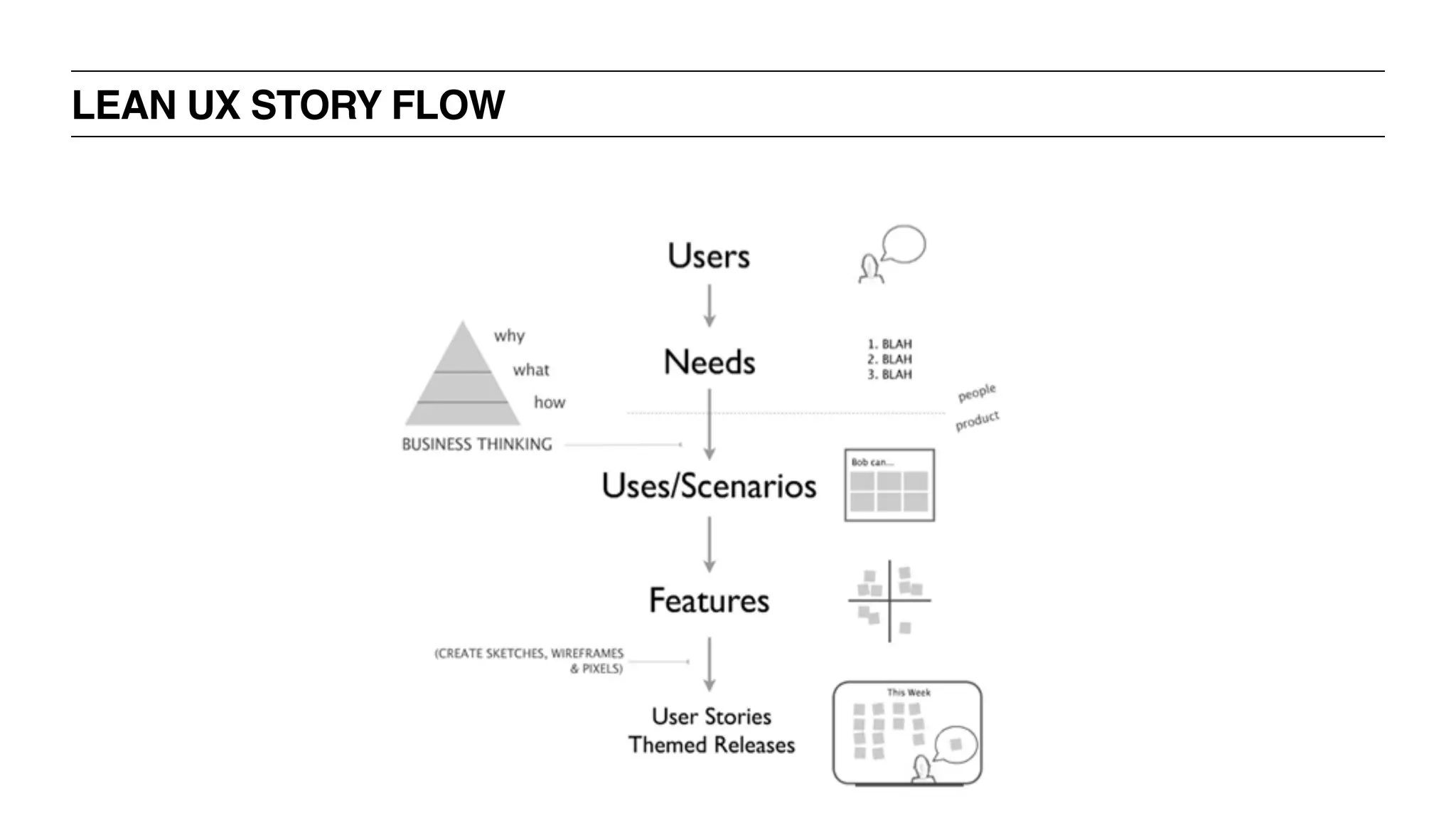
‣ UX Process: Traditional [“Waterfall”], Agile, Lean
‣ Learn to conduct UX research
LEARNING OBJECTIVES](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uxbootcamp-150316101953-conversion-gate01/75/UX-Bootcamp-General-Assembly-Atlanta-7-2048.jpg)
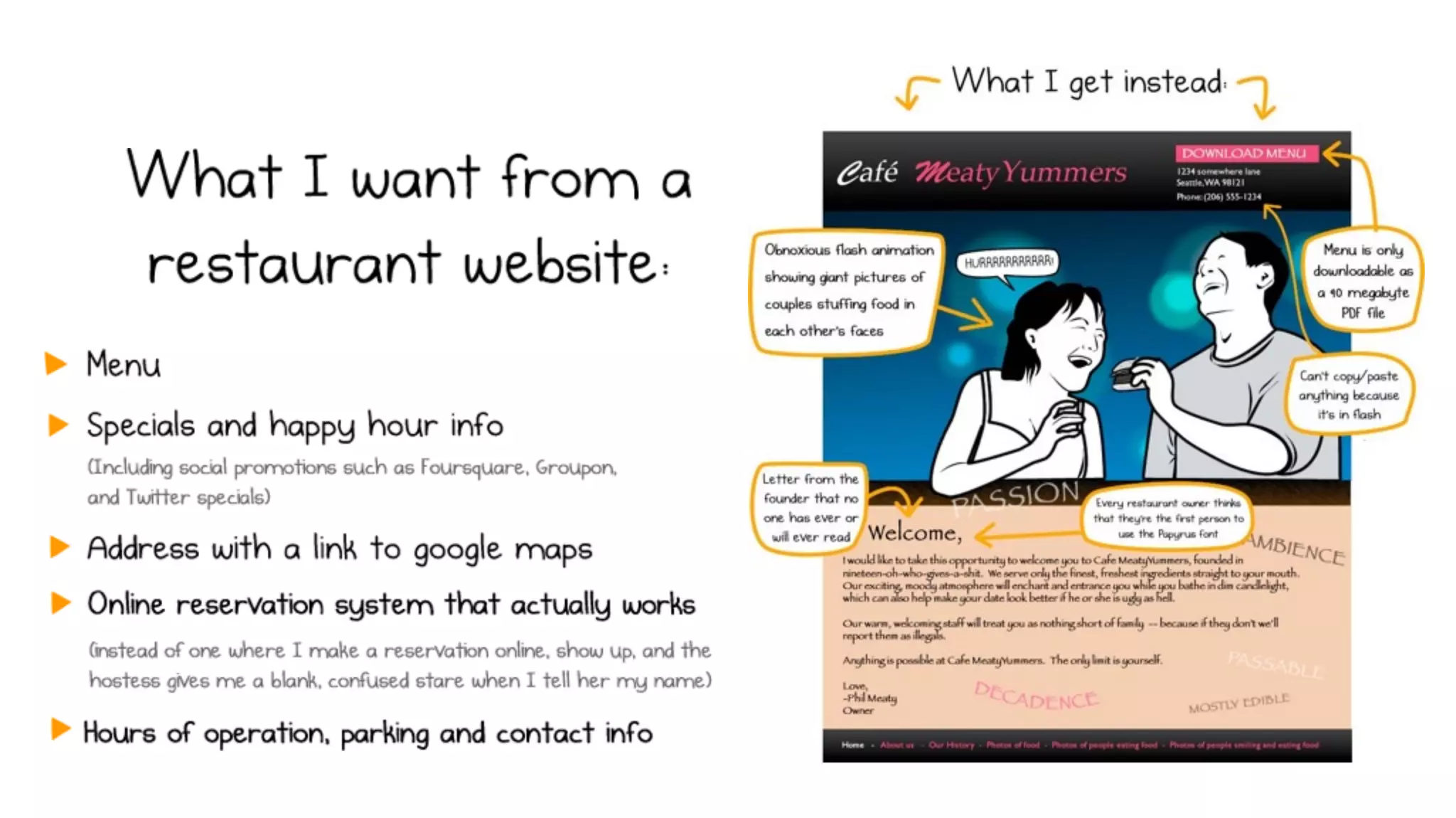
![WHAT IS USER EXPERIENCE DESIGN [UXD]?
“User experience design (UXD or UED) is the process of enhancing user
satisfaction by improving the usability, ease of use, and pleasure provided in the
interaction between the user and the product.” — Wikipedia
“The design of anything independent of medium or across [device] with human
experience as an explicit outcome and human engagement as an explicit goal”
— Jesse James Garrett, co-founder of Adaptive Path
“User experience encompasses all aspects of the end-user's interaction with the
company, its services, and its products.” — Nielsen Norman Group](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uxbootcamp-150316101953-conversion-gate01/75/UX-Bootcamp-General-Assembly-Atlanta-8-2048.jpg)


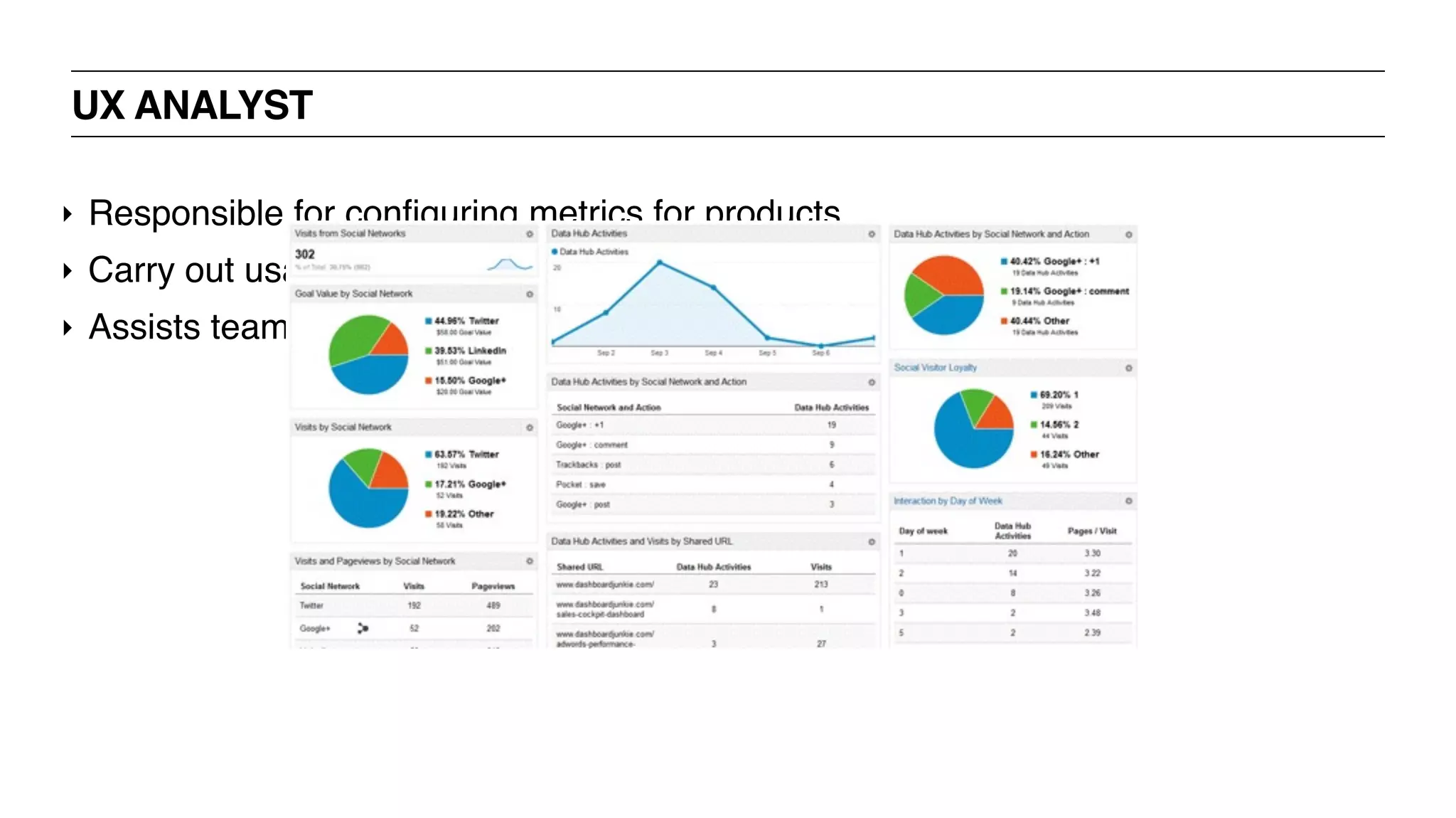
![UX JOBS + RESPONSIBILITIES: BLUEPRINT
‣ UX Designer
‣ Experience Designer
‣ Interaction Designer [IxD]
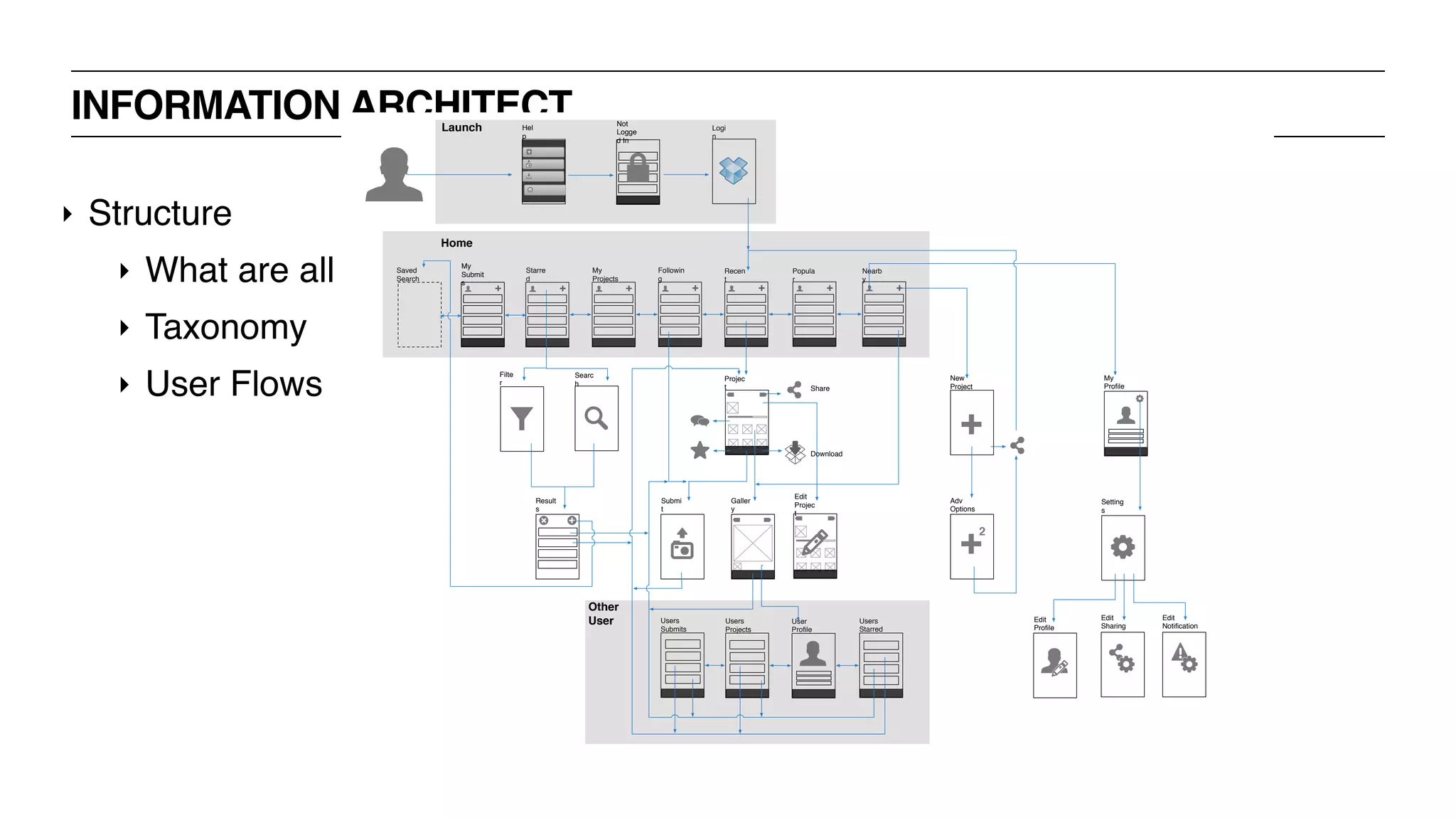
‣ Information Architect [IA]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uxbootcamp-150316101953-conversion-gate01/75/UX-Bootcamp-General-Assembly-Atlanta-11-2048.jpg)
![INTERACTION DESIGNER [IXD]
‣ Focus only on the interaction between the human + the computer
‣ Designing for affordances](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uxbootcamp-150316101953-conversion-gate01/75/UX-Bootcamp-General-Assembly-Atlanta-12-2048.jpg)
![INTERACTION DESIGNER [IXD]
‣ Focus only on the interaction between the human + the computer
‣ Designing for affordances](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uxbootcamp-150316101953-conversion-gate01/75/UX-Bootcamp-General-Assembly-Atlanta-13-2048.jpg)
![INTERACTION DESIGNER [IXD]
‣ Focus only on the interaction between the human + the computer
‣ Designing for affordances](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uxbootcamp-150316101953-conversion-gate01/75/UX-Bootcamp-General-Assembly-Atlanta-14-2048.jpg)
![INTERACTION DESIGNER [IXD]
‣ Focus only on the interaction between the human + the computer
‣ Designing for affordances](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uxbootcamp-150316101953-conversion-gate01/75/UX-Bootcamp-General-Assembly-Atlanta-15-2048.jpg)
![INTERACTION DESIGNER [IXD]
‣ Focus only on the interaction between the human + the computer
‣ Designing for affordances](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uxbootcamp-150316101953-conversion-gate01/75/UX-Bootcamp-General-Assembly-Atlanta-16-2048.jpg)
![INTERACTION DESIGNER [IXD]
‣ Focus only on the interaction between the human + the computer
‣ Designing for affordances](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uxbootcamp-150316101953-conversion-gate01/75/UX-Bootcamp-General-Assembly-Atlanta-17-2048.jpg)
![INTERACTION DESIGNER [IXD]
‣ Focus only on the interaction between the human + the computer
‣ Designing for affordances](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uxbootcamp-150316101953-conversion-gate01/75/UX-Bootcamp-General-Assembly-Atlanta-18-2048.jpg)
![INTERACTION DESIGNER [IXD]
‣ Focus only on the interaction between the human + the computer
‣ Designing for affordances](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uxbootcamp-150316101953-conversion-gate01/75/UX-Bootcamp-General-Assembly-Atlanta-19-2048.jpg)
![INTERACTION DESIGNER [IXD]
‣ Focus only on the interaction between the human + the computer
‣ Designing for affordances](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uxbootcamp-150316101953-conversion-gate01/75/UX-Bootcamp-General-Assembly-Atlanta-20-2048.jpg)
![INTERACTION DESIGNER [IXD]
‣ Focus only on the interaction between the human + the computer
‣ Designing for affordances](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uxbootcamp-150316101953-conversion-gate01/75/UX-Bootcamp-General-Assembly-Atlanta-21-2048.jpg)
![INTERACTION DESIGNER [IXD]
‣ Focus only on the interaction between the human + the computer
‣ Designing for affordances](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uxbootcamp-150316101953-conversion-gate01/75/UX-Bootcamp-General-Assembly-Atlanta-22-2048.jpg)
![INTERACTION DESIGNER [IXD]
‣ Focus only on the interaction between the human + the computer
‣ Designing for affordances](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uxbootcamp-150316101953-conversion-gate01/75/UX-Bootcamp-General-Assembly-Atlanta-23-2048.jpg)
![INTERACTION DESIGNER [IXD]
‣ Focus only on the interaction between the human + the computer
‣ Designing for affordances](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uxbootcamp-150316101953-conversion-gate01/75/UX-Bootcamp-General-Assembly-Atlanta-24-2048.jpg)
![INTERACTION DESIGNER [IXD]
‣ Focus only on the interaction between the human + the computer
‣ Designing for affordances](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uxbootcamp-150316101953-conversion-gate01/75/UX-Bootcamp-General-Assembly-Atlanta-25-2048.jpg)
![INTERACTION DESIGNER [IXD]
‣ Focus only on the interaction between the human + the computer
‣ Designing for affordances](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uxbootcamp-150316101953-conversion-gate01/75/UX-Bootcamp-General-Assembly-Atlanta-26-2048.jpg)
![INTERACTION DESIGNER [IXD]
‣ Focus only on the interaction between the human + the computer
‣ Designing for affordances](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uxbootcamp-150316101953-conversion-gate01/75/UX-Bootcamp-General-Assembly-Atlanta-27-2048.jpg)
![INTERACTION DESIGNER [IXD]
‣ Focus only on the interaction between the human + the computer
‣ Designing for affordances](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uxbootcamp-150316101953-conversion-gate01/75/UX-Bootcamp-General-Assembly-Atlanta-28-2048.jpg)
![INTERACTION DESIGNER [IXD]
‣ Focus only on the interaction between the human + the computer
‣ Designing for affordances](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uxbootcamp-150316101953-conversion-gate01/75/UX-Bootcamp-General-Assembly-Atlanta-29-2048.jpg)












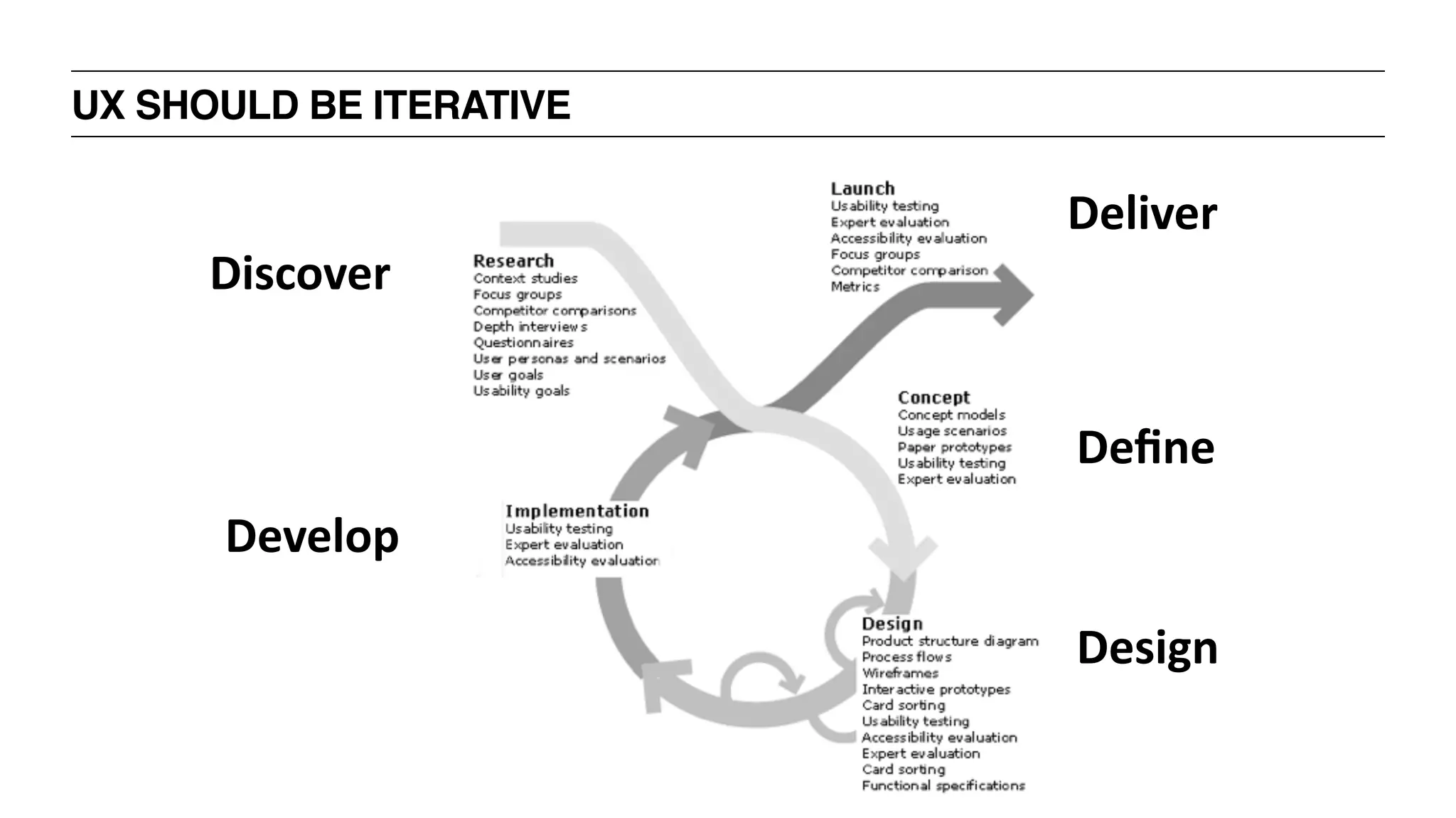
![TRADITIONAL UX PROCESS [“WATERFALL”]
‣ Discover
‣ Define
‣ Design
‣ Develop
‣ Deliver](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uxbootcamp-150316101953-conversion-gate01/75/UX-Bootcamp-General-Assembly-Atlanta-49-2048.jpg)























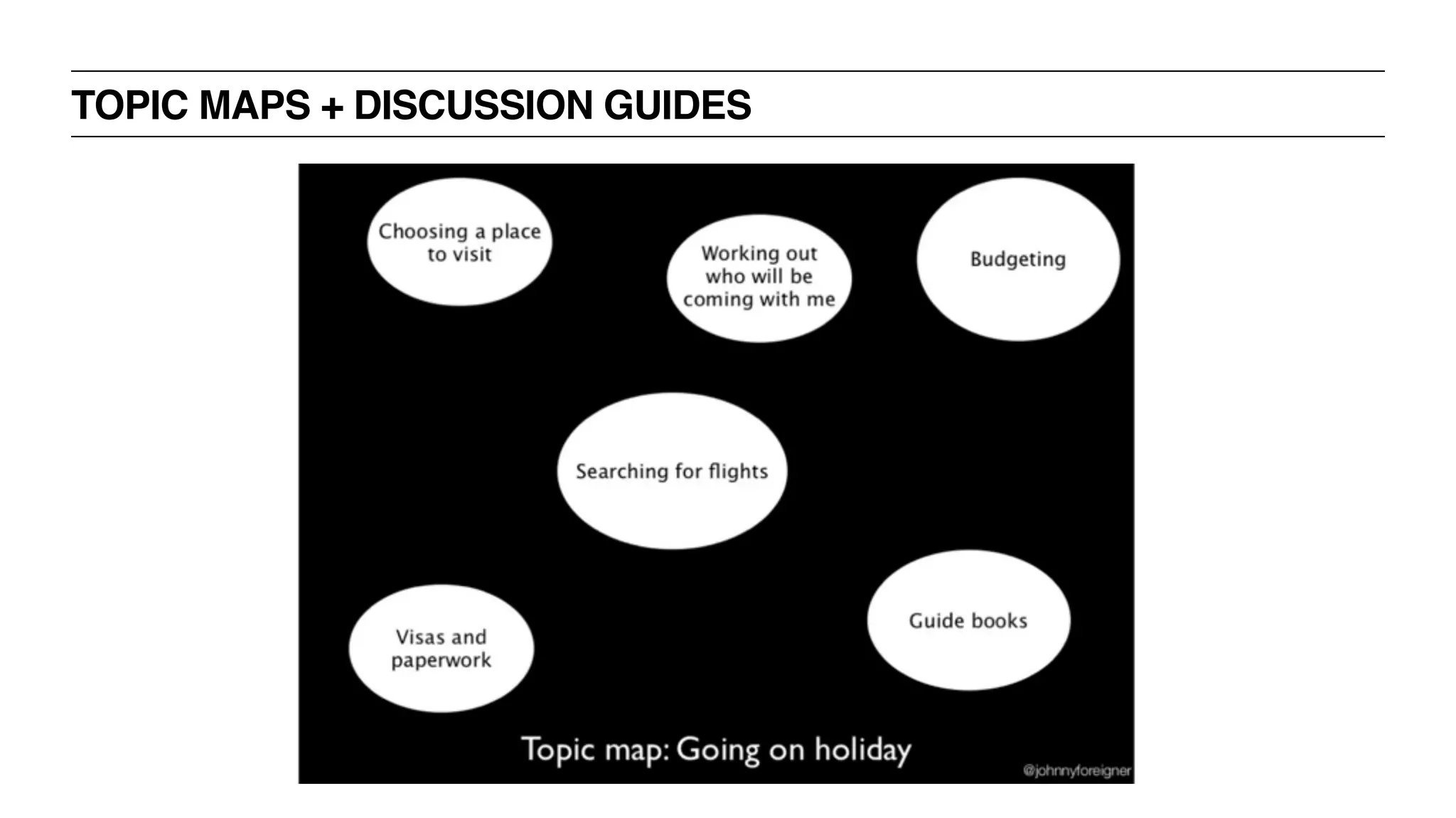
![TOPIC MAP EXERCISE! - 50 MINUTES
‣ You are going to do a user interview about online shopping in order to
better understand users’ fears + desires
‣ Prepare a topic map covering all subjects you want to know [20m]
‣ Split into groups of 3
‣ 1 person will interview, 1 will record notes on post it notes, 1 person
will be interviewed
‣ We will rotate every 10 minutes
‣ Be prepared to share!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uxbootcamp-150316101953-conversion-gate01/75/UX-Bootcamp-General-Assembly-Atlanta-81-2048.jpg)







![PERSONAS: WHY THEY’RE IMPORTANT
‣ Communication tool
‣ Useful for summarizing what you know about your user
‣ Will help to highlight pain points + opportunities to tailor your product to
your user
‣ Keep your product focused on your key users rather than building for the
whole world.
‣ [Keep in mind it’s just a framework, not a roadmap]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uxbootcamp-150316101953-conversion-gate01/75/UX-Bootcamp-General-Assembly-Atlanta-89-2048.jpg)
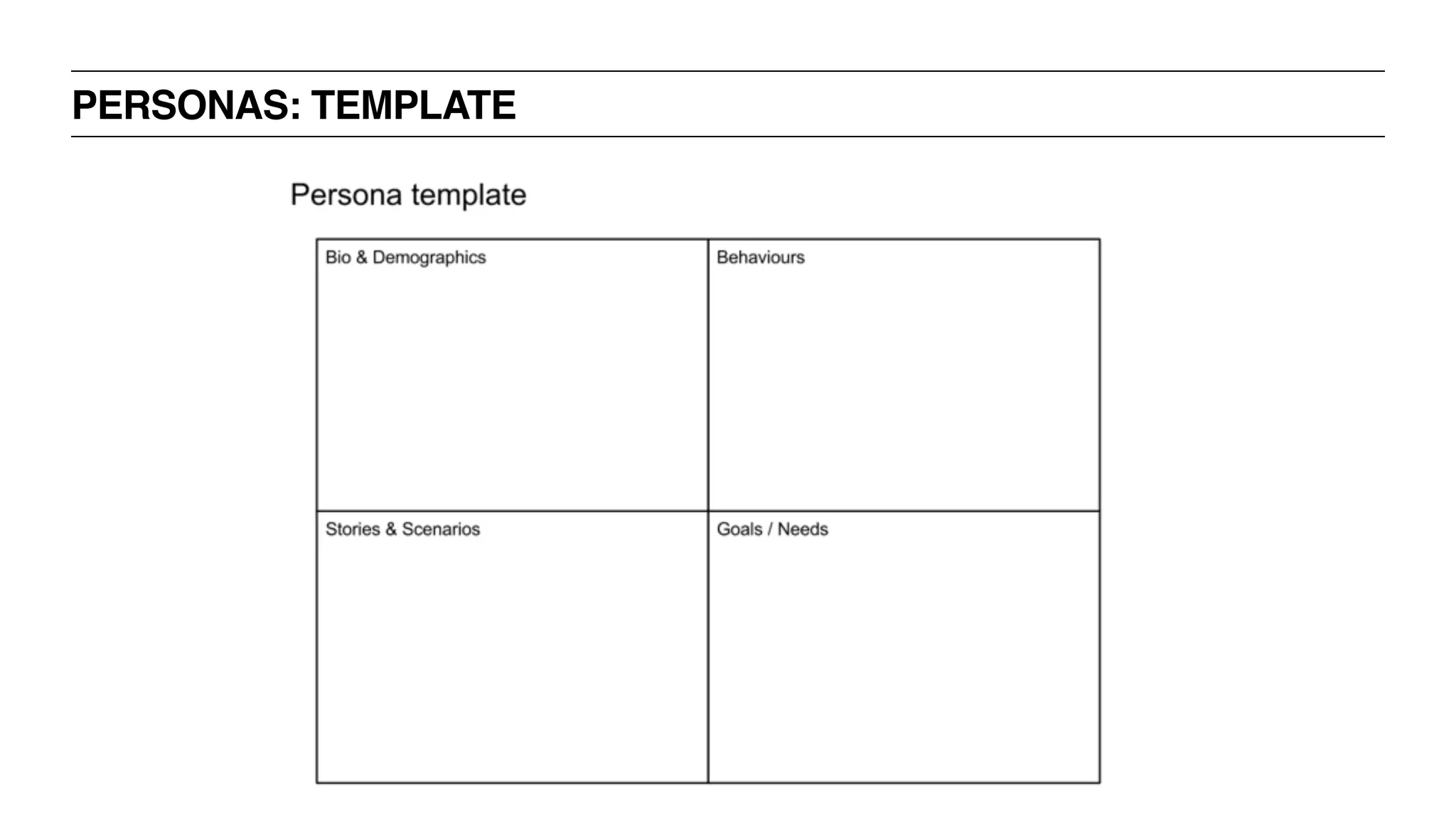
![PERSONAS: WHAT SHOULD BE INCLUDED
‣ Root it in reality not your imagination
‣ Goals / Needs
‣ Behaviors
‣ Biographical information [name, age, gender, location, income, etc]
‣ Optionally assign it personality traits [again, based on your research]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uxbootcamp-150316101953-conversion-gate01/75/UX-Bootcamp-General-Assembly-Atlanta-90-2048.jpg)





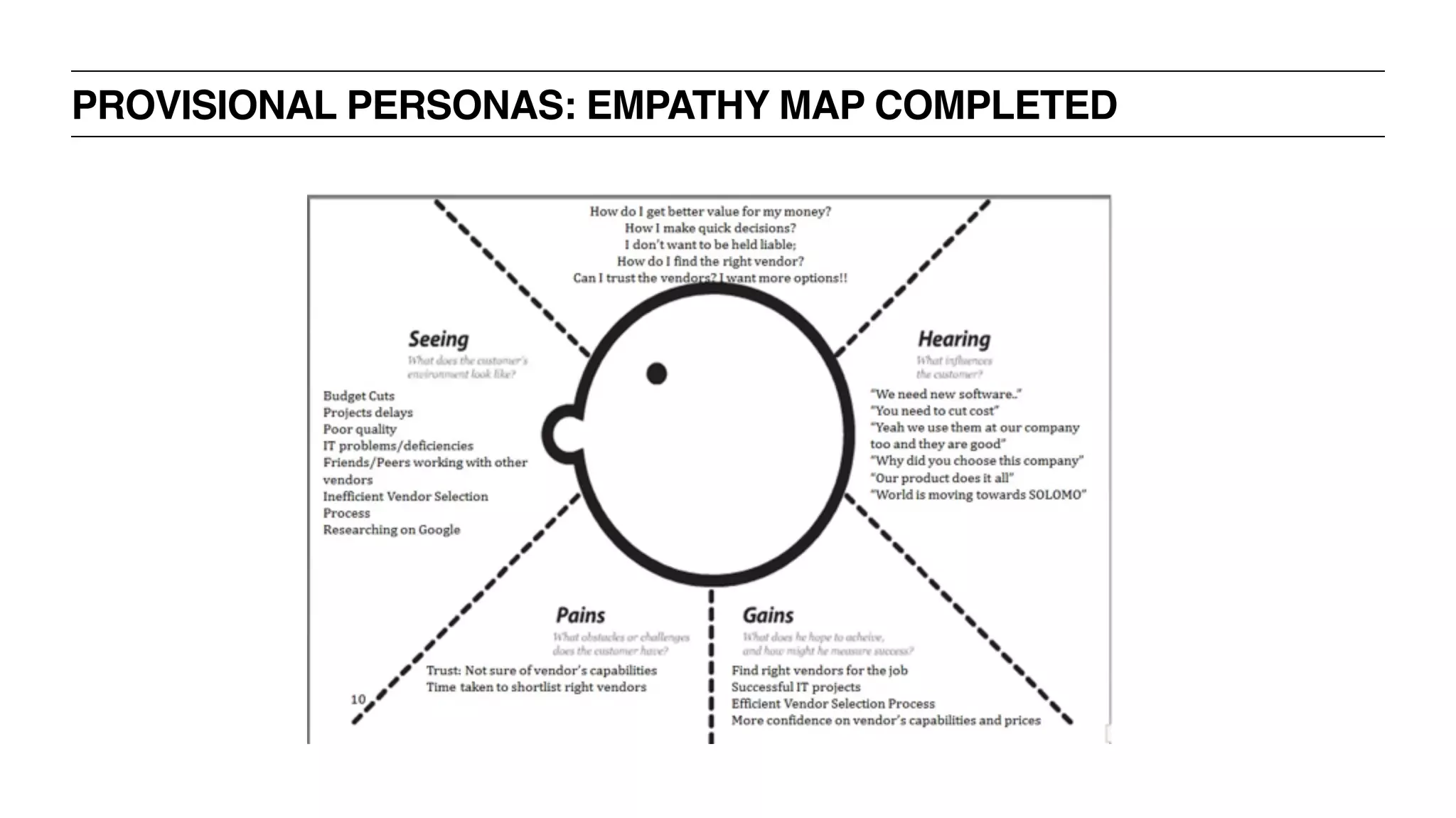

![PROVISIONAL PERSONAS: EMPATHY MAP
‣ What does she Think or Feel? [What matters?]
‣ What does she See? [environment, friends, solutions in the market]
‣ What does she Say + Do? [appearance, activities, behaviors]
‣ What does she Hear? [What do friends, boss, colleagues say?]
‣ Pain [fears, frustrations, obstacles]
‣ Goals [wants, needs, desires]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uxbootcamp-150316101953-conversion-gate01/75/UX-Bootcamp-General-Assembly-Atlanta-100-2048.jpg)