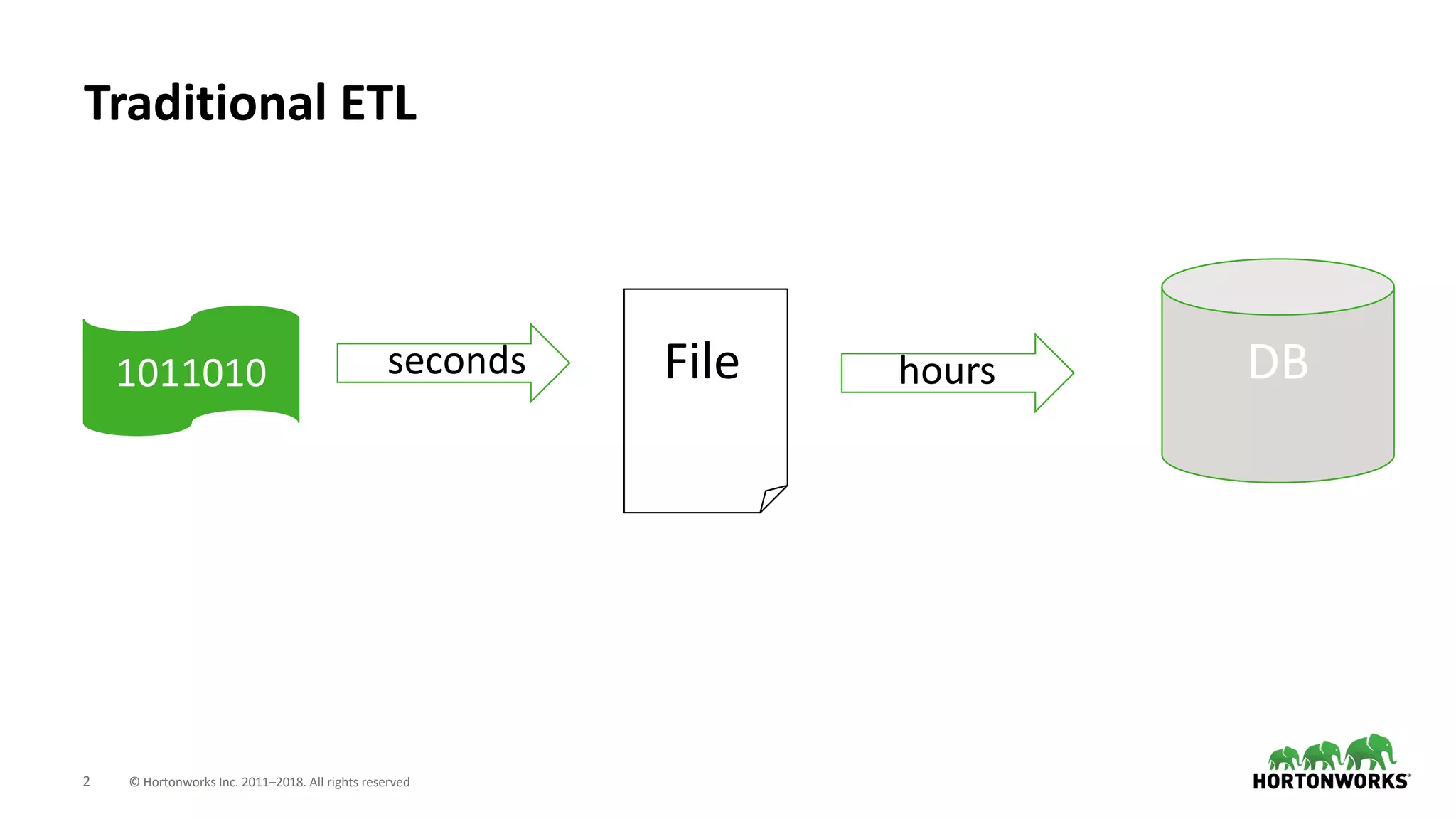
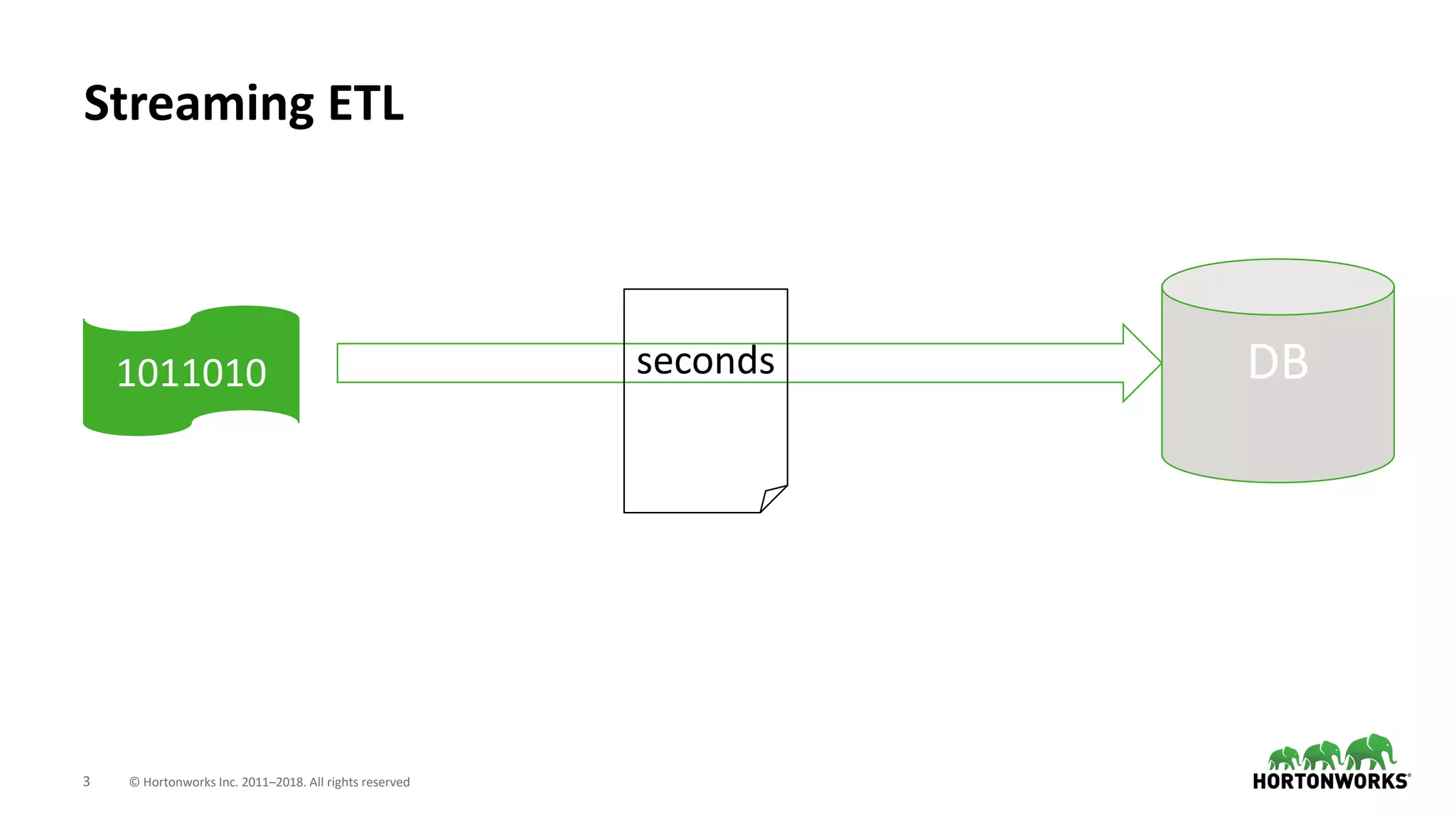
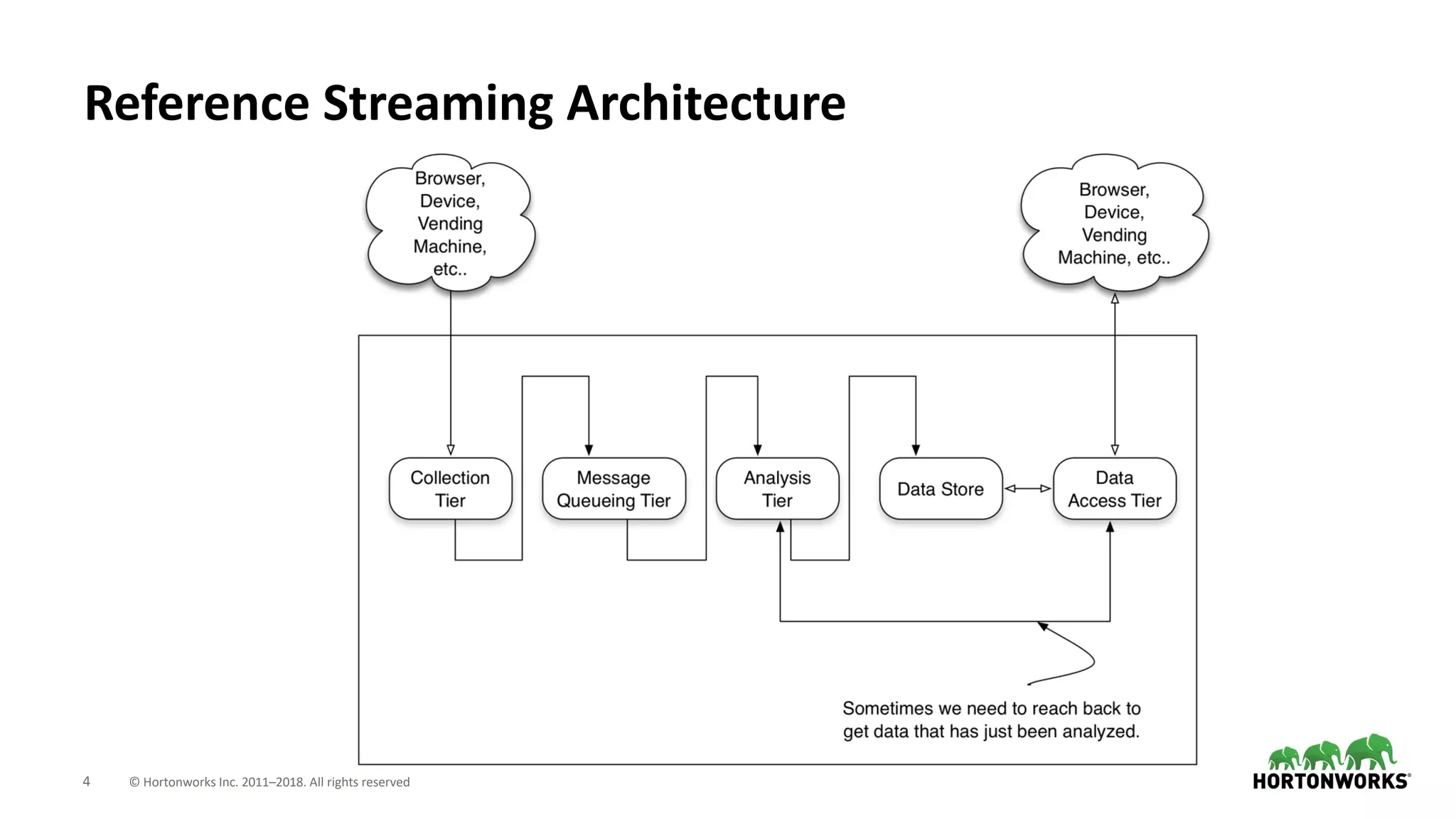
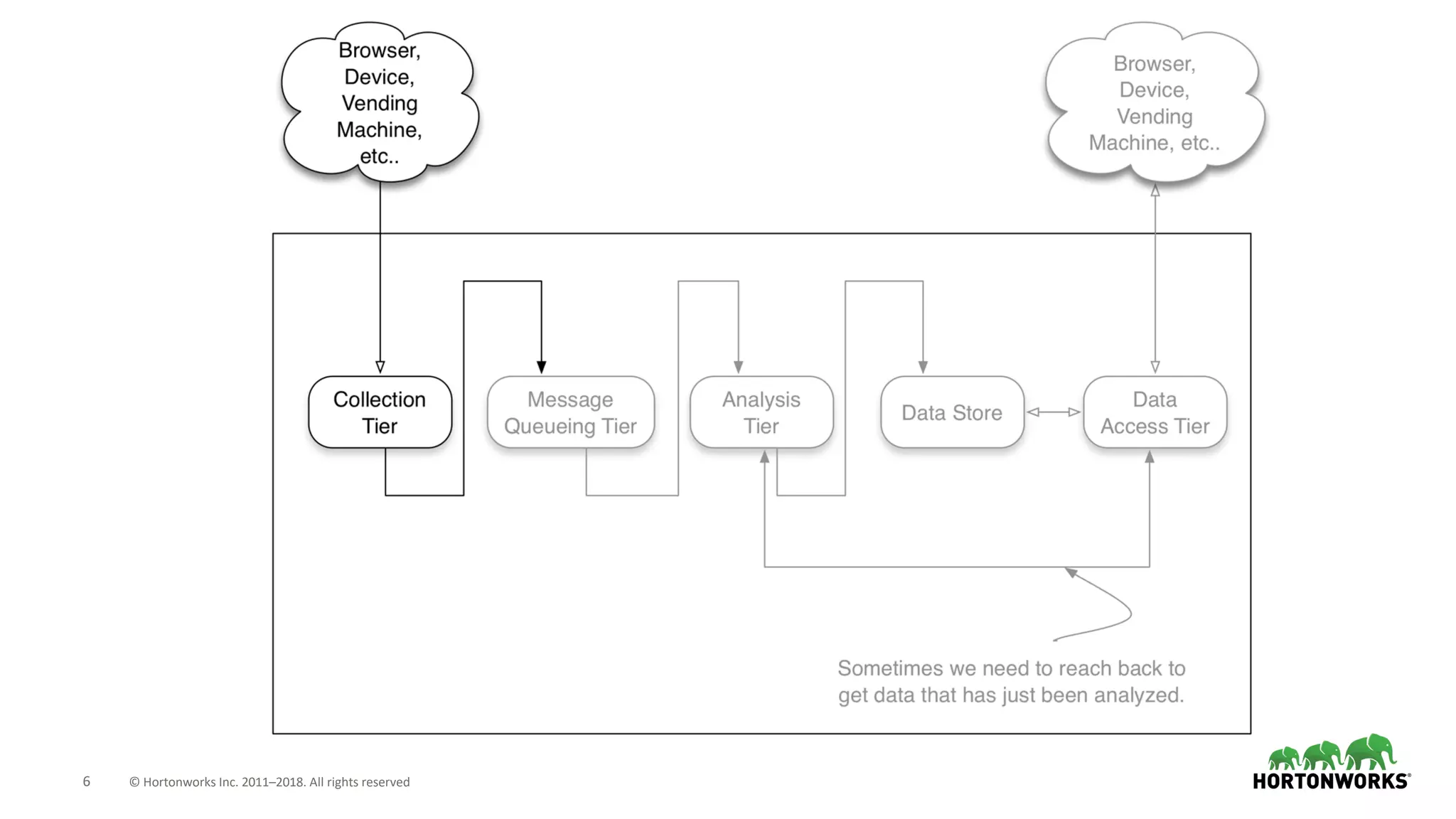
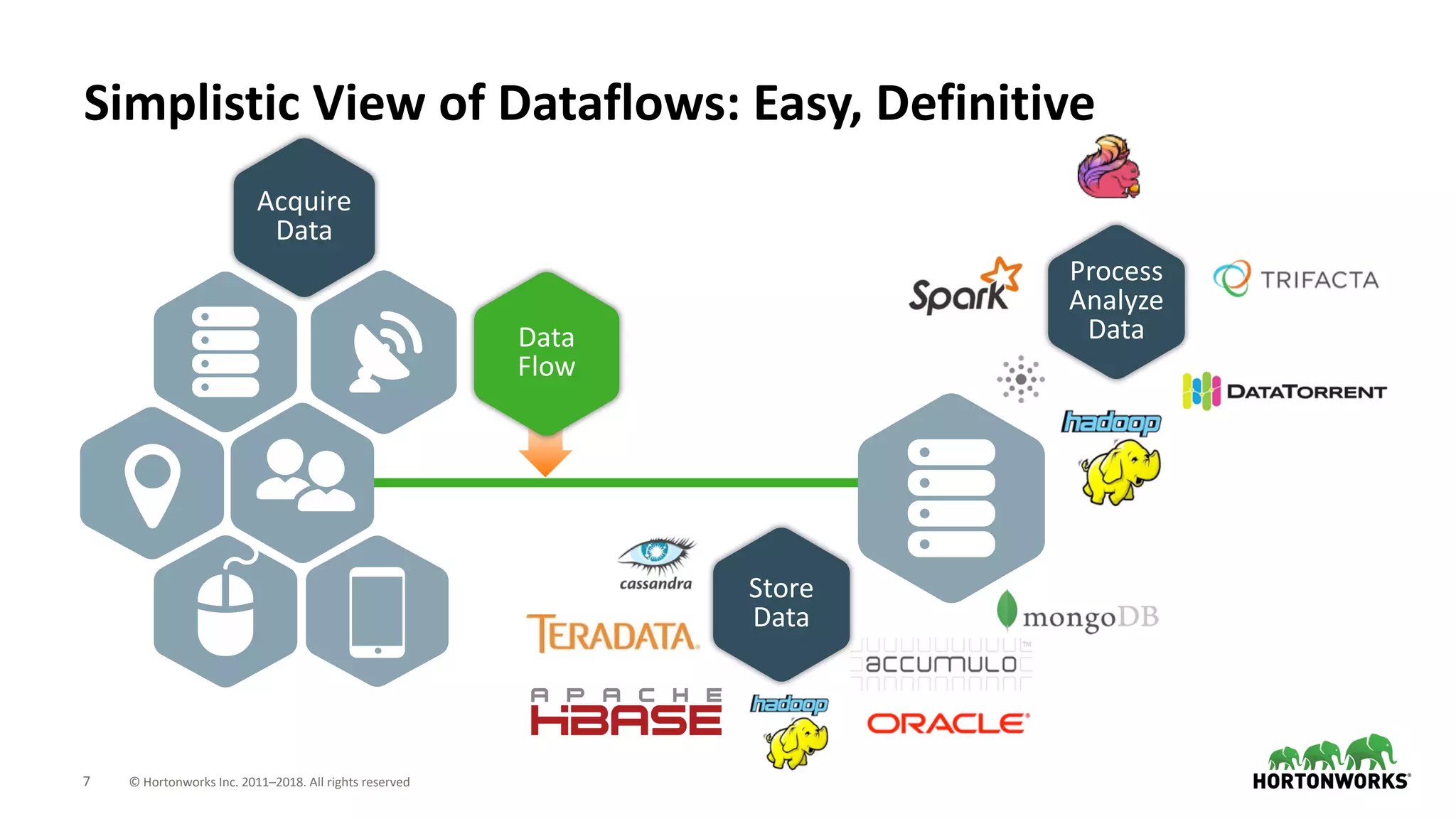
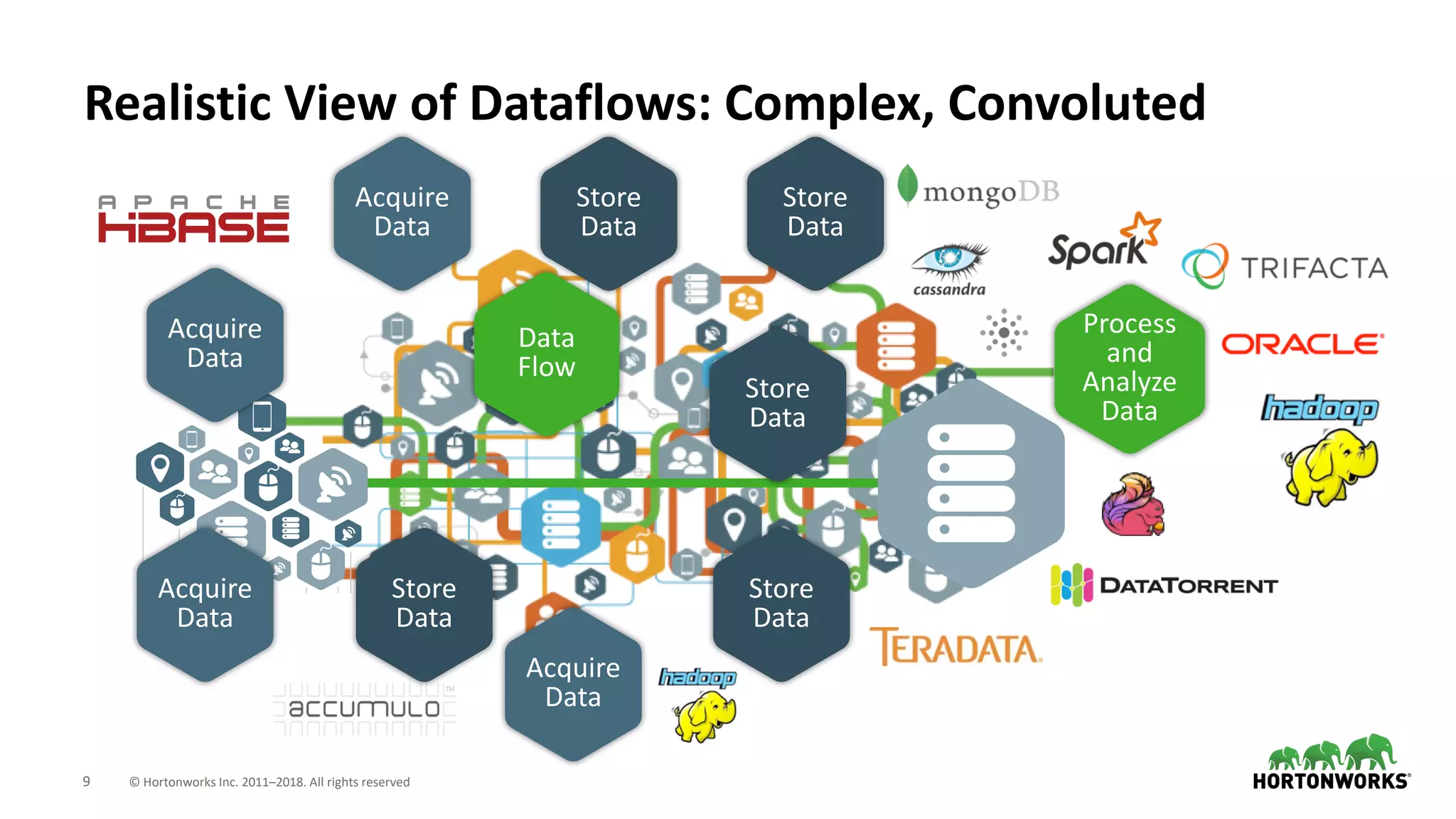
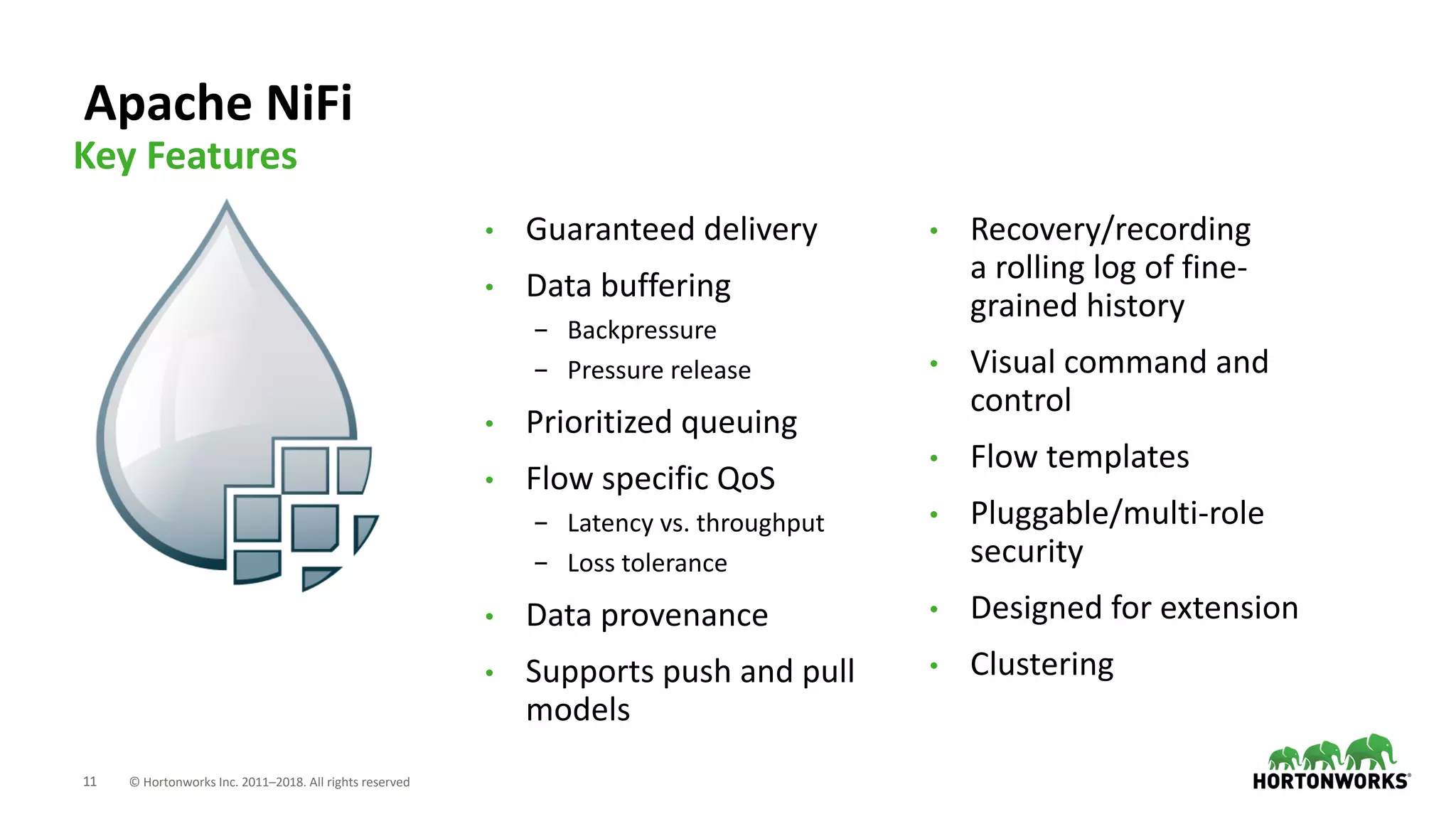
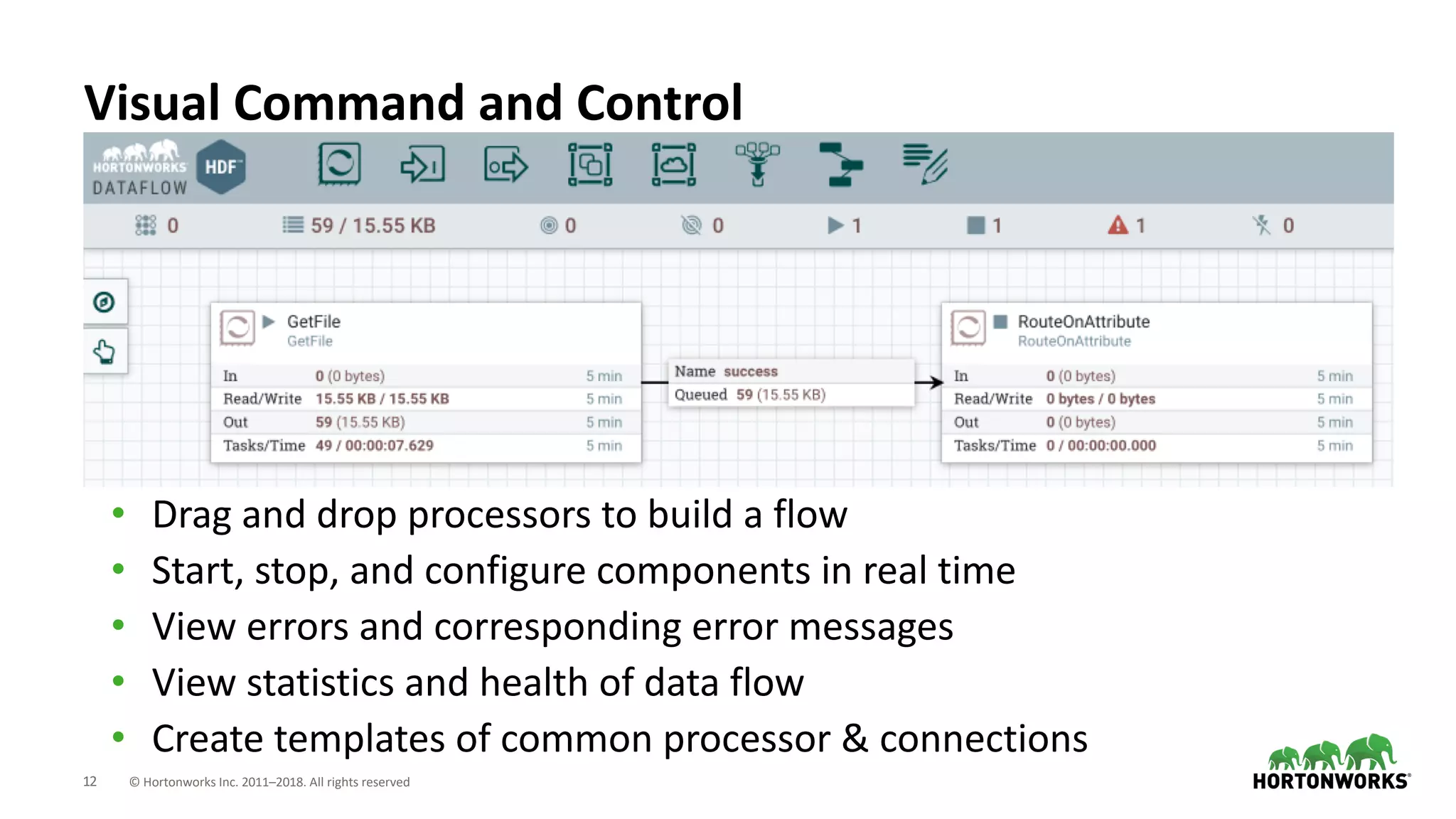
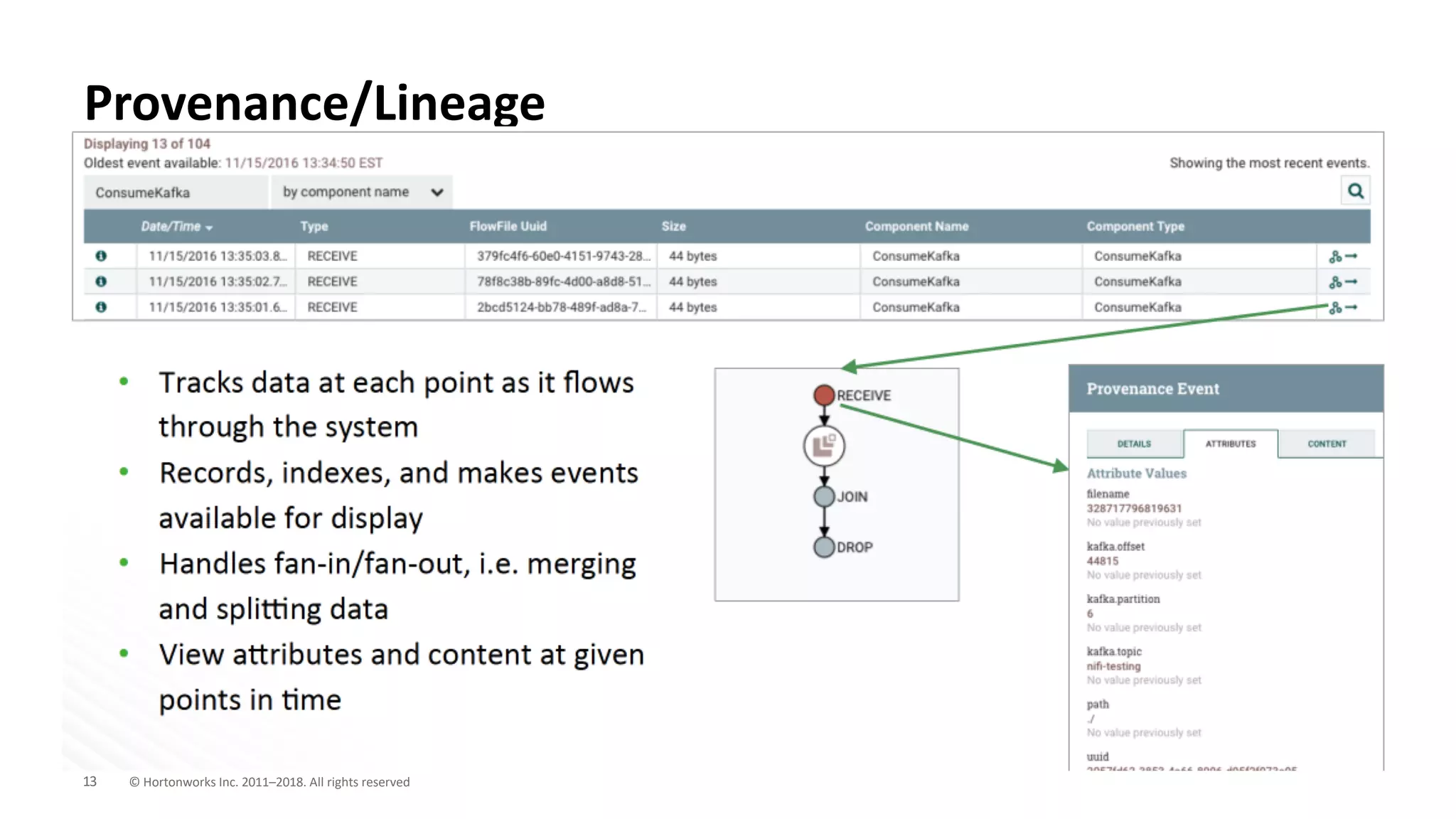
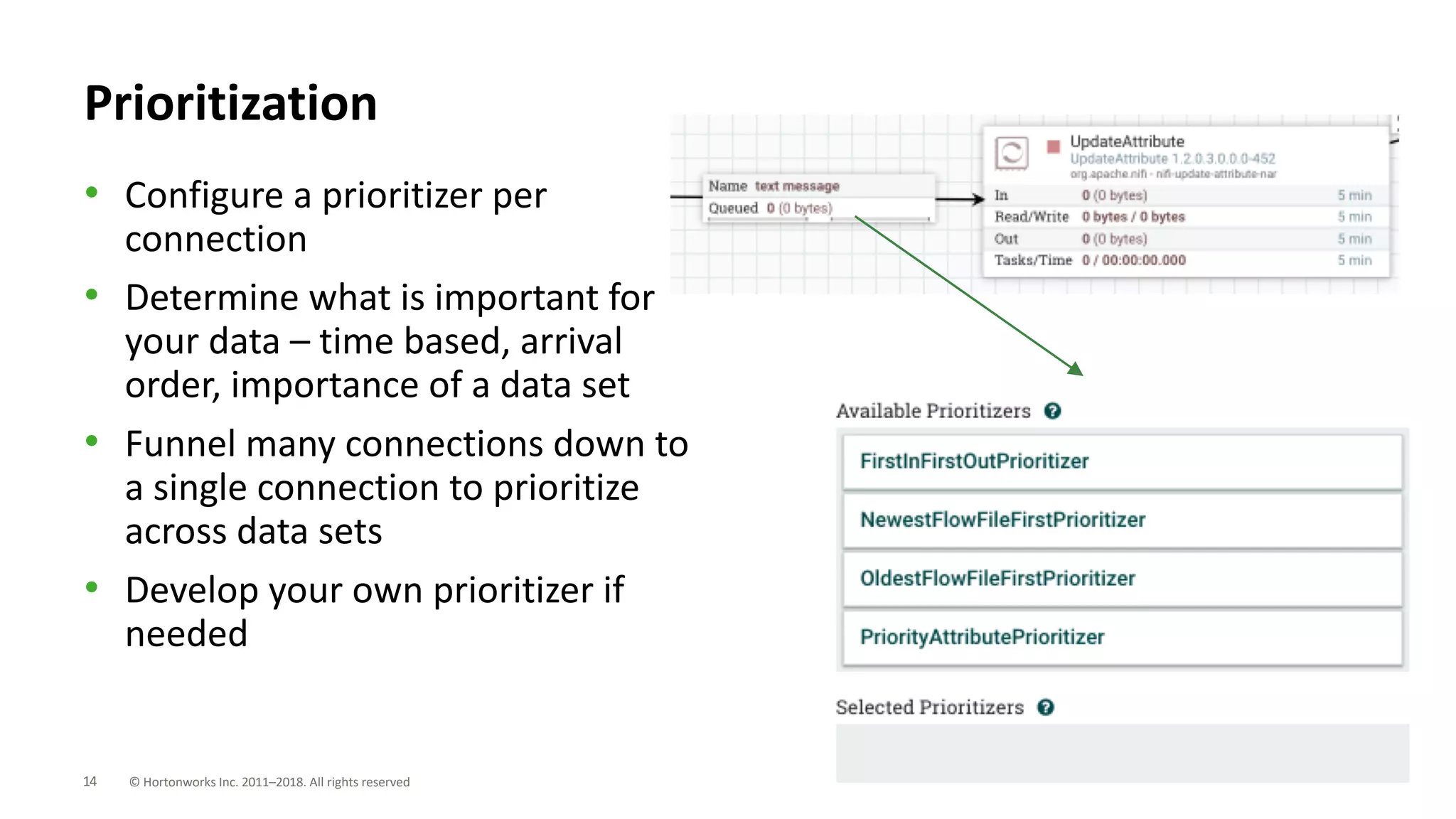
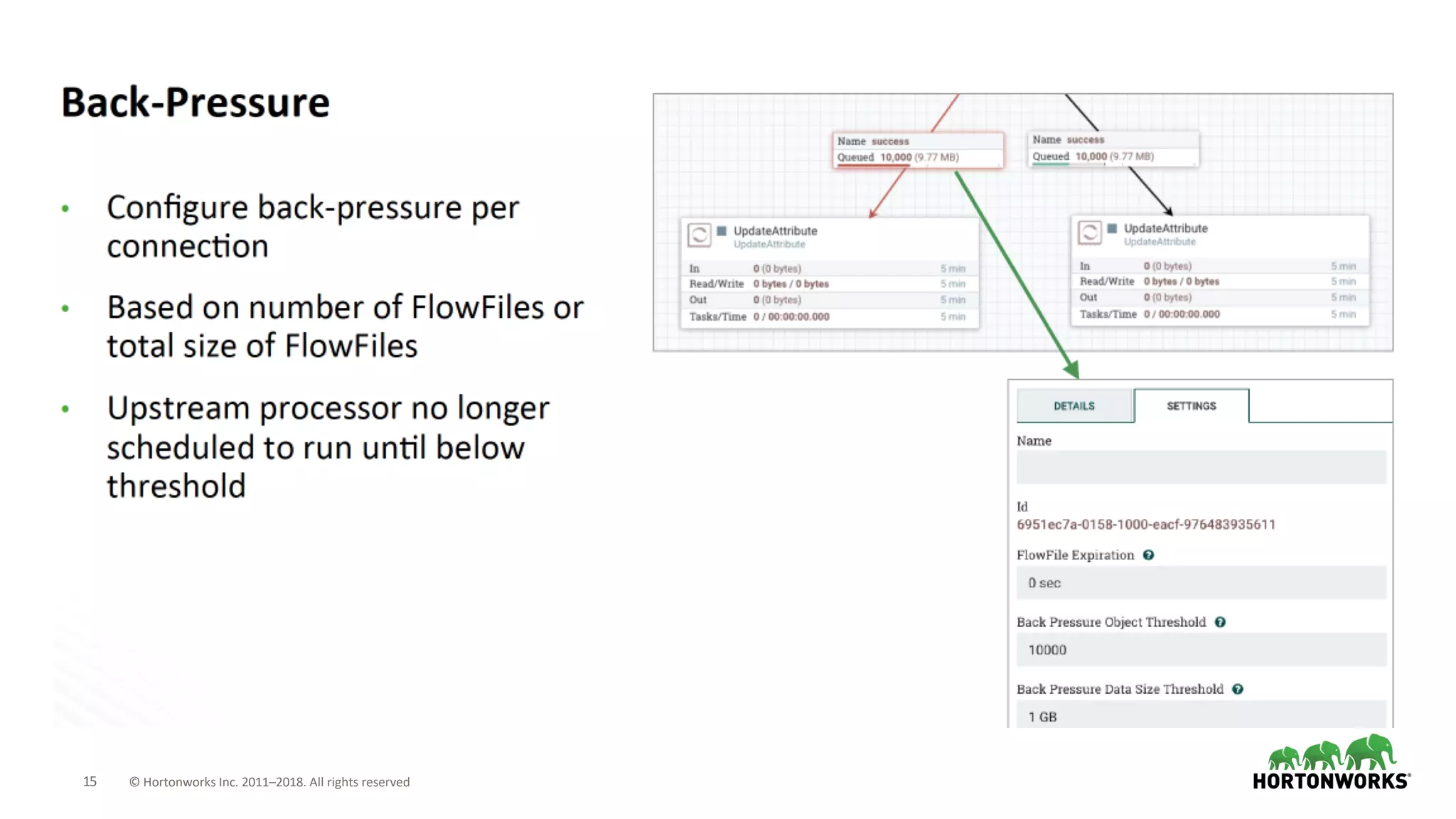
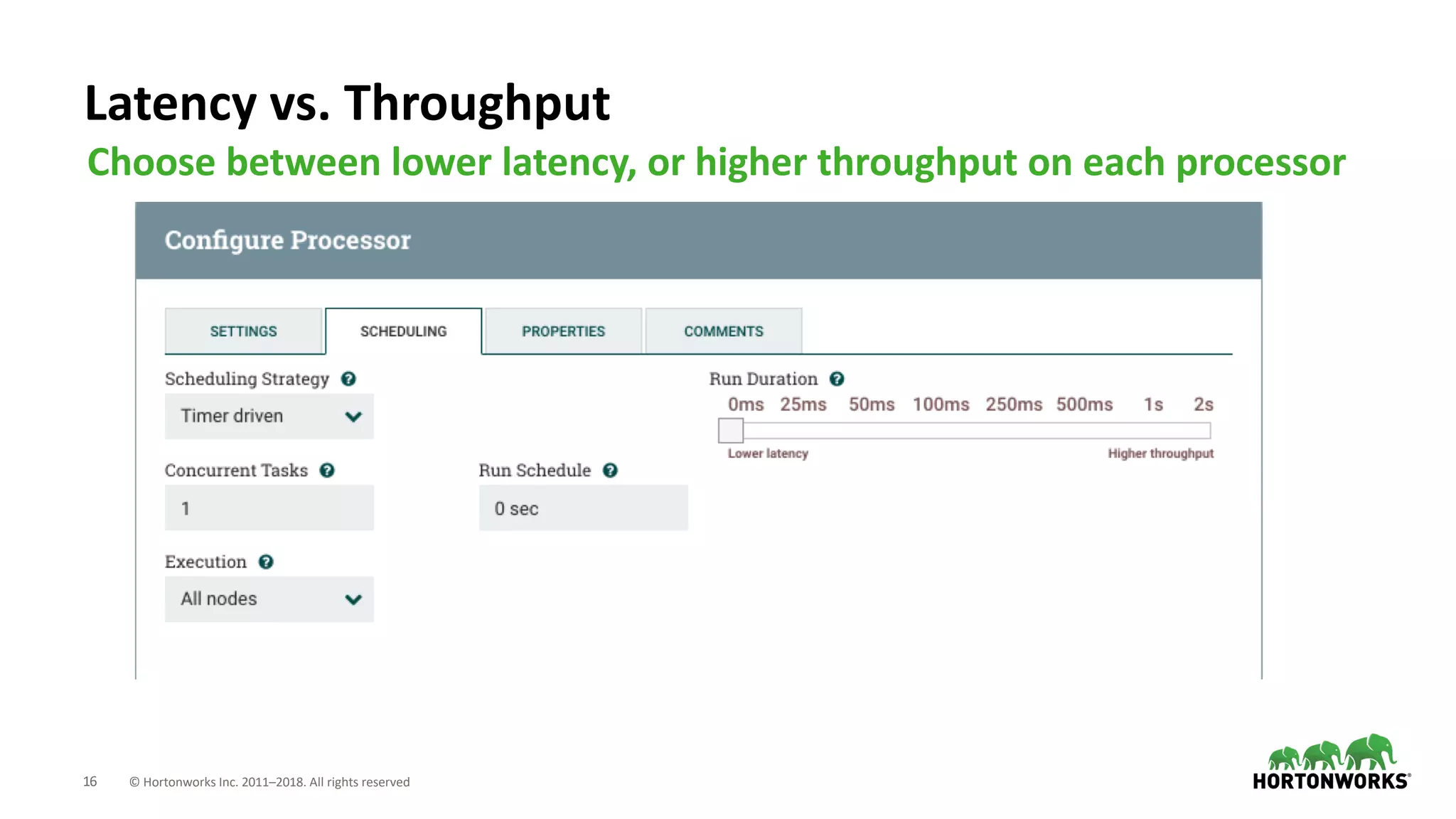
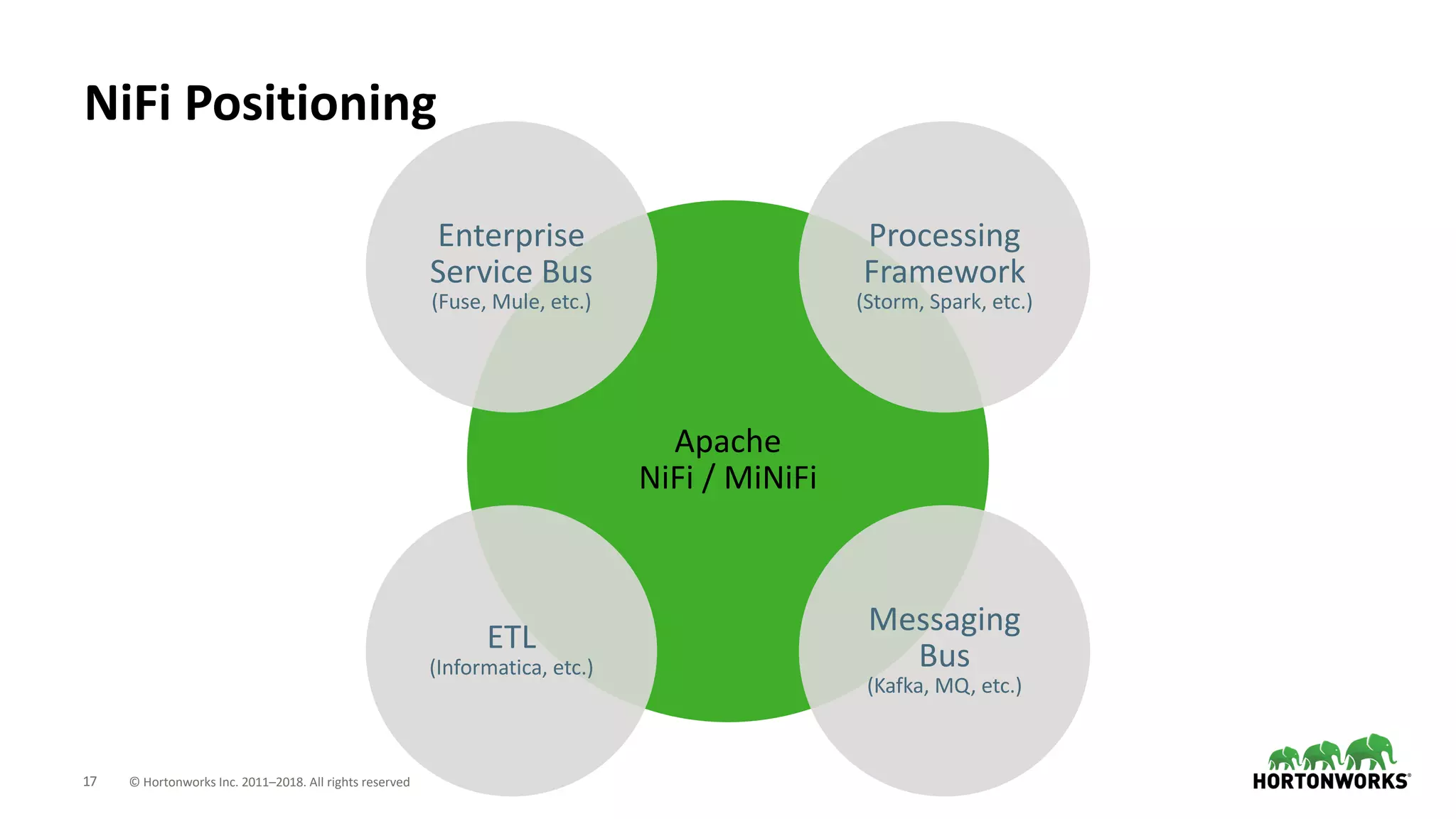
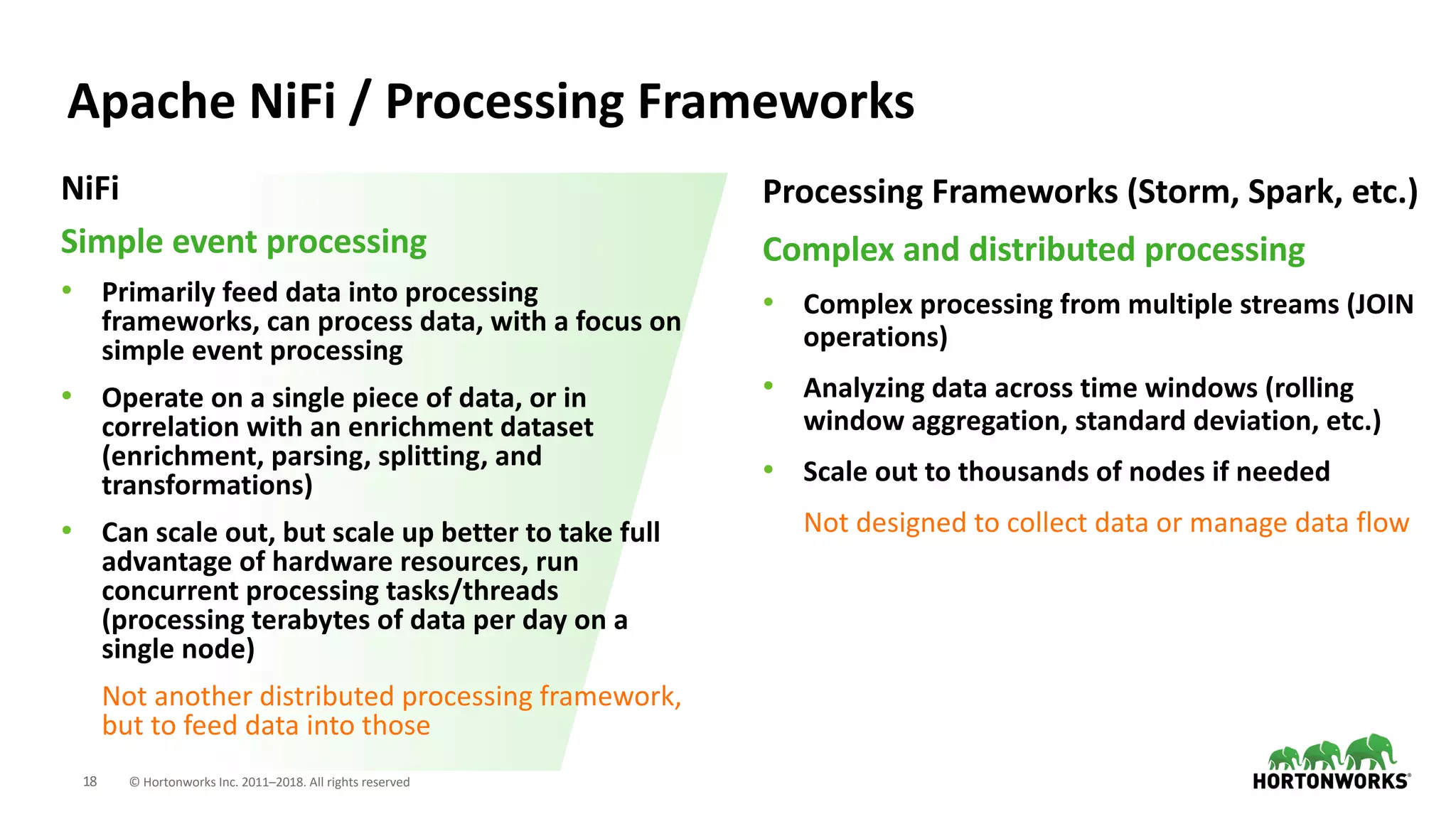
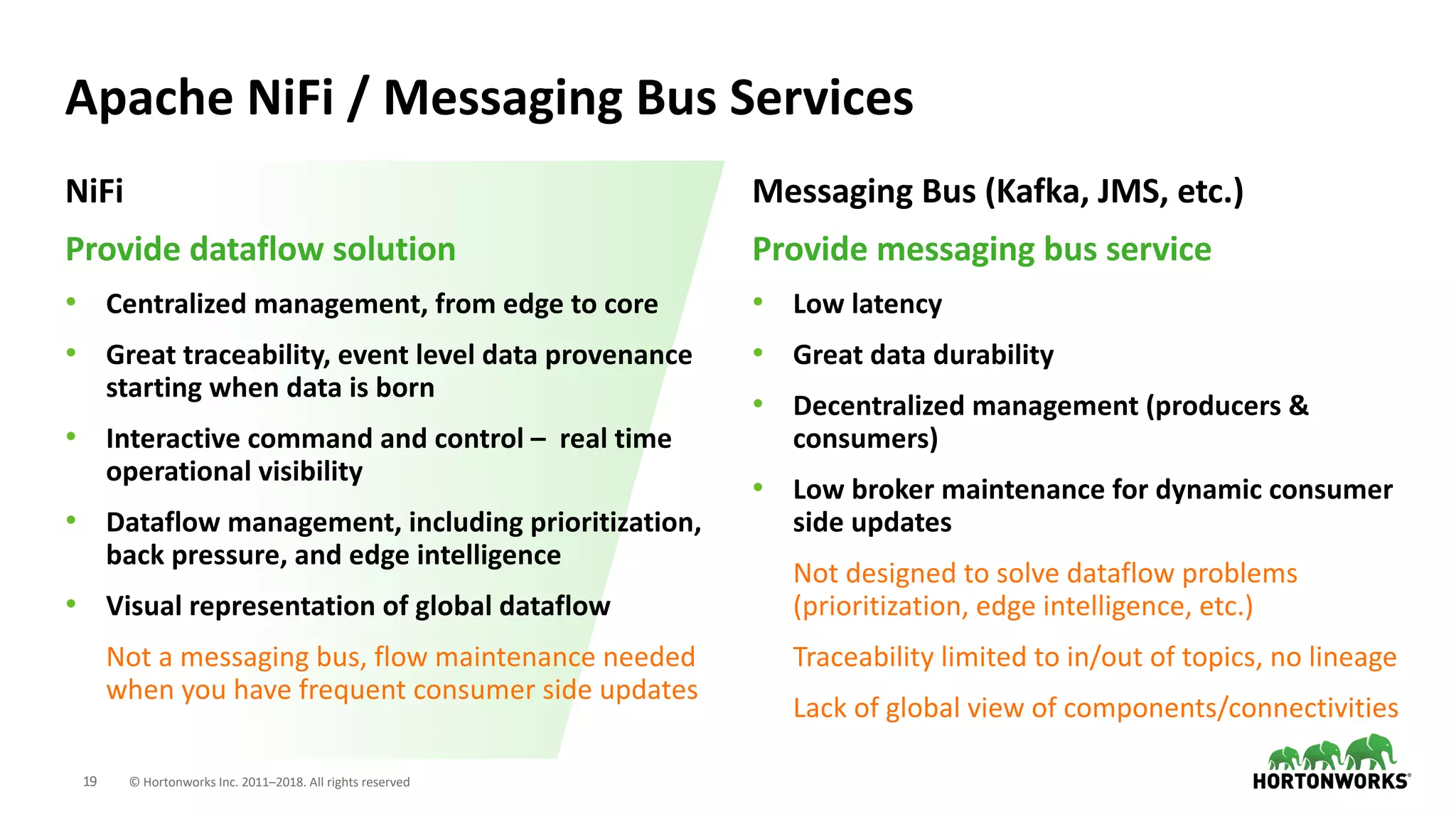
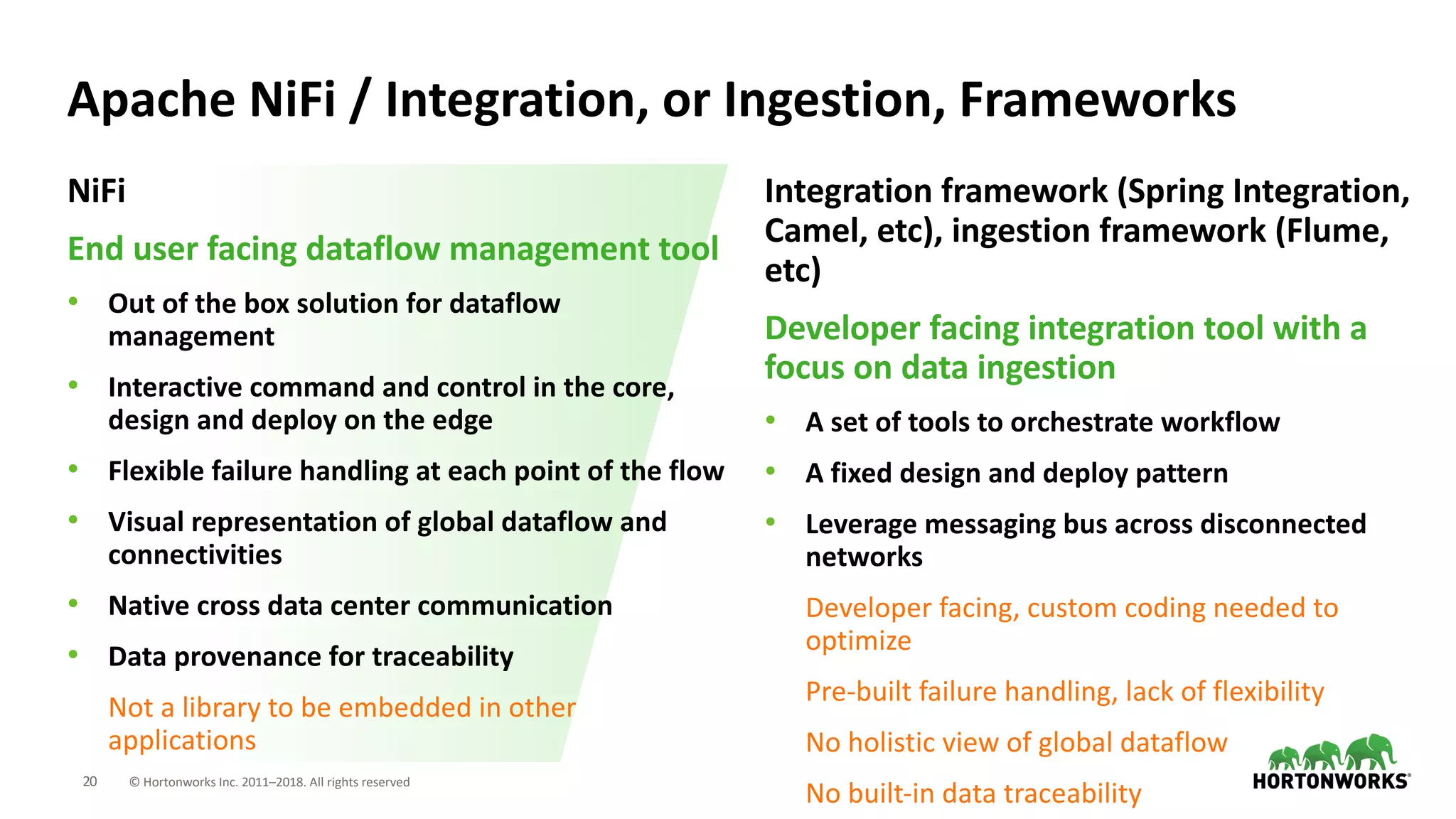
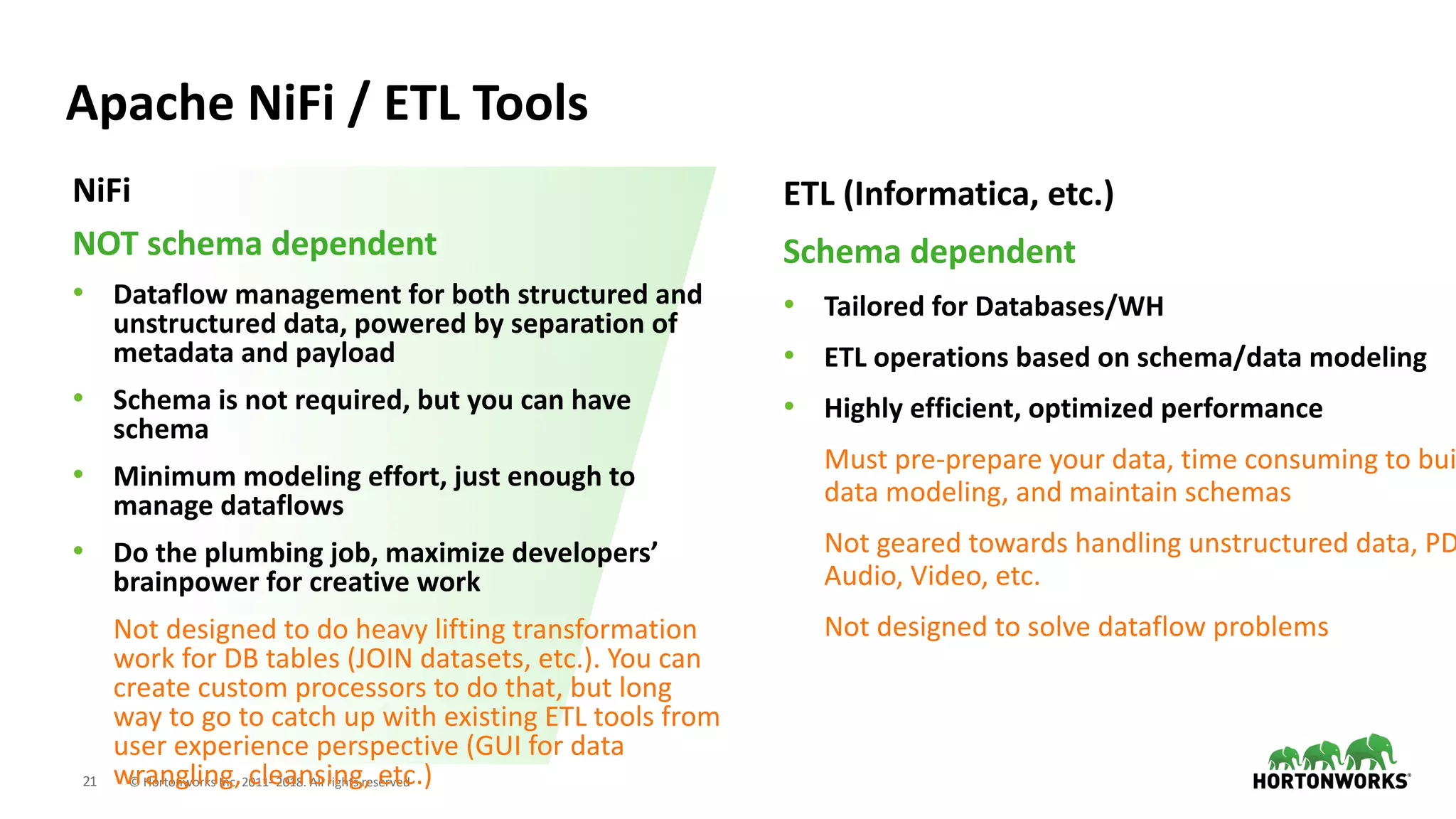
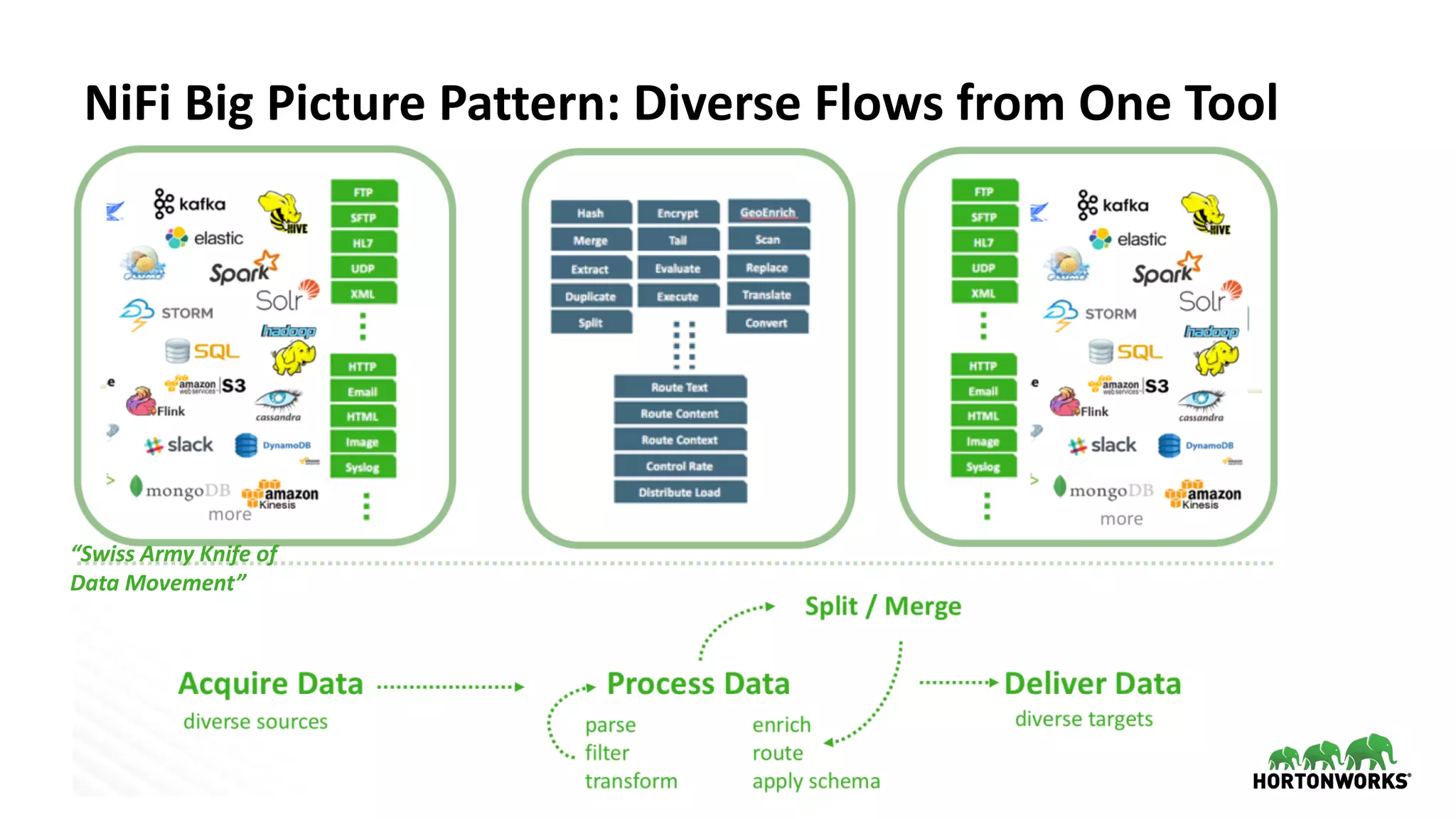
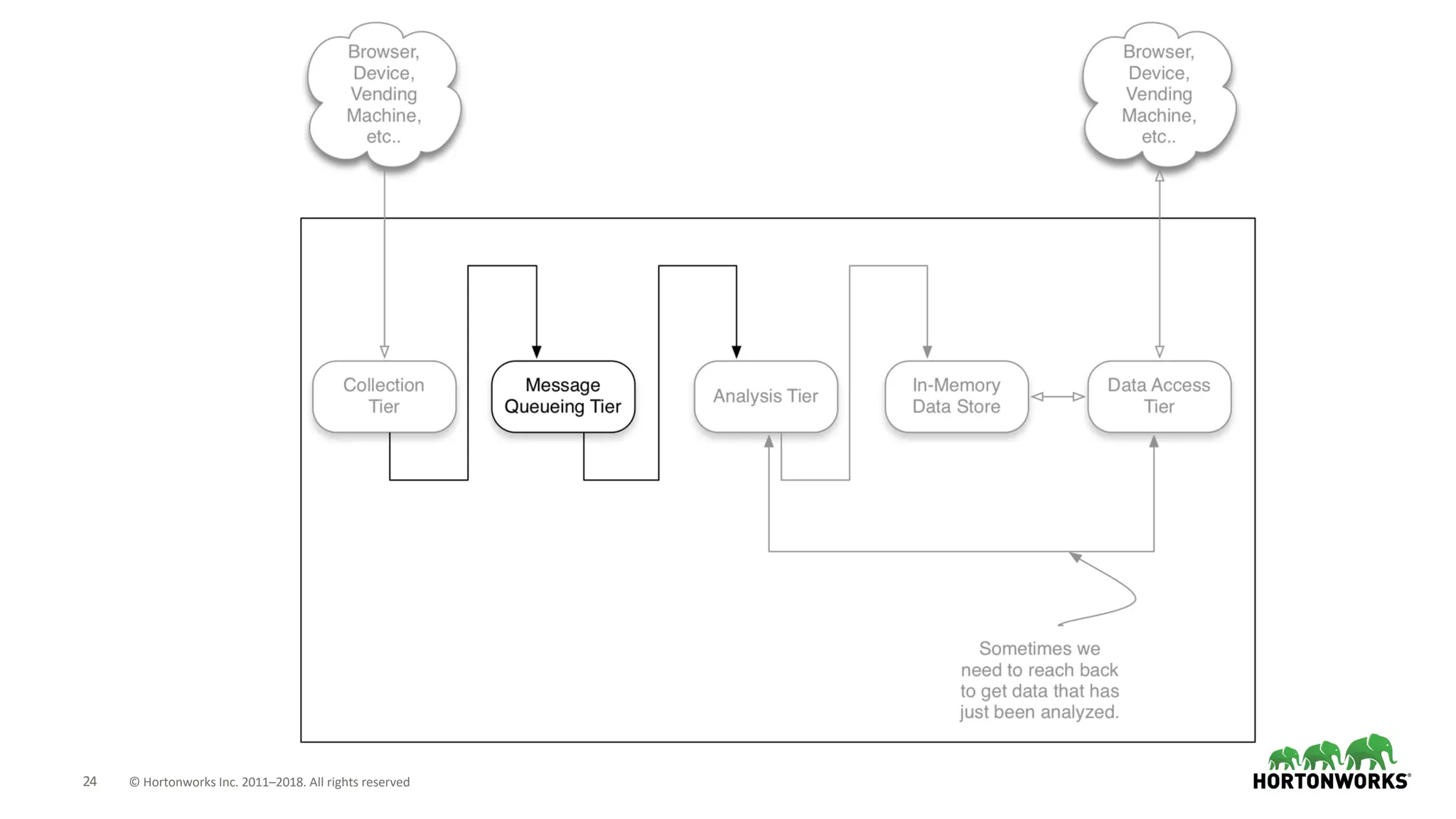
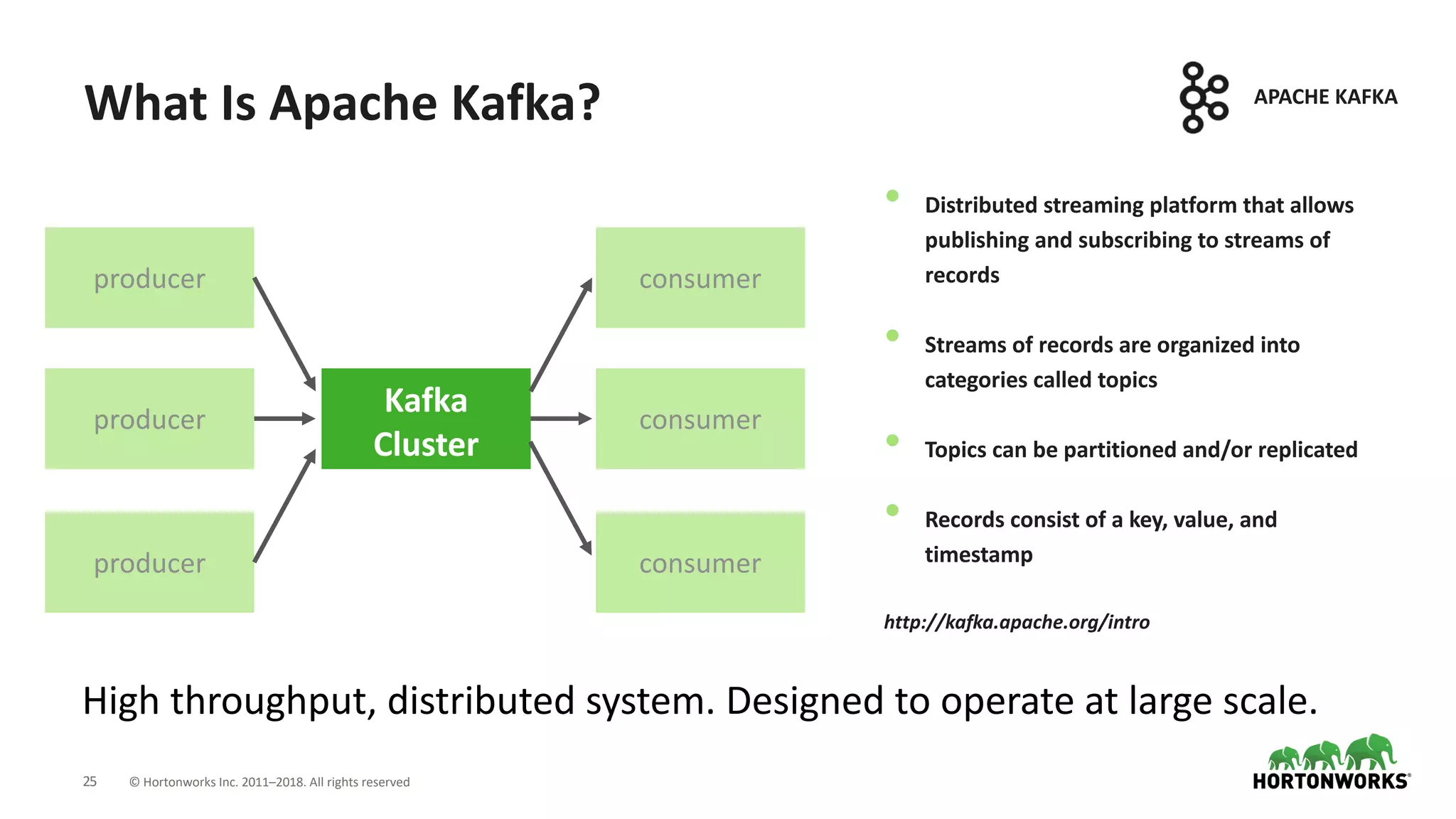
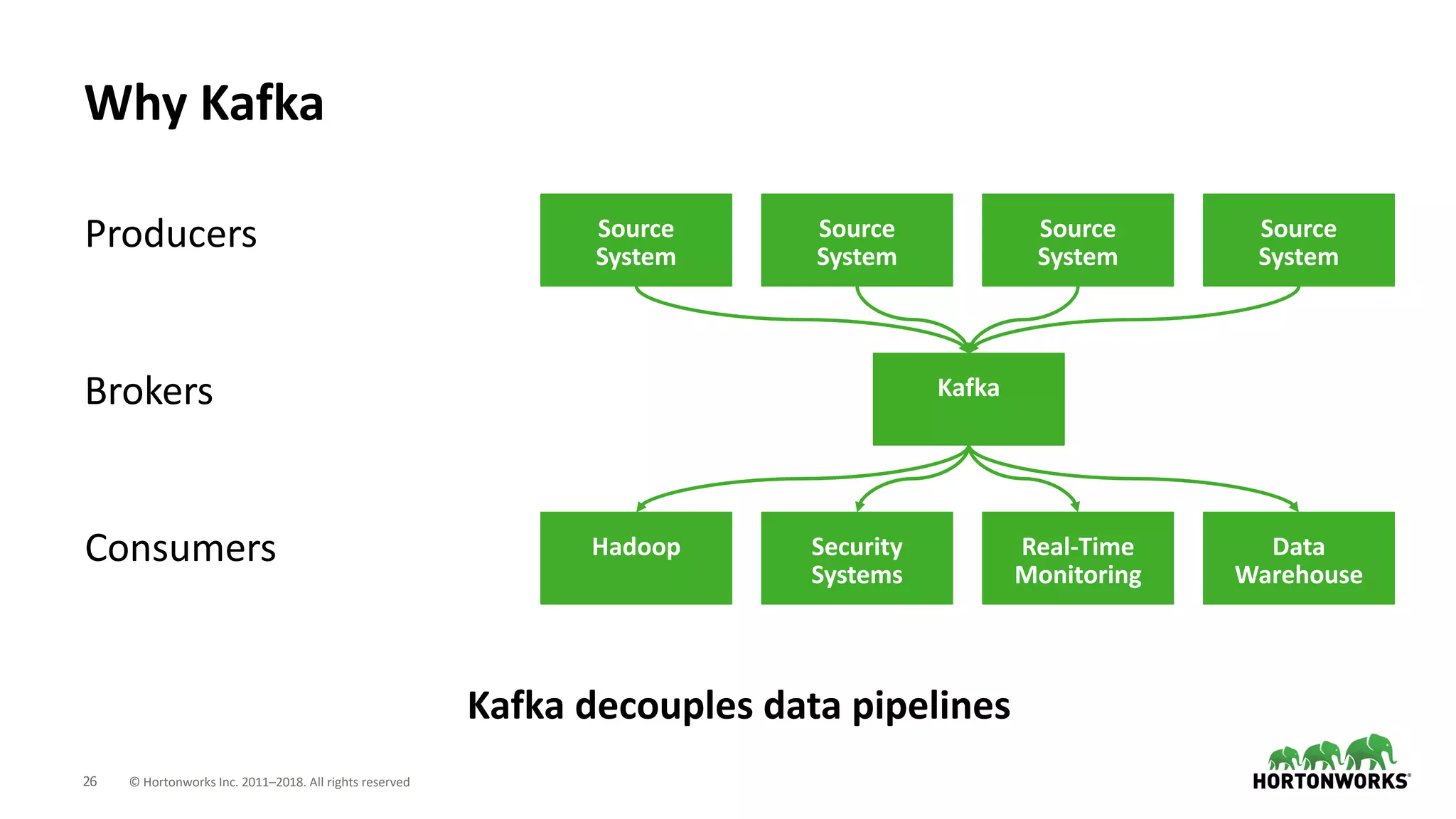
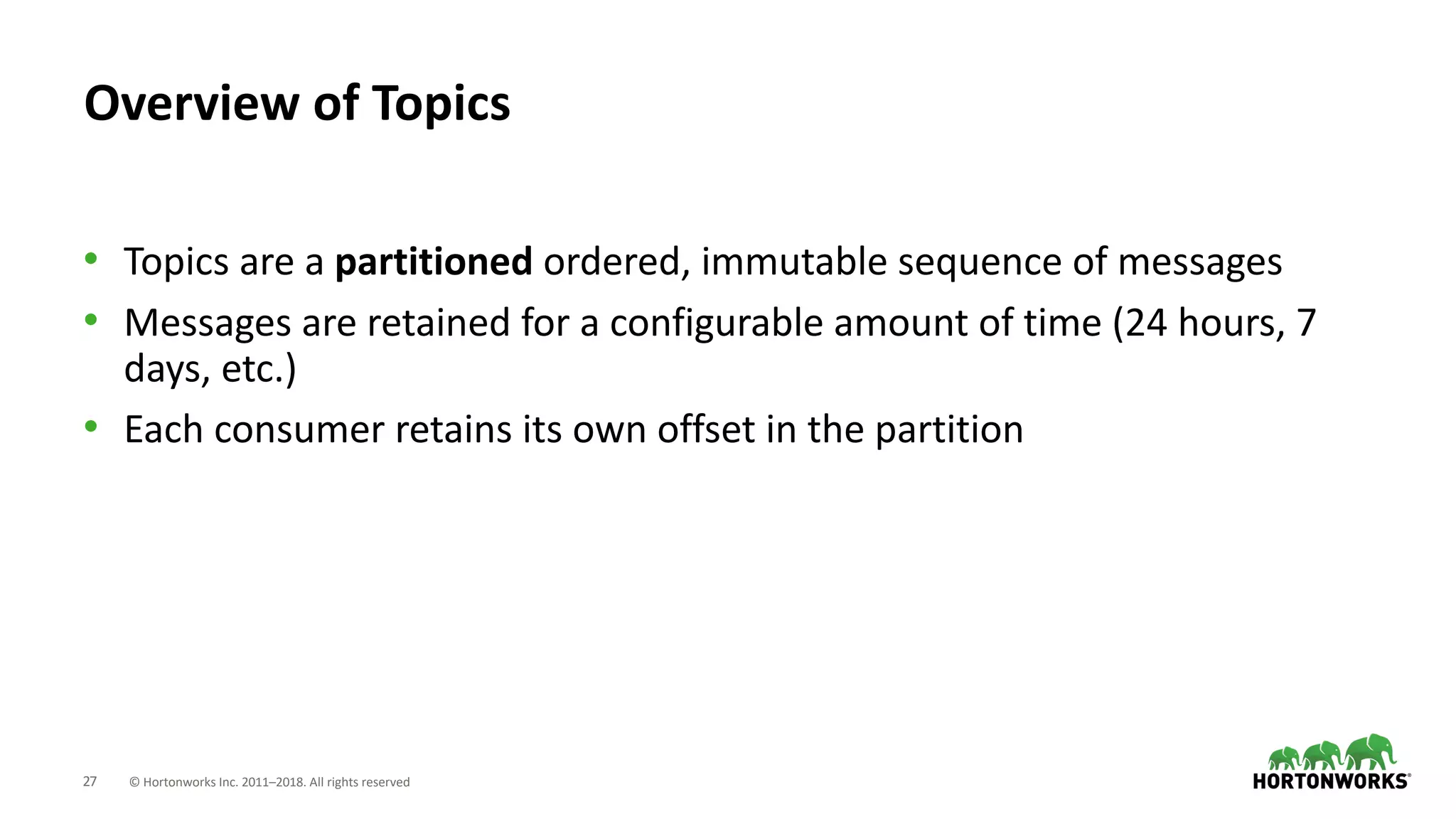
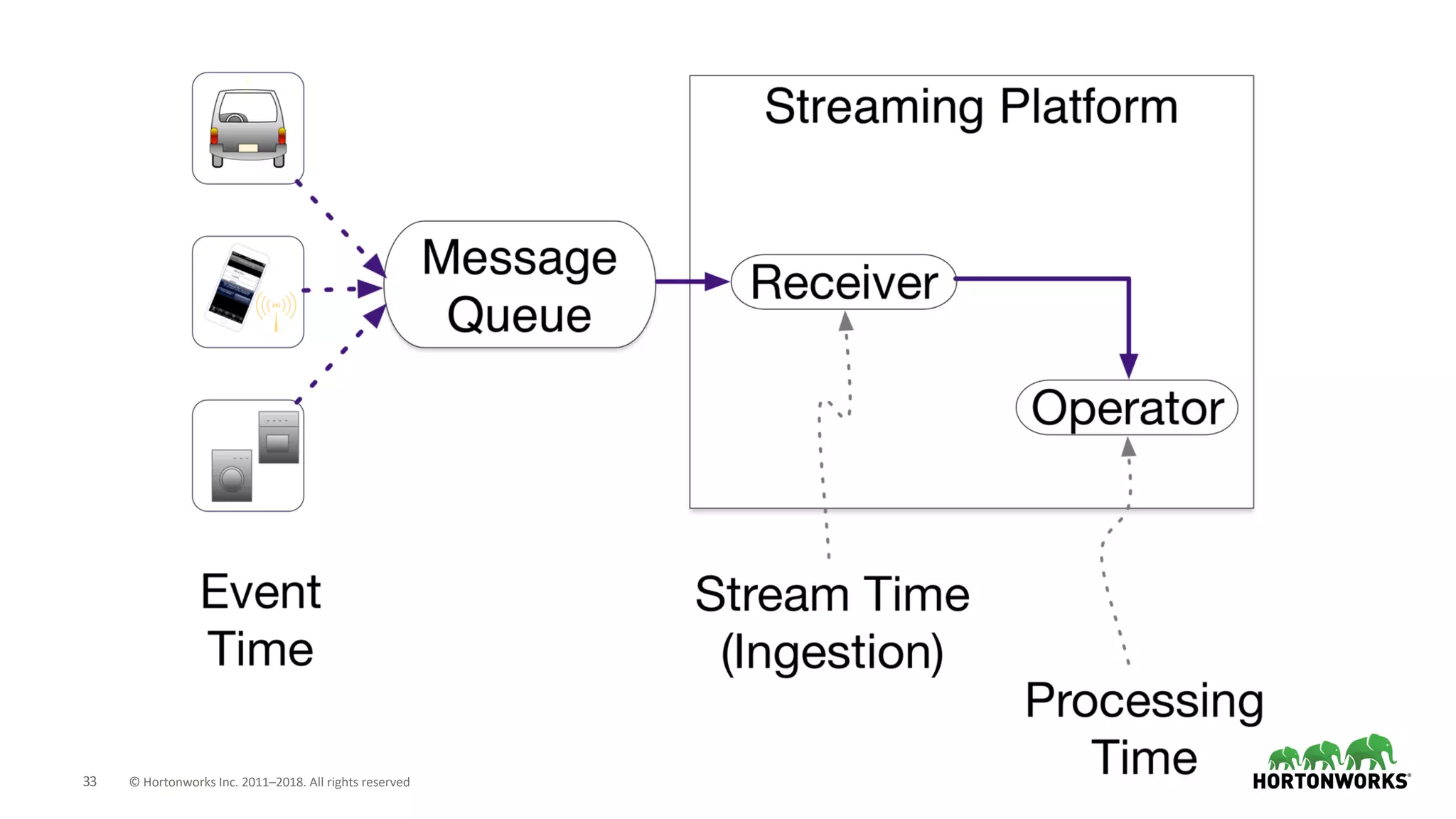
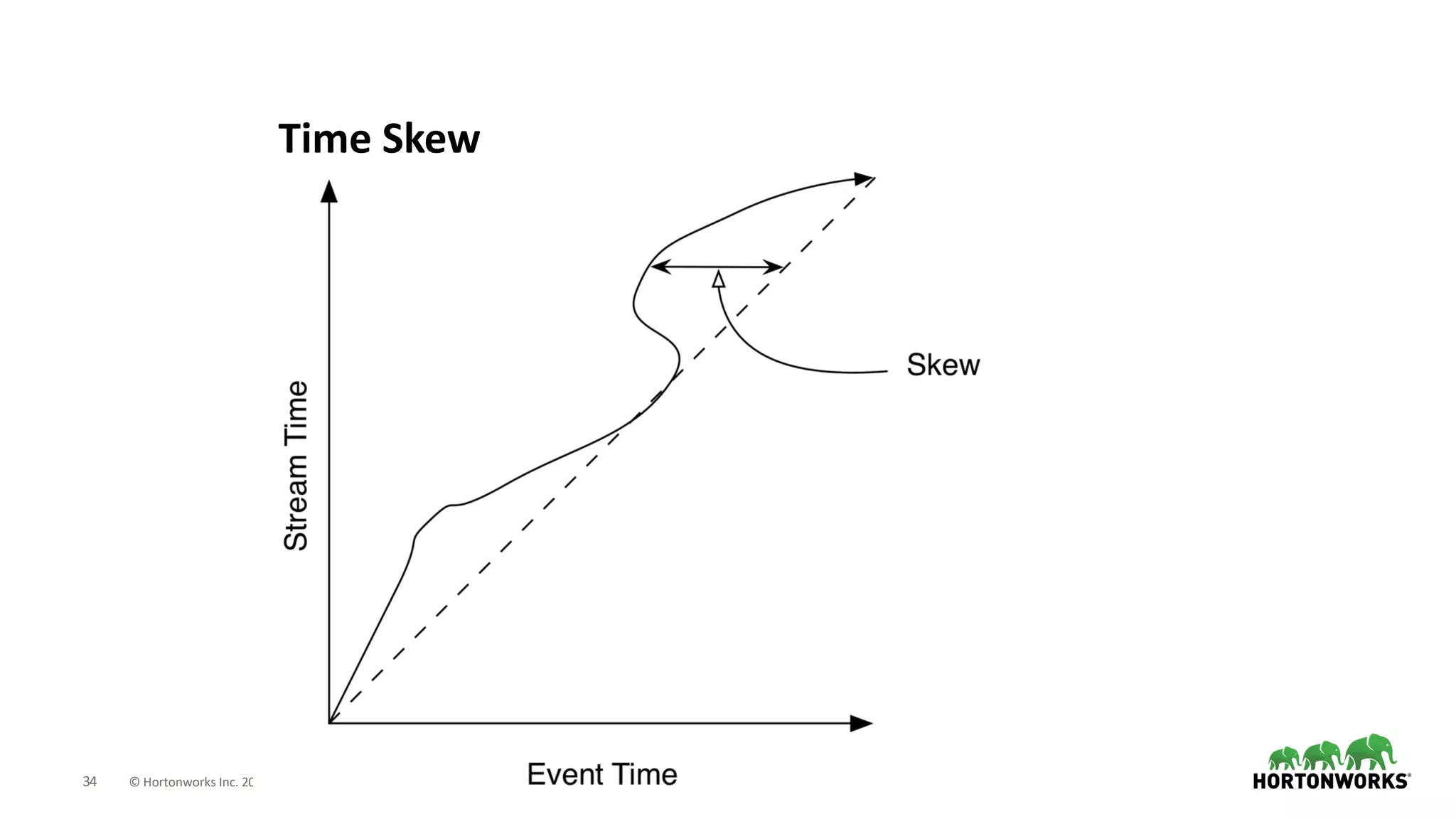
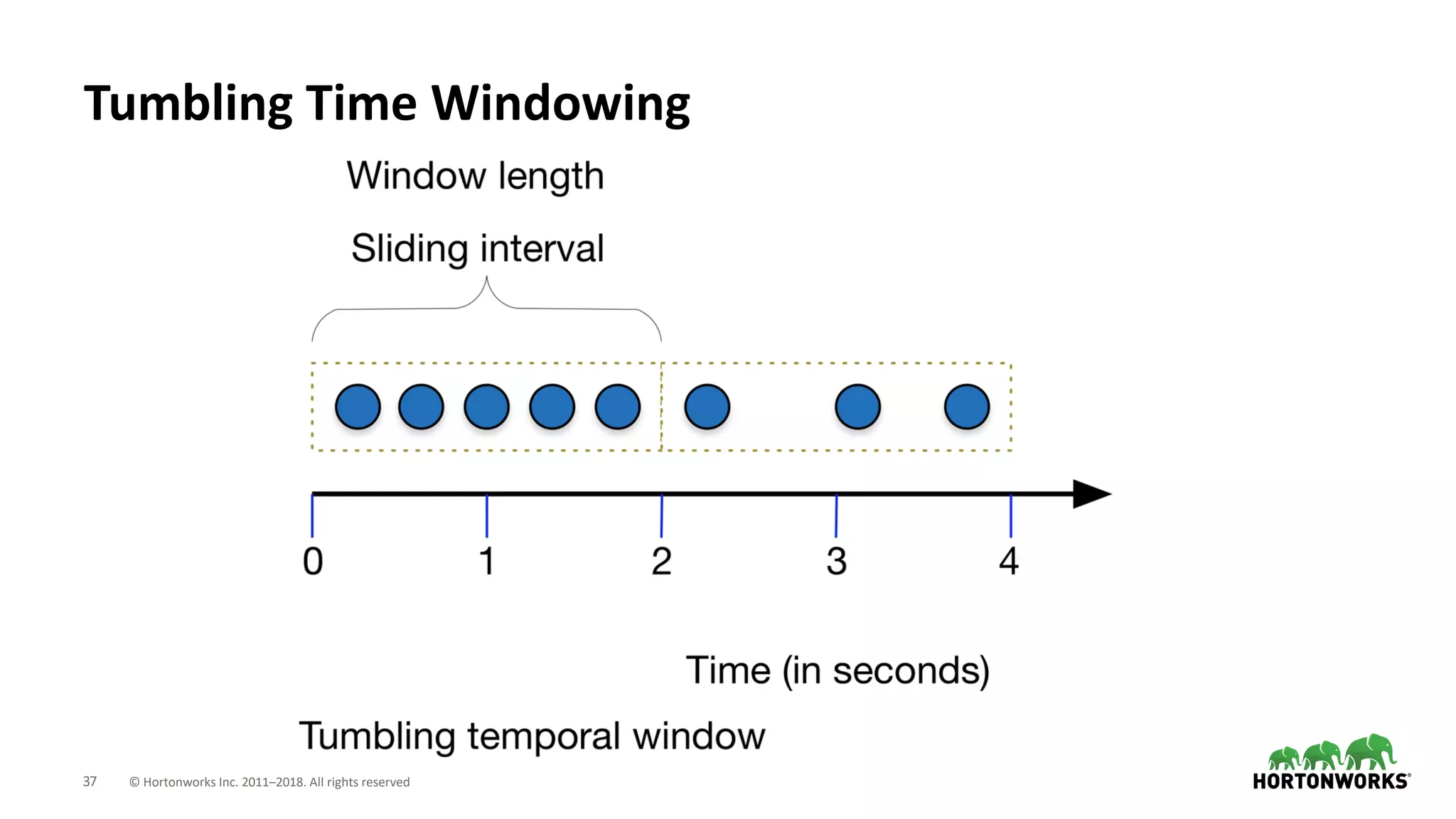
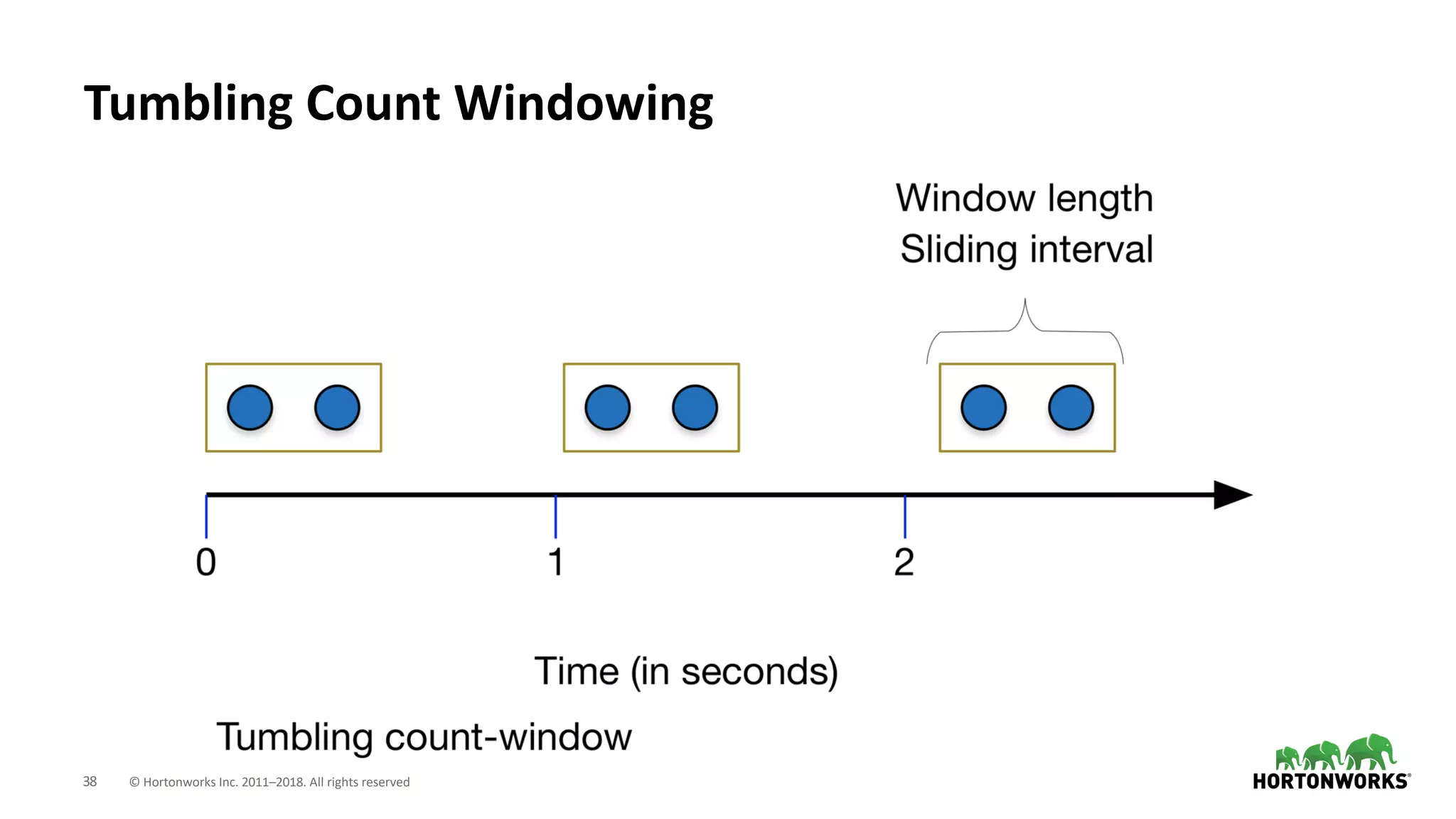
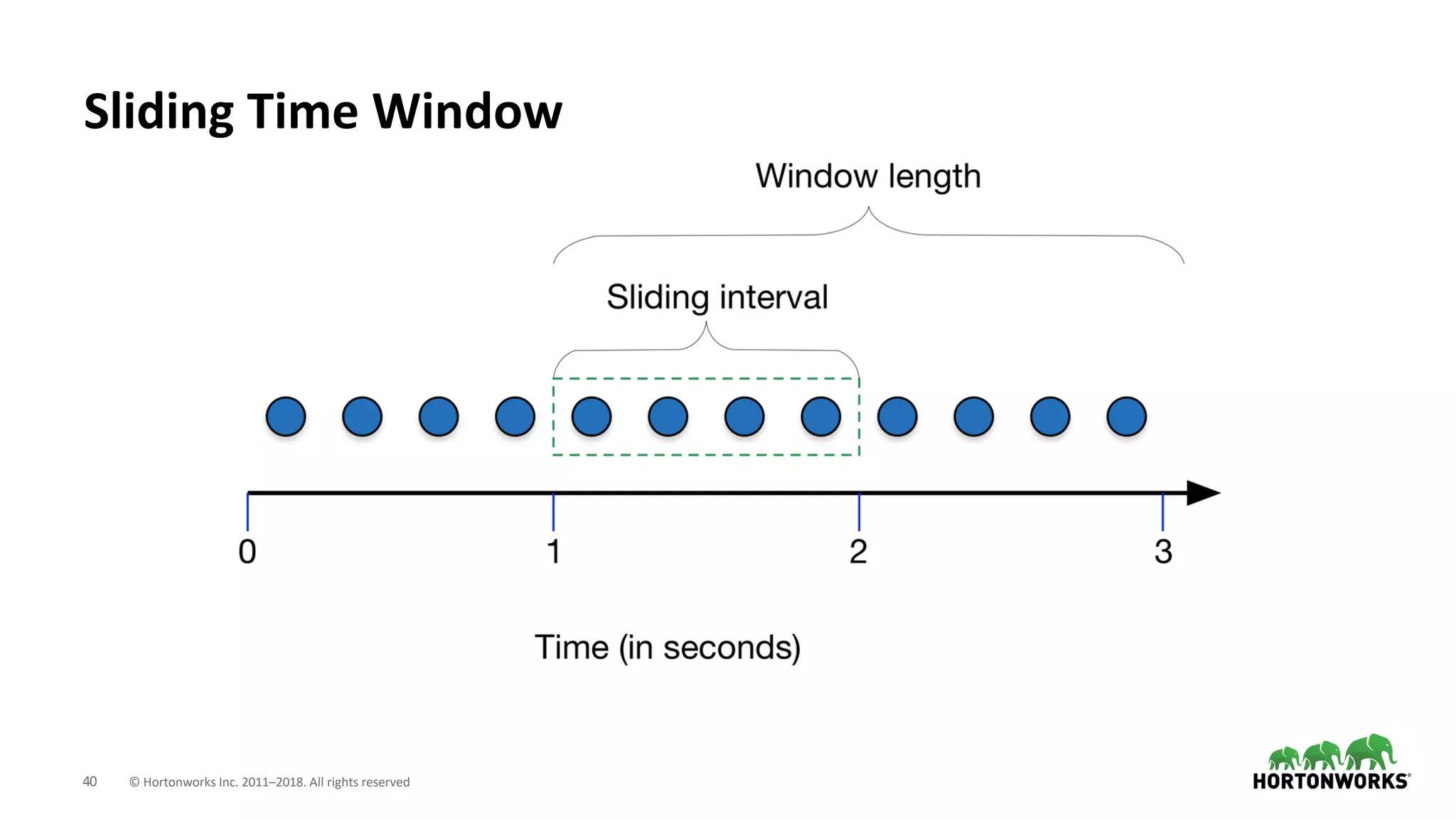
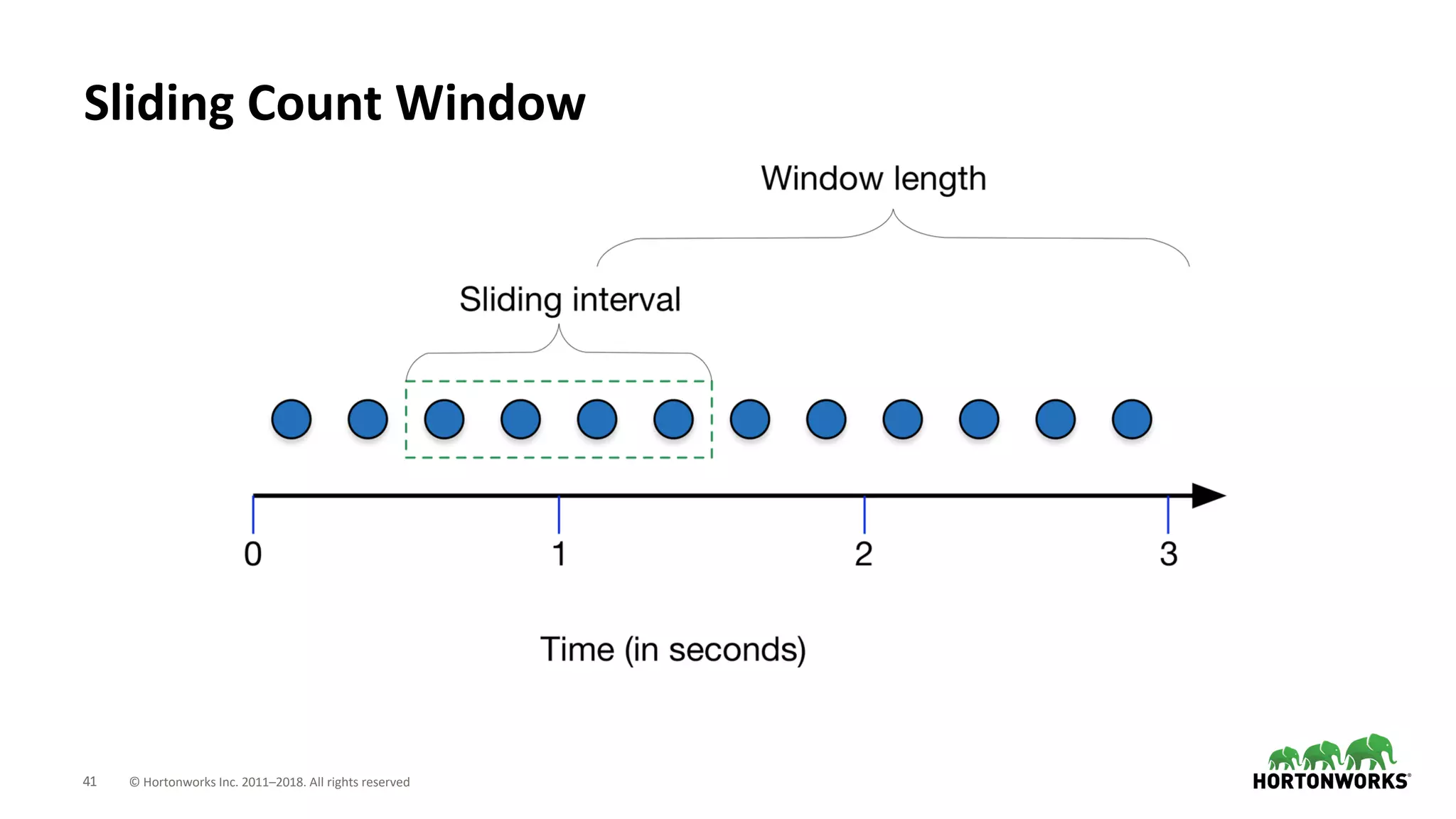
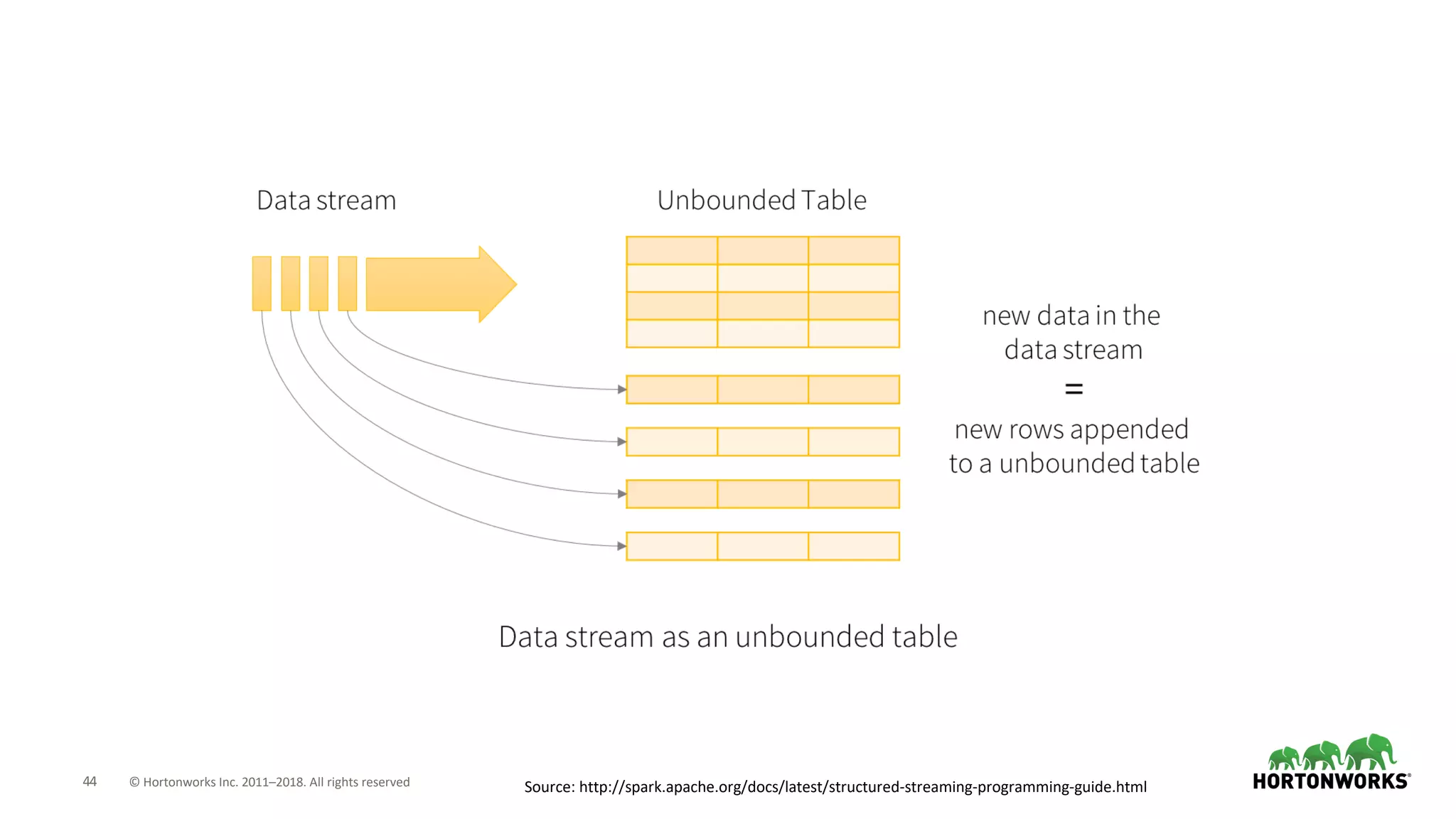
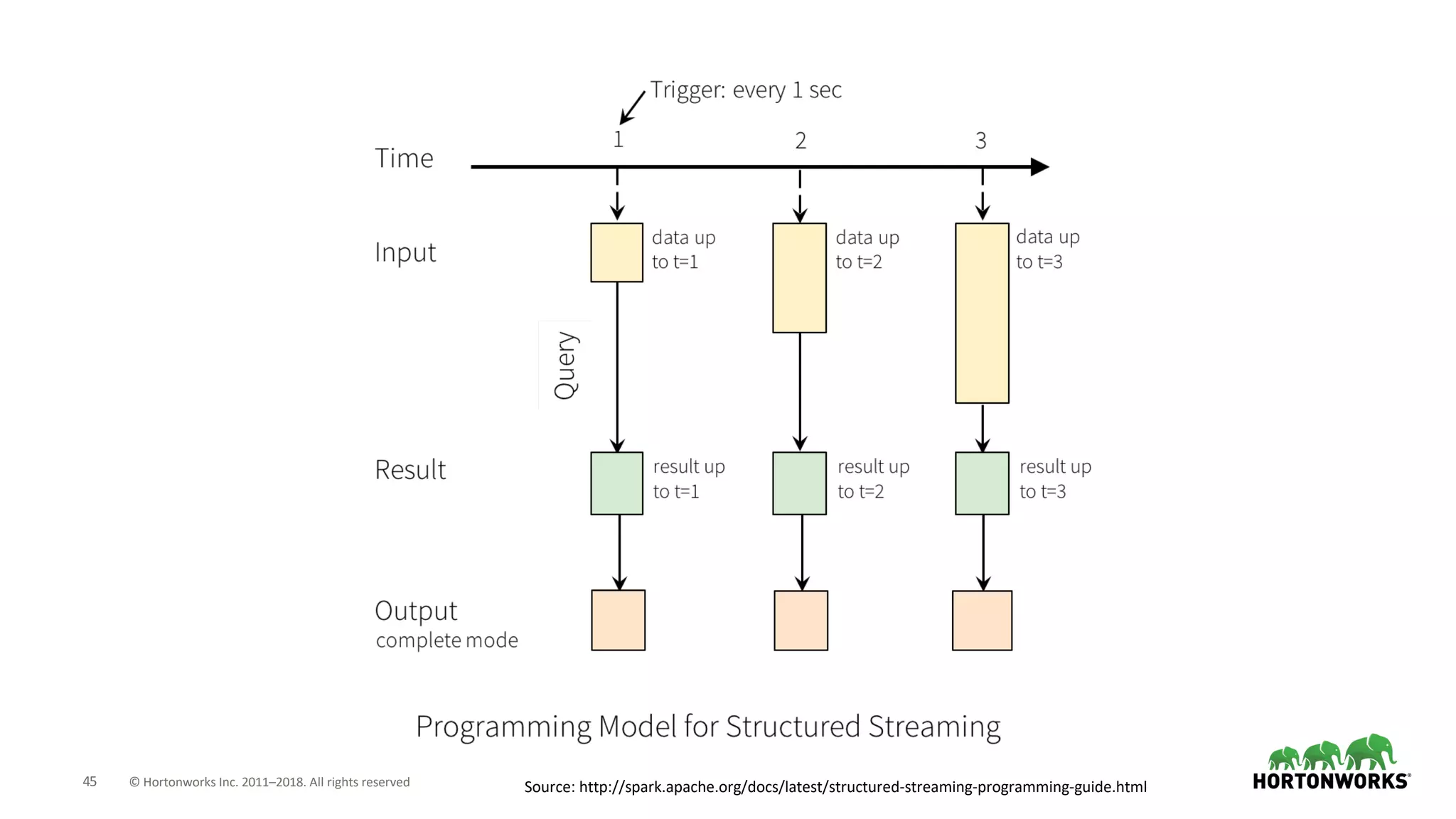
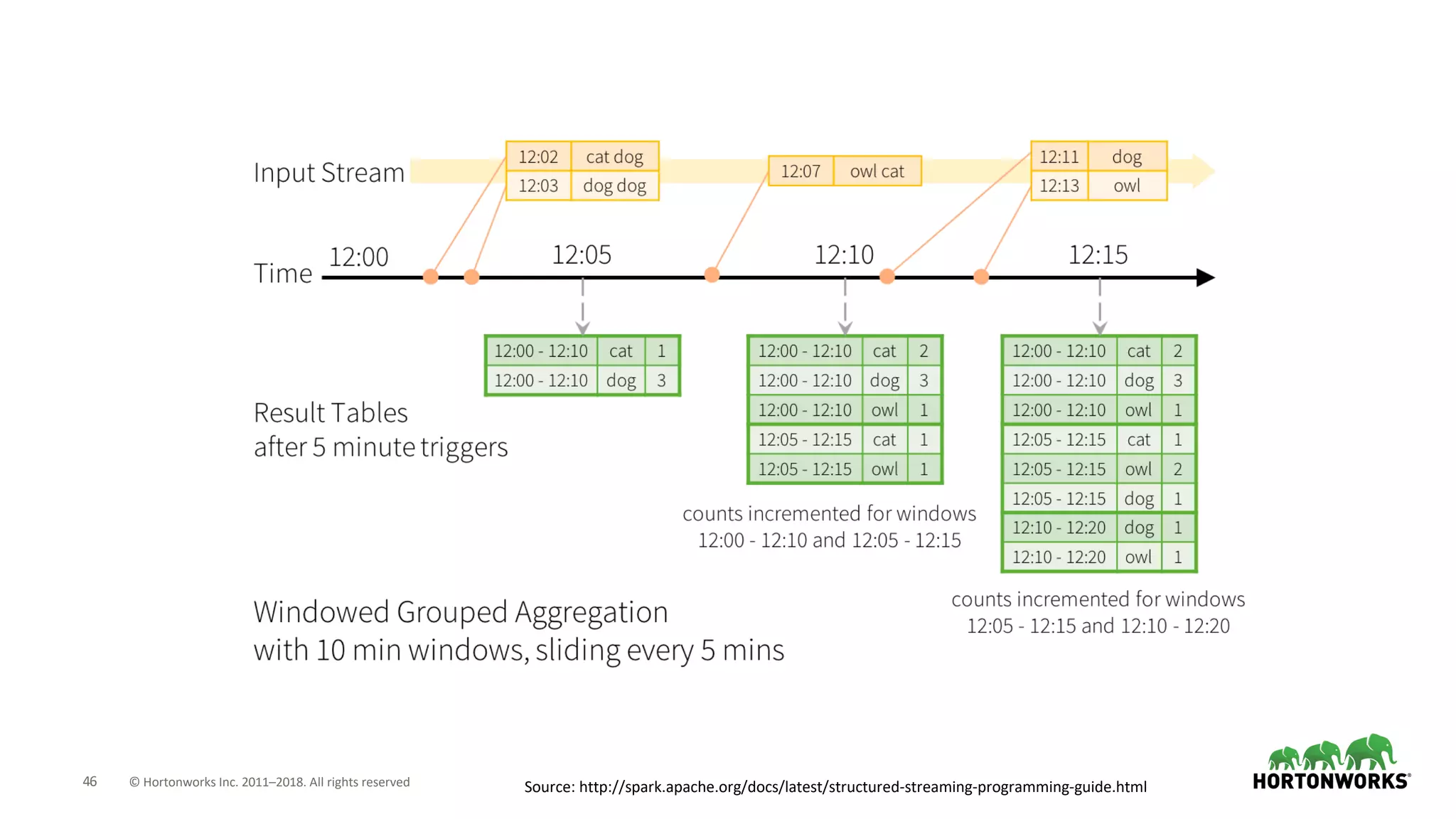
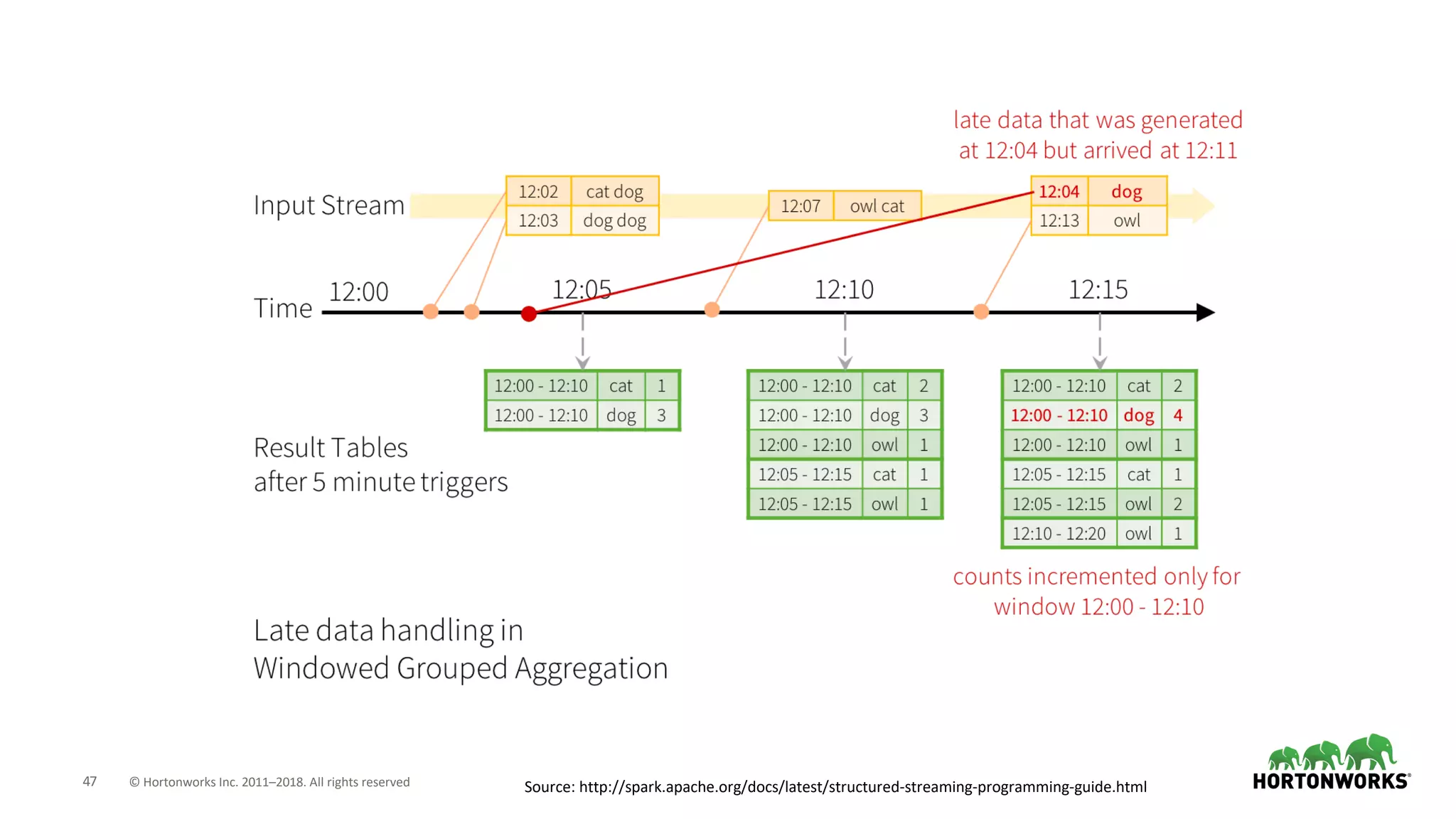
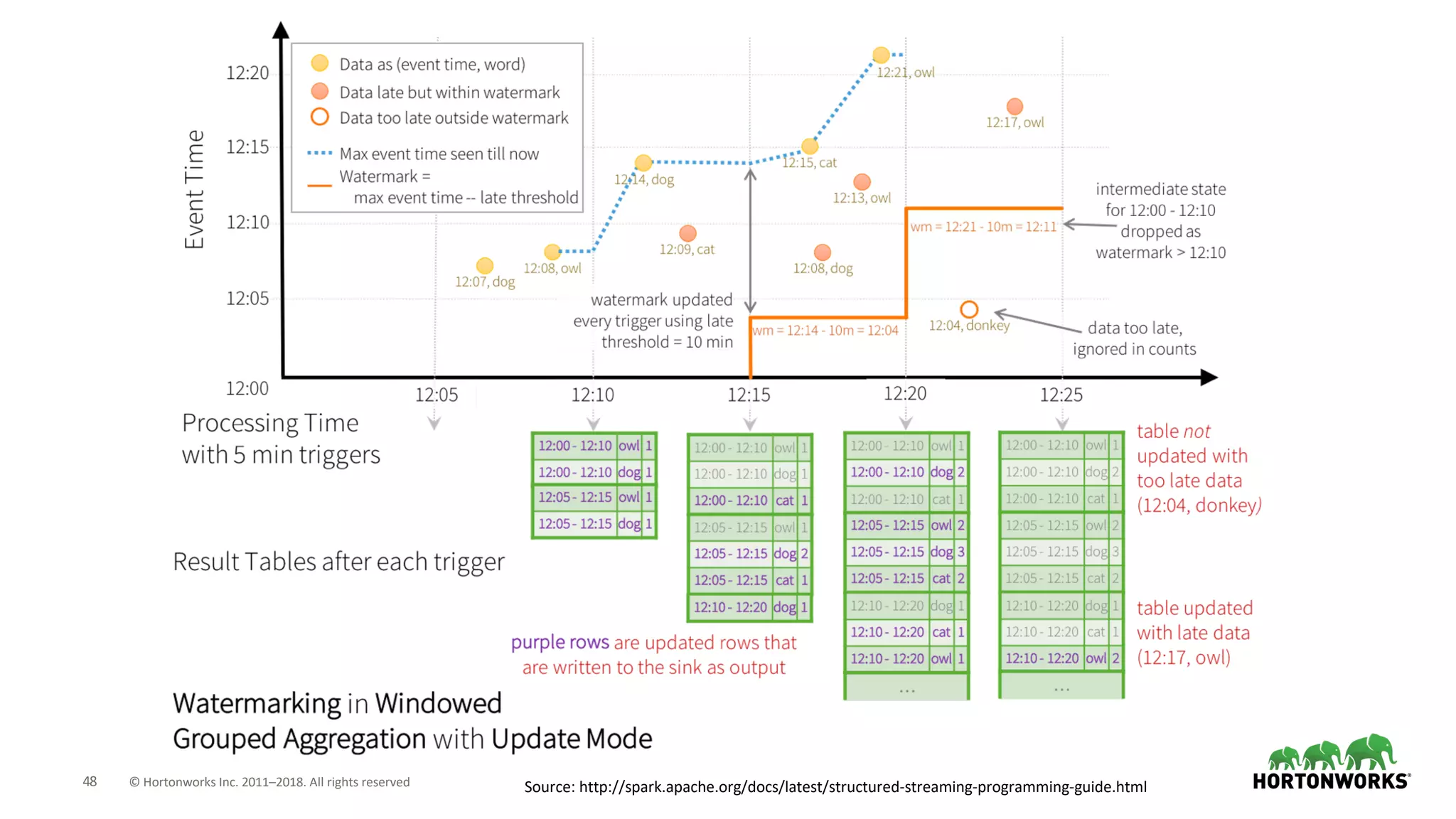
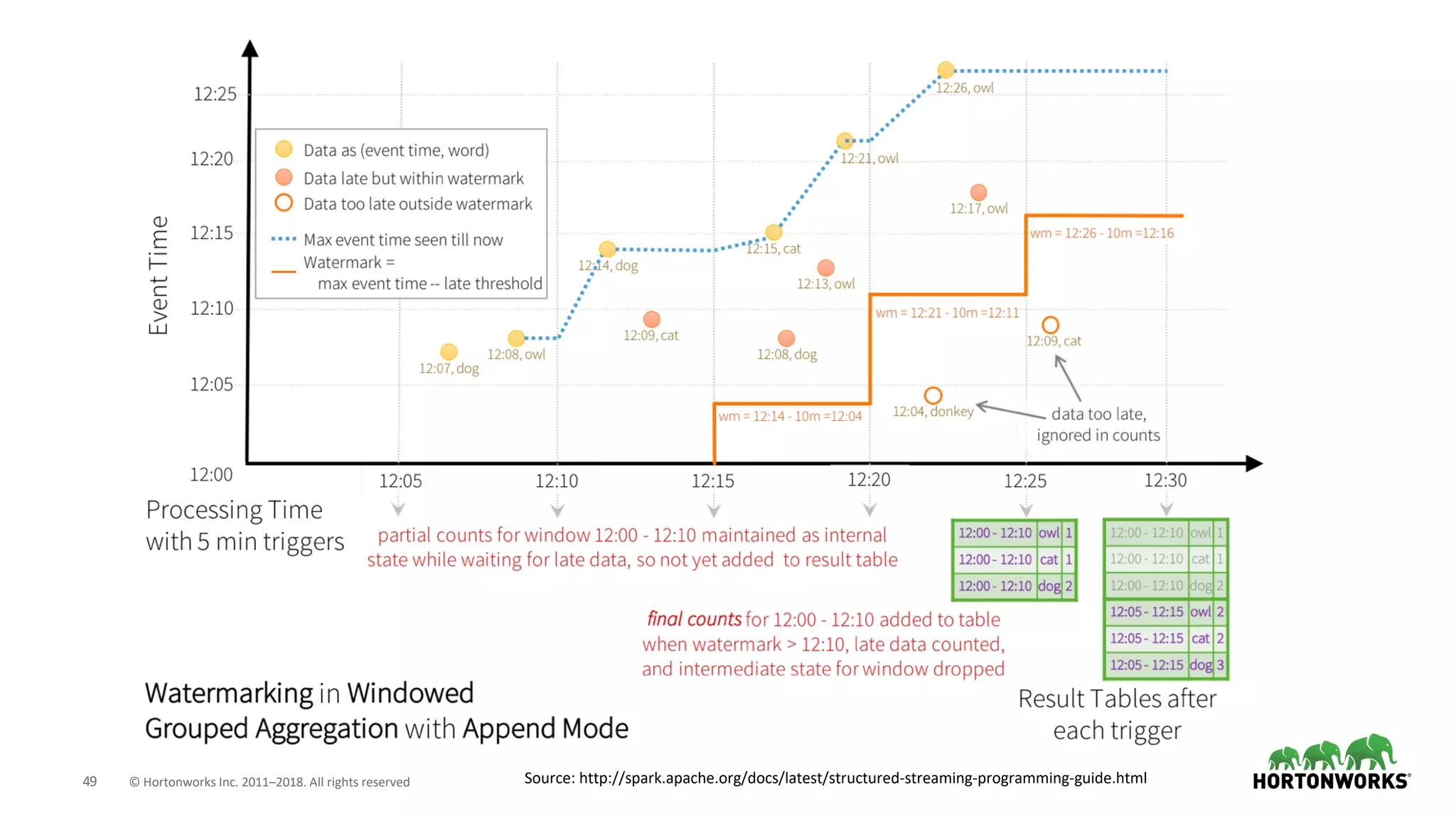
The document discusses the use of Apache NiFi and Kafka for next-generation ETL processes, highlighting their features, advantages, and positioning within dataflow management. It contrasts NiFi's capabilities in handling structured and unstructured data with traditional ETL tools, while also detailing Kafka's role as a distributed streaming platform. Key aspects include data ingestion, real-time processing, and the importance of visual command and control in managing complex data flows.