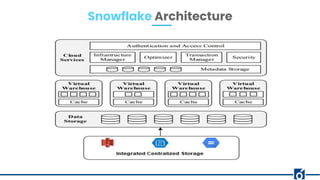
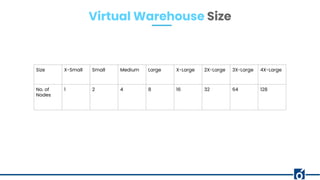
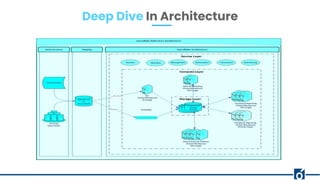
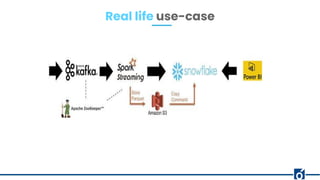
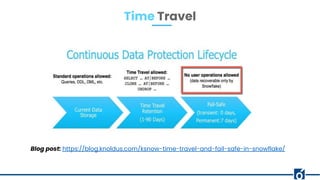
The document provides an overview of Snowflake, a cloud-based data warehouse, highlighting its features, advantages, and architecture. It compares Snowflake to traditional big data tools like Apache Hive and Spark, emphasizing its scalability, ease of use, and lack of maintenance requirements. The document also discusses the virtual warehouse concept, data storage layers, and introduces concepts like time travel within Snowflake.