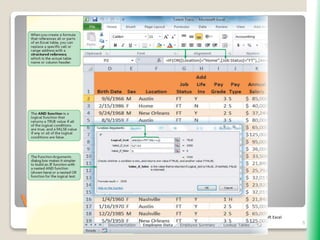
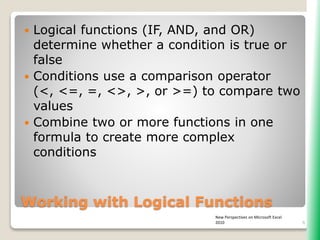
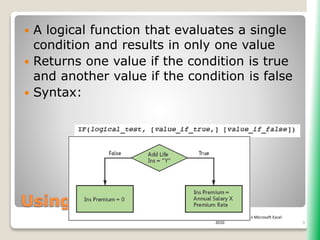
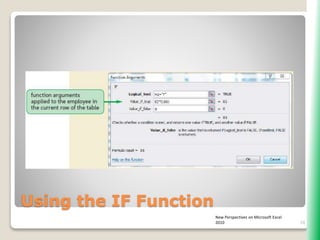
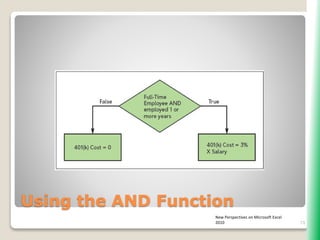
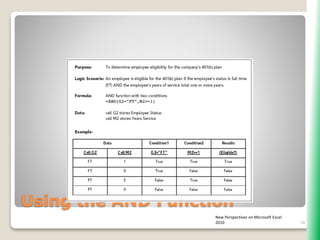
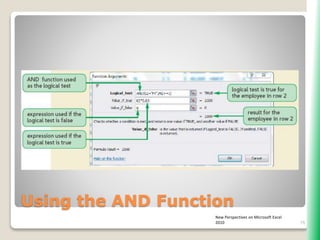
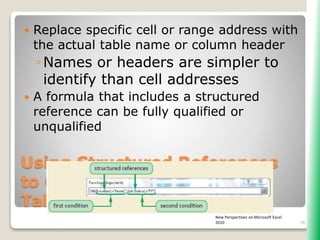
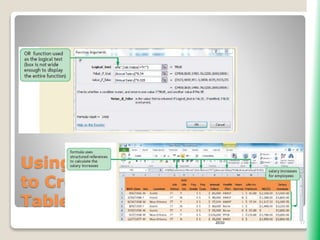
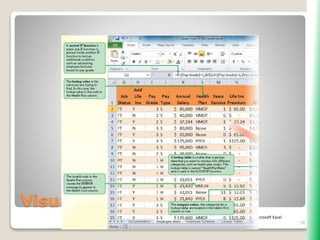
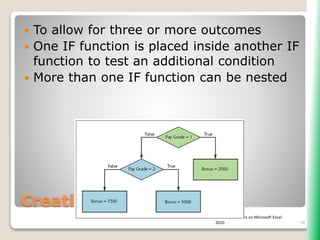
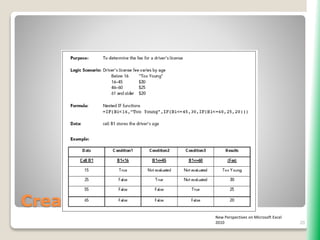
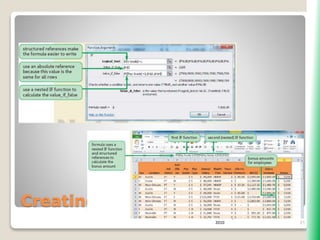
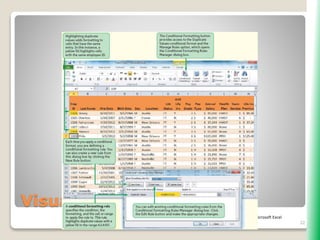
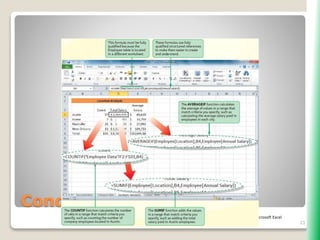
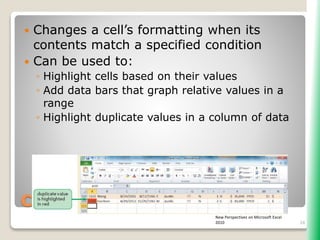
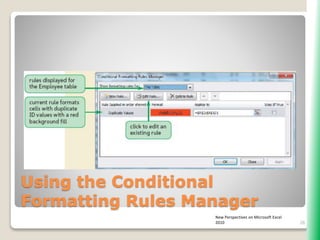
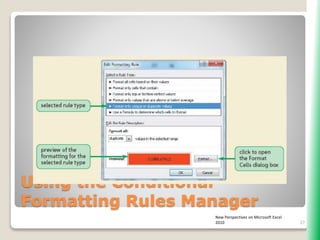
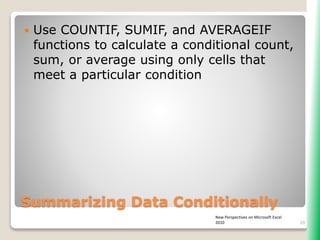
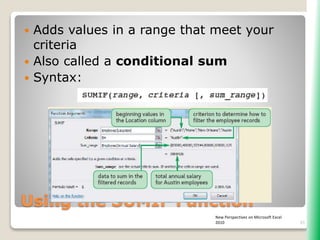
The document outlines key functionalities in Microsoft Excel 2010, focusing on advanced functions such as logical functions (IF, AND, OR), structured references, and conditional formatting. It details the use of COUNTIF, SUMIF, and AVERAGEIF functions for summarizing data based on specific conditions. Additionally, it provides instructions on creating calculated columns in tables and utilizing nested IF statements for complex conditions.