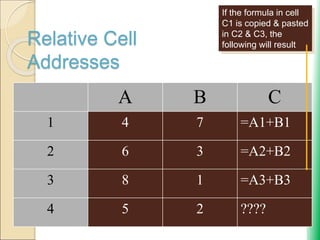
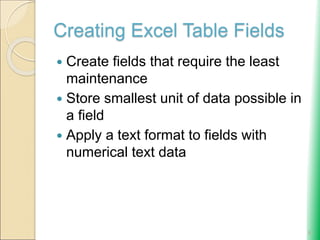
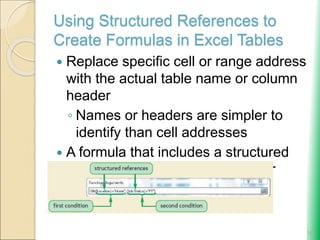
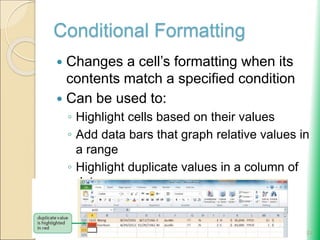
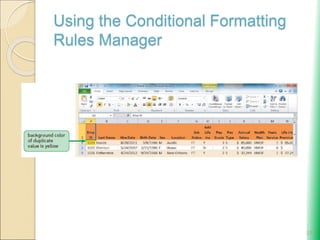
Microsoft Excel: Using Advanced Functions and Conditional Formatting document provides an overview of advanced Excel functions and conditional formatting. It discusses how to [1] use the IF, AND, and OR logical functions to evaluate conditions, [2] nest IF functions to test multiple conditions, [3] use structured references in formulas, and [4] apply conditional formatting to highlight or format cells based on their values. The document also demonstrates how to [3] summarize data using COUNTIF, SUMIF and AVERAGEIF functions to conditionally count, sum or average values that meet certain criteria.