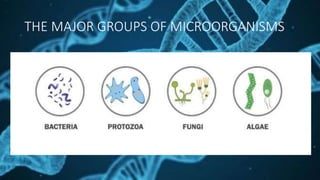
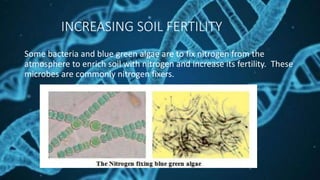
Microorganisms can be classified into four major groups. They can live in various environments ranging from cold climates to hot springs. Microorganisms play both helpful and harmful roles. Some microorganisms like yeast and bacteria are used to produce food items like bread and curd, while other microbes decompose organic waste. However, some microbes cause diseases in humans, plants and animals. Common human diseases from microbes include colds, tuberculosis, cholera, while plant diseases include those that affect wheat, rice, and sugarcane.