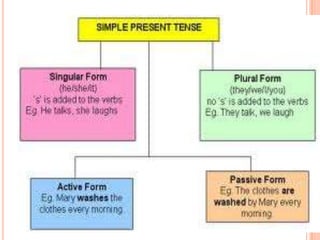
The document discusses the use of the simple present tense in English. It can be used to express habitual or repeated actions, facts that are generally true, and scheduled events in the near future. The simple present can also refer to actions happening now with non-continuous verbs. It also covers the forms of the verb "to be" and how to form negatives and questions. Finally, it provides rules for making the third person singular form of regular and irregular verbs.













![ -s or -es ?
With most verbs, the third person singular form is created
simply by adding -S. However, with some verbs, you need to
add -ES or change the ending a little. Here are the rules:
Verb ending in... How to make the 3rd person singular
S Add –ES He passes
Z Add –ES She waltzes
Sh Add –ES She wishes
Ch Add –ES He watches
X Add –ES She mixes
O Add –ES He goes
consonant + y Change Y to I, then add ES It flies
[anything else] Add –S He sings](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/usethesimplepresenttoexpresstheidea-111031150034-phpapp02/85/Use-the-simple-present-to-express-the-idea-14-320.jpg)