This document provides a summary and examples of different English verb tenses including:
1. Simple Present, Present Continuous, Present Perfect, Simple Past, Past Continuous, Past Perfect, Would Like To, Future with Will, and Future: Be Going To.
2. Each tense is defined and examples are provided to illustrate their structure and usage. Key points about when each tense is used are highlighted such as to describe habitual actions, ongoing actions, completed actions, plans/predictions for the future.
3. Over 20 verb tense examples are given for each one to demonstrate them in full sentences. The document serves as a helpful reference guide for the different English verb tenses.












![Structure:
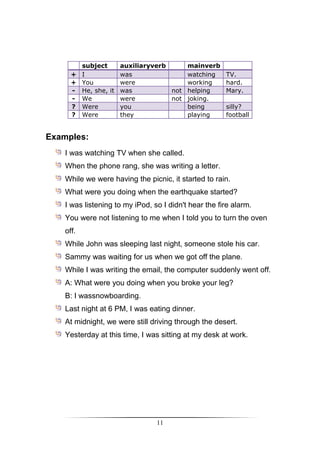
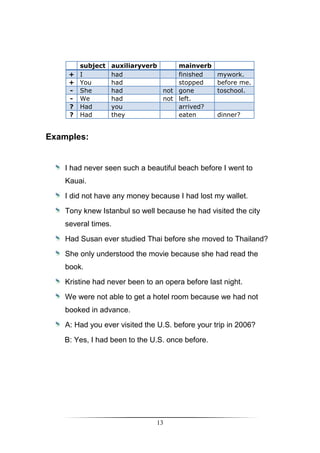
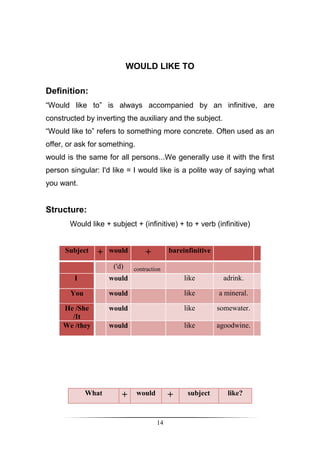
Positive
Subject + [WILL + Infinitive verb] + Complement
Negative
Subject + [WILL NOT (WON'T)+ Infinitive verb] + Complement
Question
Question Word + [WILL + Subject + Infinitive verb] + Complement
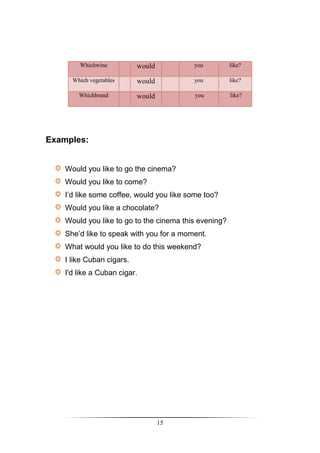
Examples:
Tom will never get married.
She will pay you next week.
It won’t rain today
Seth and Tom won’t come to class today.
I won’t be late anymore.
What will youstudy?
Will Maria live in Spain?
How long will Mark stay in Peru?
17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/colegioparticularautoguardado-121227125933-phpapp01/85/Colegio-particular-autoguardado-17-320.jpg)


