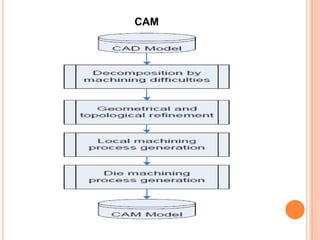
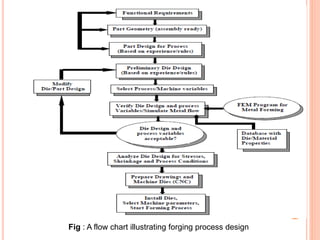
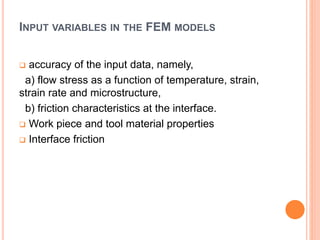
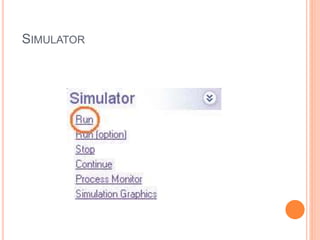
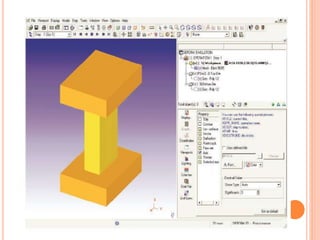
This document summarizes a technical seminar on the use of computer technology in the forging industry. It discusses how computer aided design (CAD), computer aided manufacturing (CAM), and computer aided engineering (CAE) help the forging industry design and manufacture dies more rapidly and cost effectively. Finite element analysis (FEA) simulation software is now integral to analyzing forging processes to optimize metal flow and die stresses before trials. Specific CAD, CAM, and FEA software and processes are also outlined.