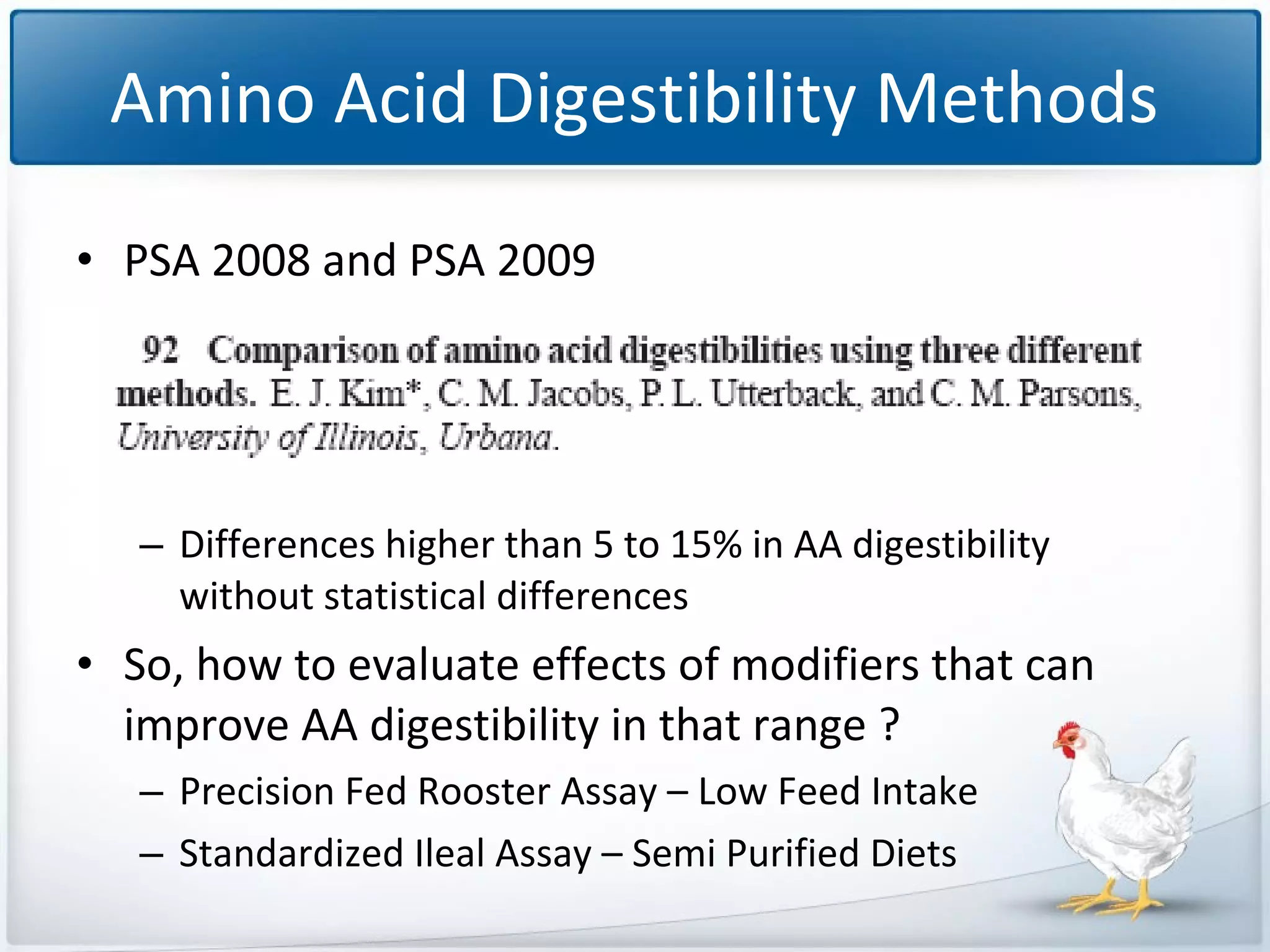
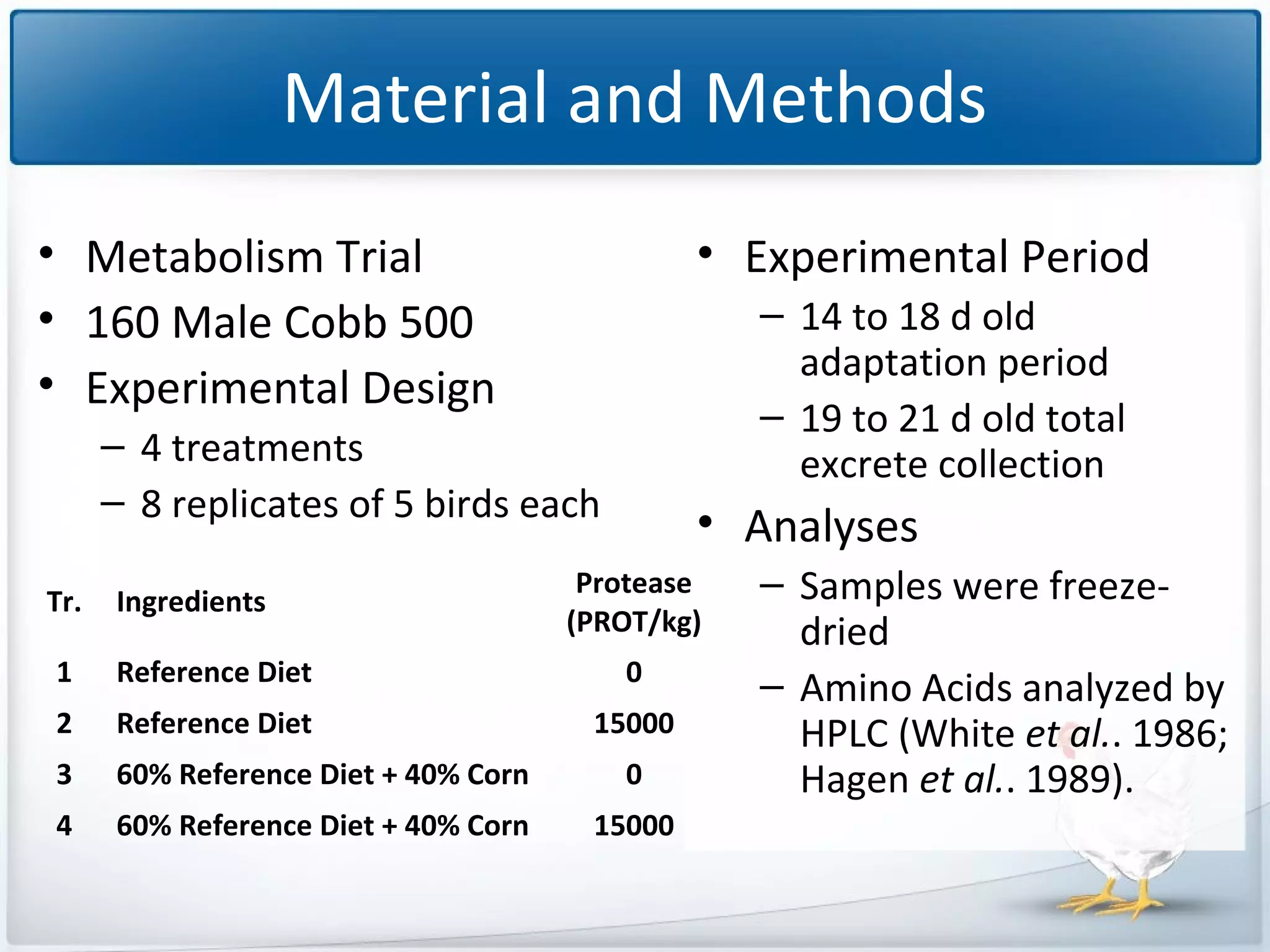
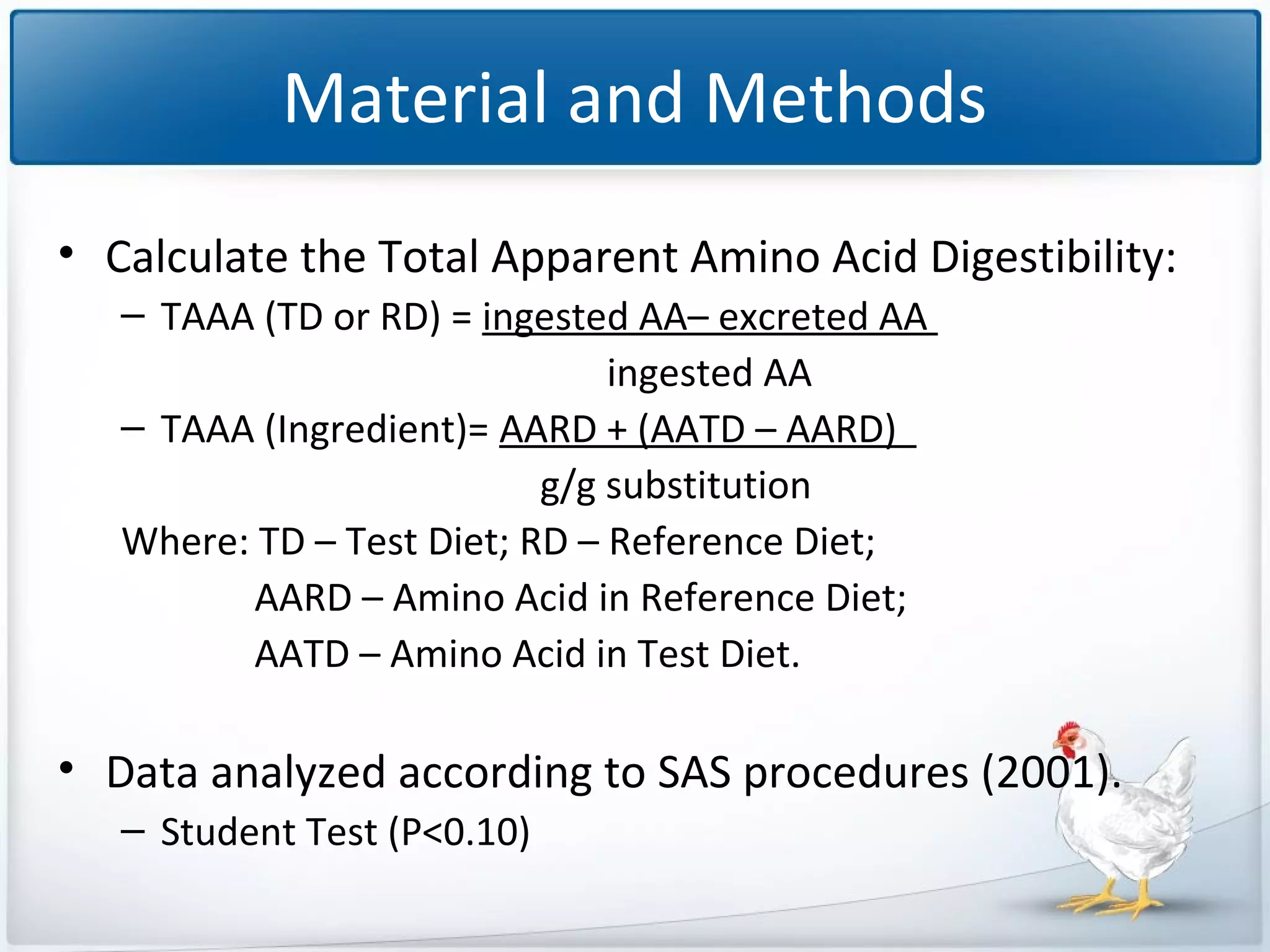
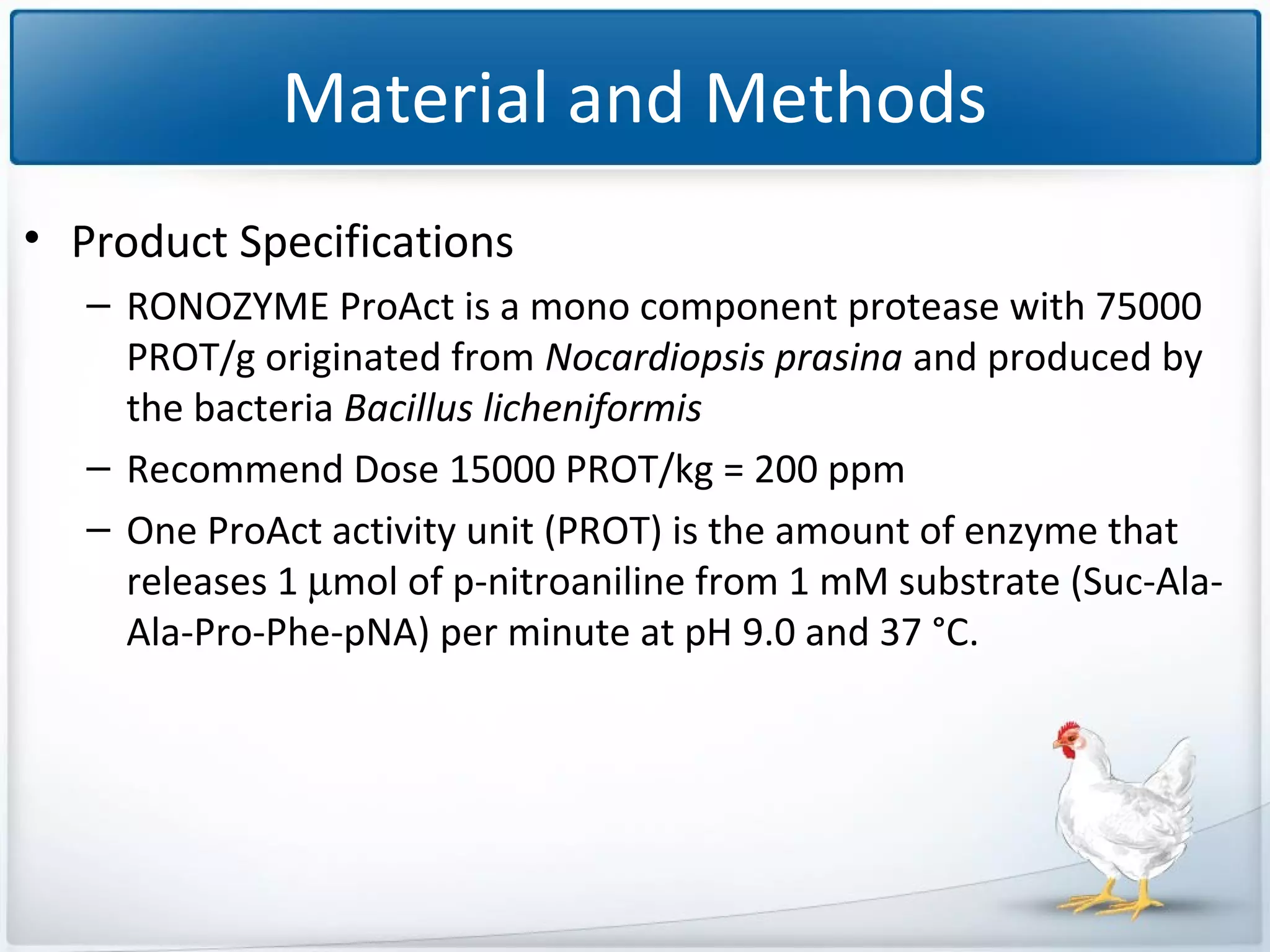
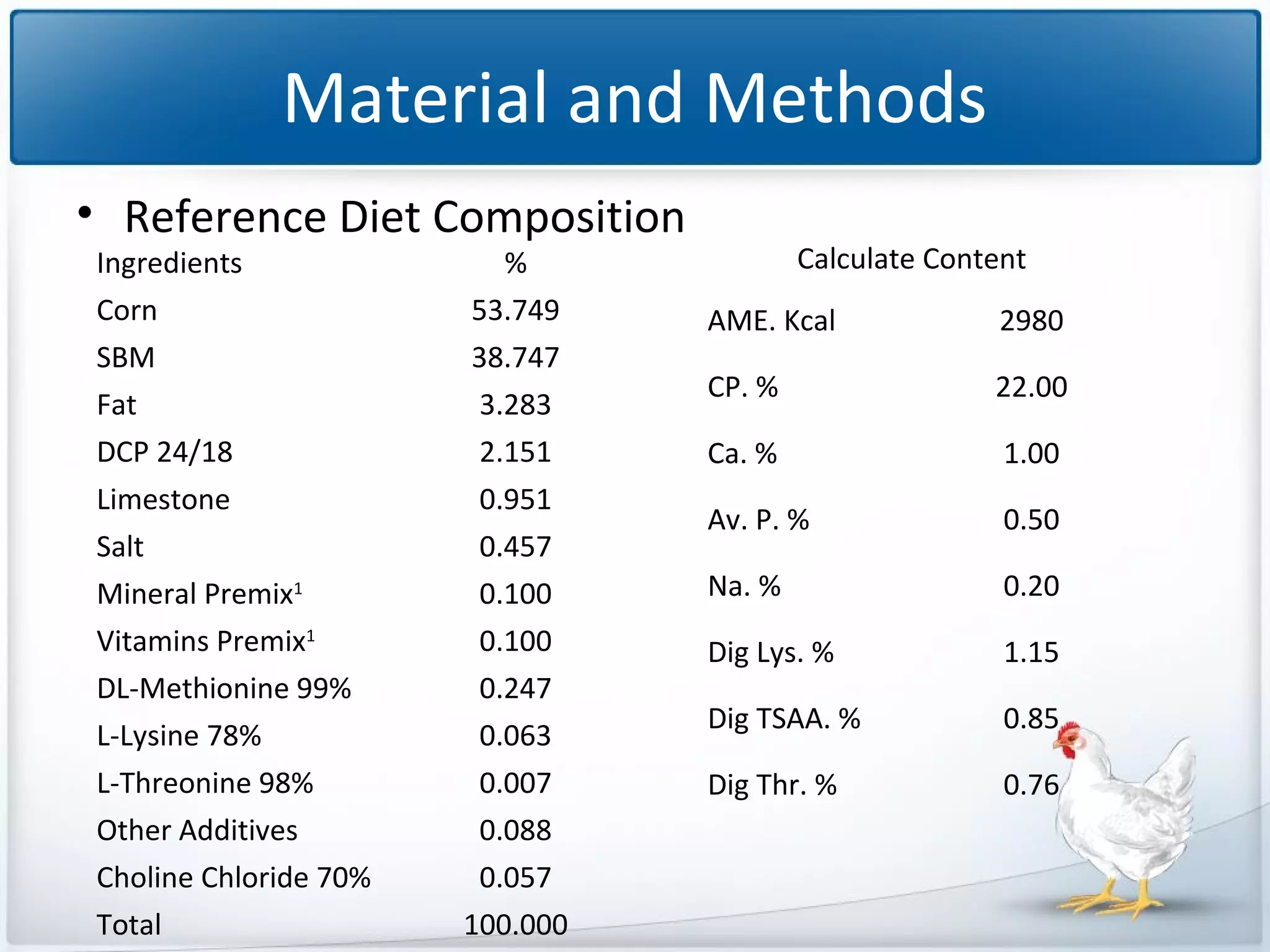
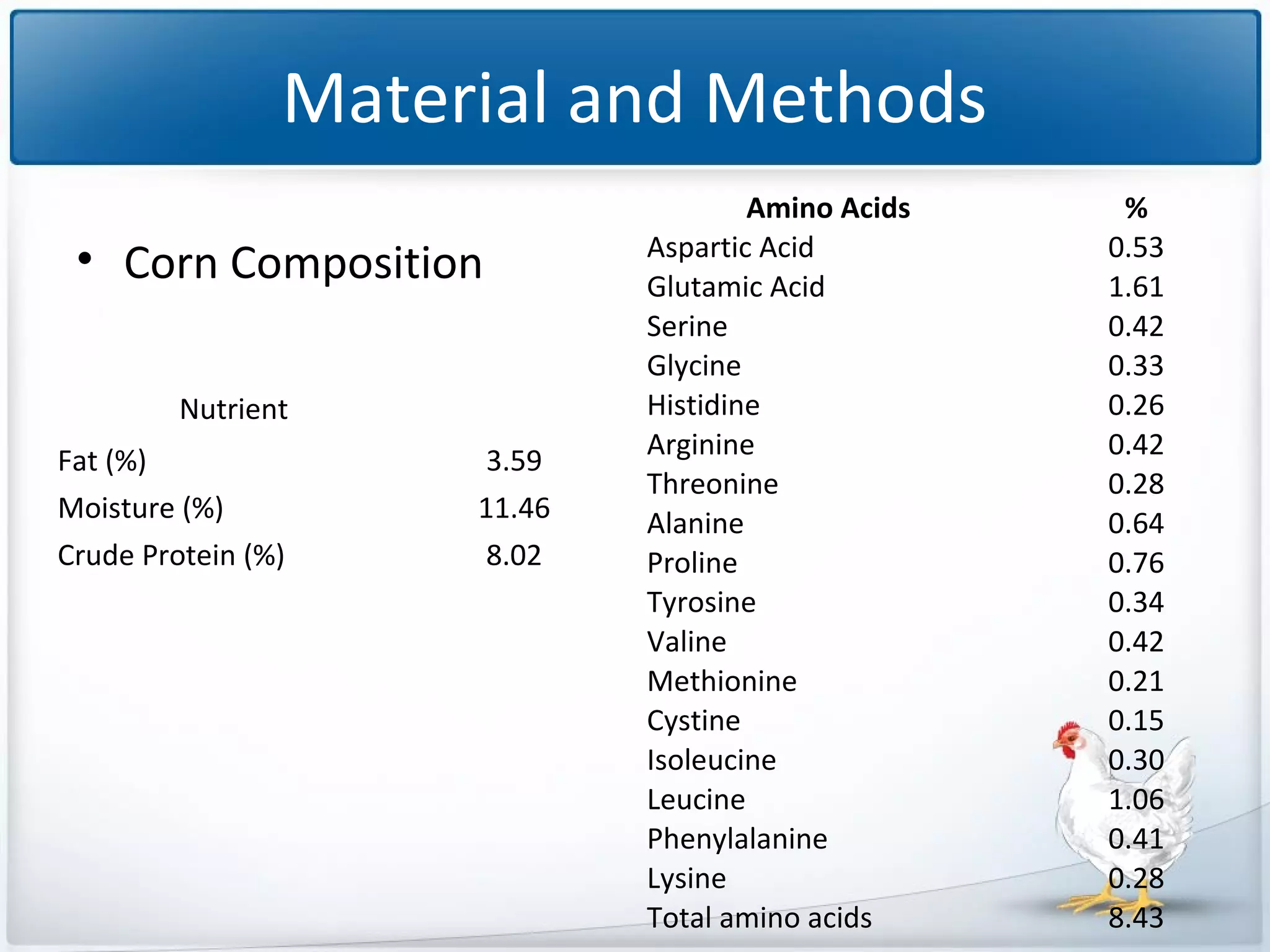
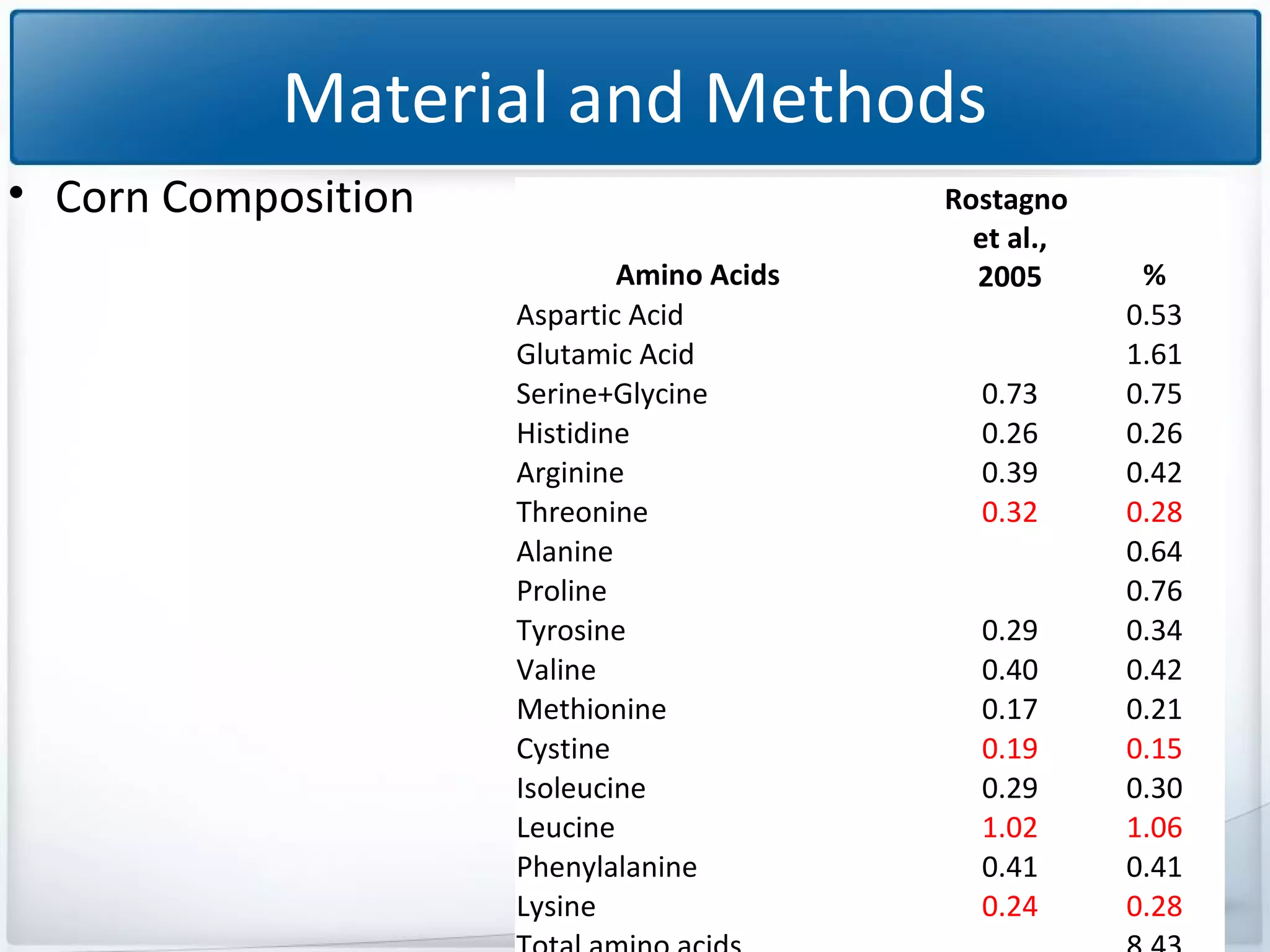
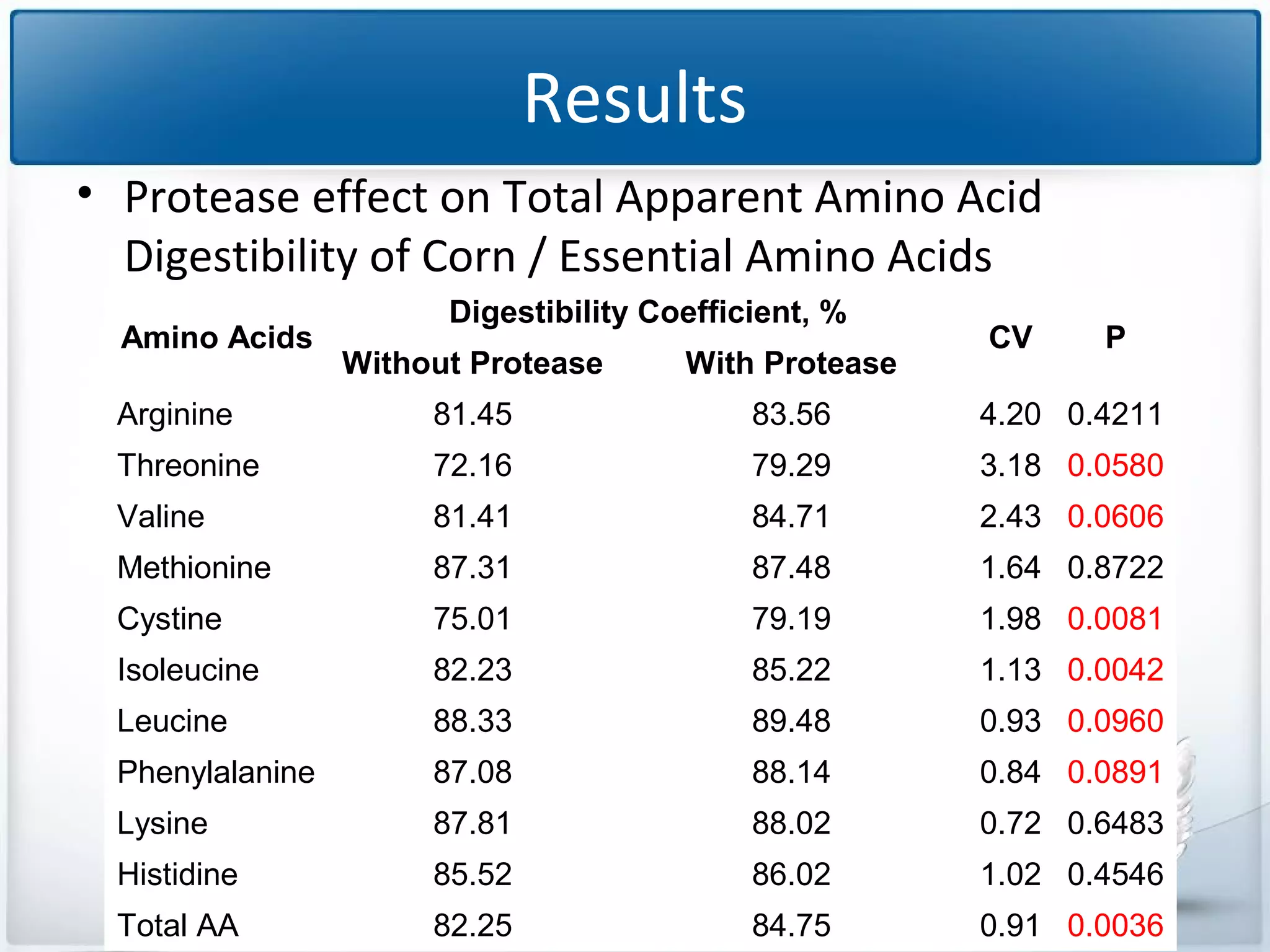
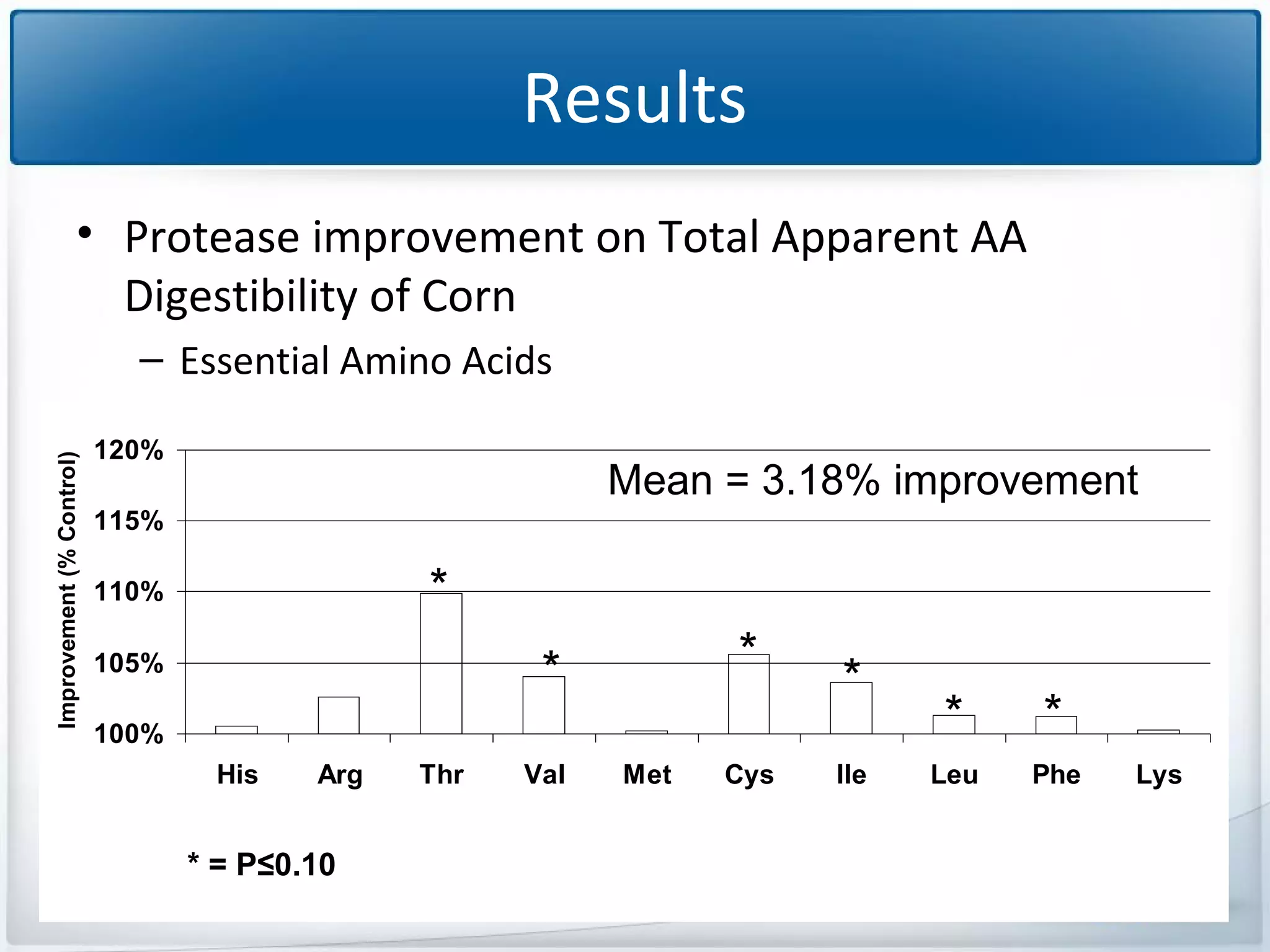
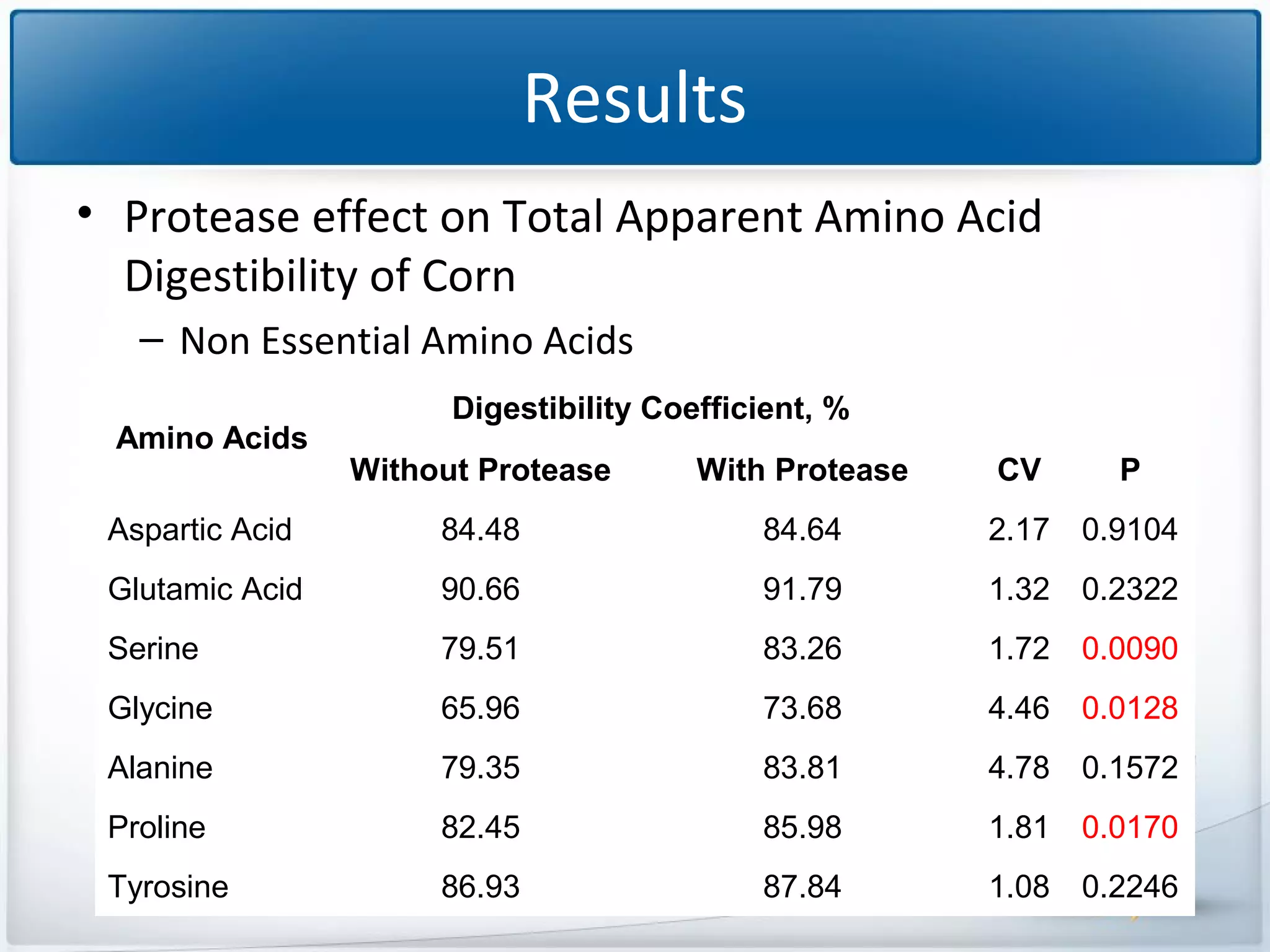
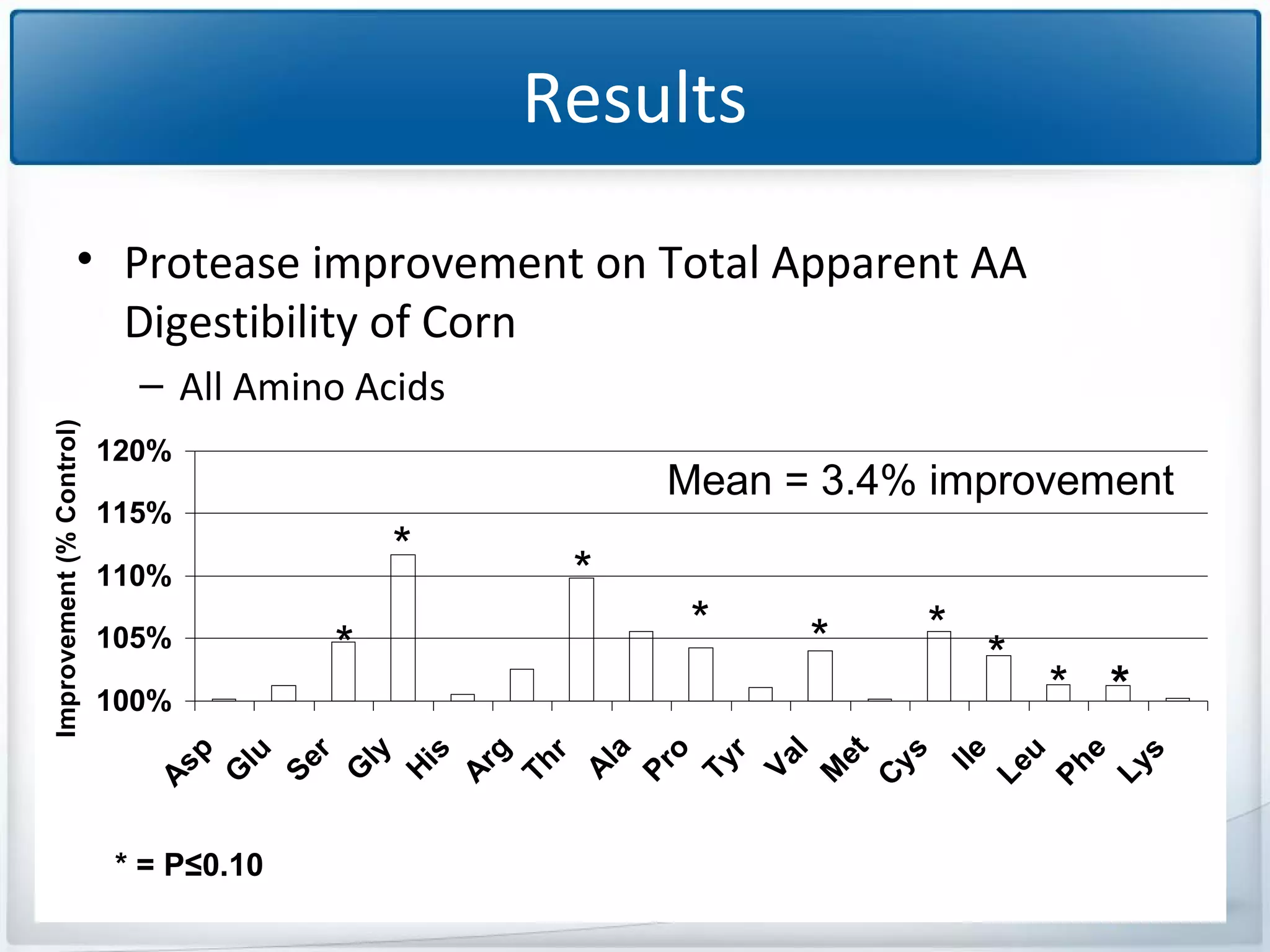
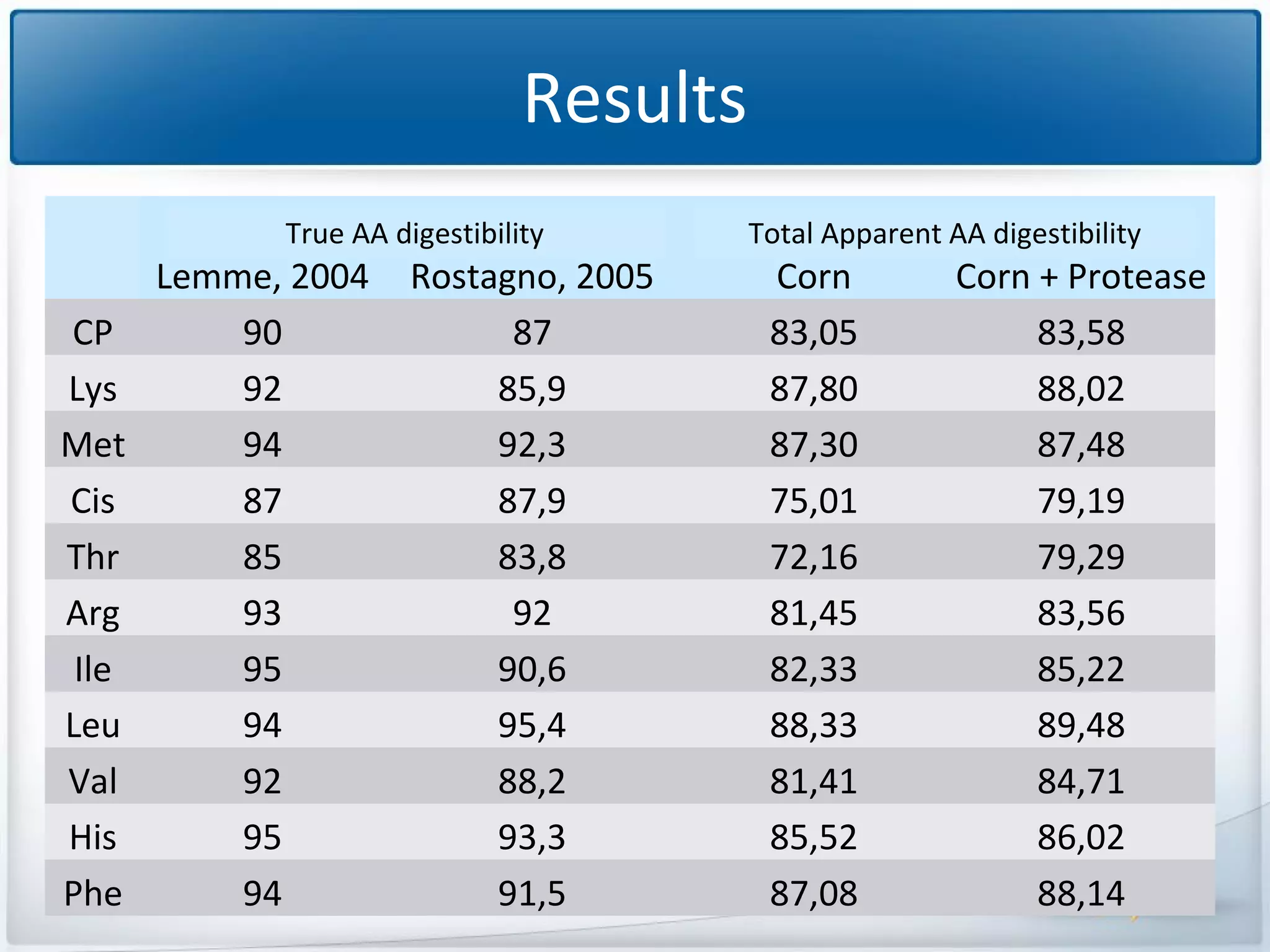
The study tested the effectiveness of a protease, Ronozyme Proact, in enhancing amino acid digestibility in corn for broilers. Results showed a significant improvement of approximately 3.18% in total apparent amino acid digestibility when the protease was included in the diet. The research indicates that using 200 ppm of this protease can effectively increase the utilization of amino acids in corn-based diets for broilers.