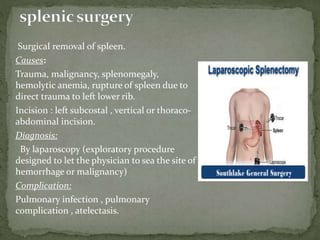
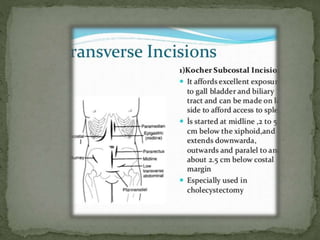
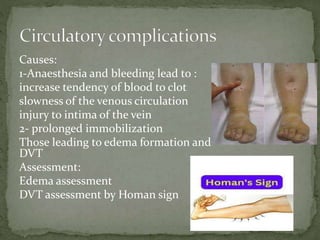
This document summarizes upper abdominal surgery, including common procedures like splenectomy, gastric surgery, cholecystectomy, herniotomy, and hepatic surgery. It describes the definition, incisions, causes, diagnosis, and complications for each procedure. Postoperative rehabilitation is discussed over three stages: the first two days focusing on pain management and respiratory care; days three to four adding circulatory exercises and abdominal muscle strengthening; and from day five until discharge addressing any lingering pulmonary issues as well as posture and gait training.