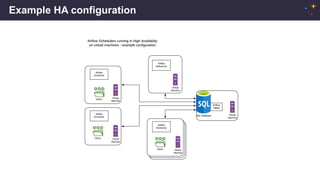
This document summarizes some of the key upcoming features in Airflow 2.0, including scheduler high availability, DAG serialization, DAG versioning, a stable REST API, functional DAGs, an official Docker image and Helm chart, and providers packages. It provides details on the motivations, designs, and status of these features. The author is an Airflow committer and release manager who works on Airflow full-time at Astronomer.