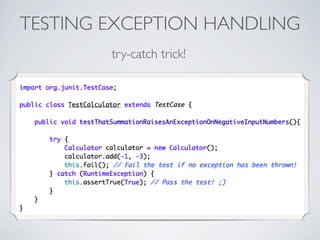
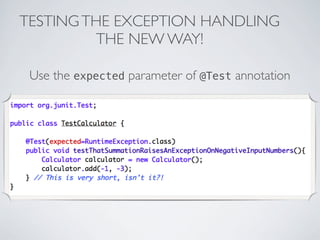
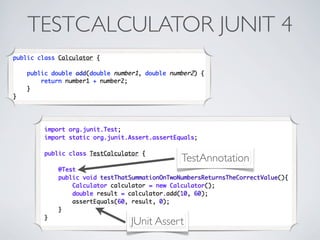
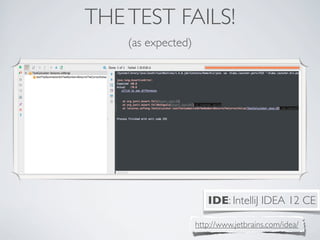
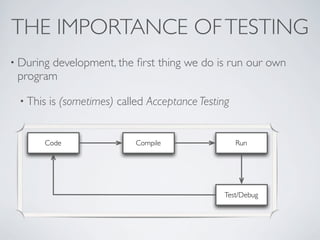
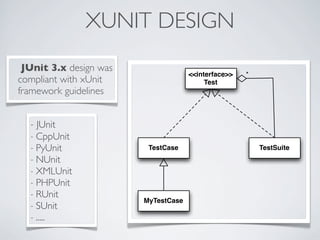
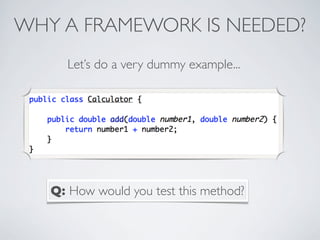
This document discusses unit testing with JUnit. It provides an introduction to JUnit, explaining that JUnit is a testing framework for writing and running repeatable tests of units of Java code. It describes the basics of JUnit, including how tests are organized using annotations in JUnit 4 like @Test and how assertions are used to validate expected outcomes. The document also demonstrates a simple example of writing a JUnit test for a calculator class.




















![JUNIT ASSERT STATEMENTS
• assertNotNull([message], object)
• Test passes if Object is not null.
• assertNull([message], object)
• Test passes if Object is null.
• assertEquals([message],expected, actual)
• Asserts equality of two values
• assertTrue(true|false)
• Test passes if condition isTrue
• assertNotSame([message], expected, actual)
• Test passes if the two Objects are not the same Object
• assertSame([message], expected, actual)
• Test passes if the two Objects are the same Object](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unittestingwithjunit-130627042731-phpapp02/85/Unit-testing-with-Junit-24-320.jpg)