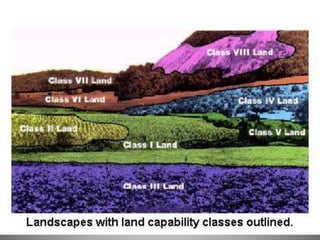
Land capability classification assigns numbers from I to VIII to rate land based on its suitability for agricultural uses without long-term damage. Class I land has very few limitations and can be cropped every year, while Class II land requires conservation practices and Class III land requires careful crop selection. Land in Classes V through VIII is generally not suitable for row crops due to limitations like slope, wetness, or rockiness, but can be used for pastures, forestry, or wildlife habitat. The system considers factors like soil depth and drainage, slope, erosion susceptibility, and climate.