UNIT – 5
NLP • Perception/Action • Machine Learning
1. Complexity of the Problem (Language Problems)
Natural language is difficult for computers because of the following reasons:
1. Ambiguity: A single word or sentence may have multiple meanings.
Example: “Bank” = river bank / financial bank.
2. Synonyms: Different words may have similar meanings.
Example: big, huge, large.
3. Grammar Rules: Languages have complex and irregular grammar structures.
4. Context Understanding: Meaning changes depending on the situation.
Example: “He is cold” → temperature OR behavior?
Because of these problems, computers find it hard to interpret human language
accurately.
2. Natural Language Processing (NLP) Stages
NLP converts human language into a form machines can understand.
It works in three main levels:
(a) Syntactic Processing (Structure / Grammar Level)
Deals with how words form sentences.
Includes:
• Sentence structure analysis
• Phrase detection (NP, VP)
• POS Tagging (noun, verb, adjective, etc.)
Example:
“The dog runs fast.”
POS = (Det, Noun, Verb, Adv)
(b) Semantic Analysis (Meaning Level)
Extracts actual meaning of words and relations.
Includes:
• Word meanings
• Synonyms
• Semantic roles (who did what)
Example:
“Ram ate an apple.”
Ram = agent
Apple = object
(c) Pragmatic Processing (Context Level)
Interprets intended meaning, not literal words.
Example:
“Can you pass the salt?”
Not asking about ability → It is a request.
Pragmatics = real-world meaning using context.
3. Perception & Action (Robotics Context)
Robotic systems need to sense and act.
(a) Perception
• Collecting information from the environment.
• Done using sensors:
o Cameras
o Microphones
o Touch sensors
o Lidar
Goal:
Convert raw sensor data → useful understanding.
Example: Detecting obstacles using camera or lidar.
(b) Action
• Acting based on perception.
• Uses actuators:
o Motors
o Wheels
o Arms
o Grippers
Example:
Robot sees an object → picks it up.
Perception + Action = Intelligent Robot Behavior
4. Machine Learning
Machine learning allows systems to learn patterns from data.
It has two main tasks:
1. Clustering
2. Classification
4.1 Clustering (Unsupervised Learning)
Clustering groups similar data points together.
A. Standard K-Means (Lloyd Algorithm)
Steps:
1. Select k initial cluster centers.
2. Assign each point to the nearest center.
3. Update centers (mean of assigned points).
4. Repeat until centers do not change.
Advantages:
• Simple
• Fast
Disadvantages:
• Depends on initial choice of centers
• Stuck in local minima
B. Generalized Clustering Techniques
Used when data is more complex.
1. Over-Partitioning
• K-means may create more clusters than necessary.
• Leads to incorrect grouping.
2. Merging
• Combines similar clusters when they are too close.
C. Modifications of K-Means
1. Better Initialization Techniques
• K-Means++
• Random multiple restarts
2. Avoid Local Minima
• Use different starting points
• Use K-harmonic means
3. Faster Update Methods
• Use efficient distance



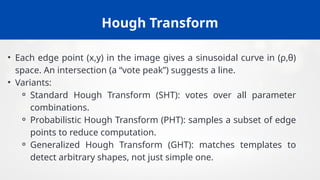
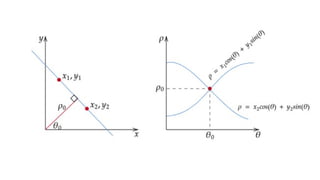






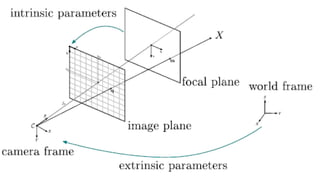




![Extracting Camera Parameters from Projection
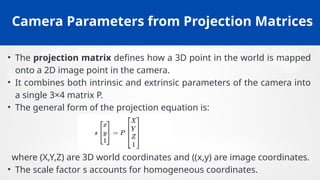
Matrix
• The projection matrix P can be decomposed as:
P=K[R t]
∣
where:
⚬ K = intrinsic parameter matrix (focal length, principal point, skew).
⚬ R = rotation matrix (orientation of camera).
⚬ t= translation vector (camera position).
• Decomposition allows us to find both internal characteristics of the
camera and its position/orientation in the world.
• This approach is fundamental for 3D reconstruction, stereo calibration,
and motion tracking.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-2modelfitting-251207154144-e8042604/85/Unit-2-Model_Fitting-computervision-pptx-23-320.jpg)





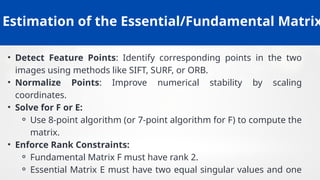
![The Essential Matrix
• The essential matrix encodes the epipolar geometry between two
calibrated cameras.
• It is defined as E = [t]ₓ R, where R is the relative rotation and t is the
relative translation between cameras.
• The essential matrix relates normalized image coordinates of
corresponding points in the two views.
• It has special properties: it is a rank 2 matrix with singular values of
the form (σ, σ, 0).
• Decomposition of the essential matrix allows recovery of the
relative camera motion (rotation and translation).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-2modelfitting-251207154144-e8042604/85/Unit-2-Model_Fitting-computervision-pptx-35-320.jpg)