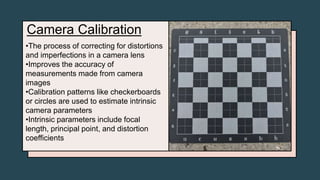
The document explores image-to-image mapping techniques such as homographies, warping images, and creating panoramas, highlighting their applications in image manipulation and registration. It also discusses the fundamentals of camera models, calibration, and pose estimation, which are essential for augmented reality (AR) applications. Finally, it emphasizes how AR technology merges virtual content with real-world environments for interactive experiences.