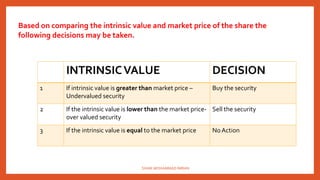
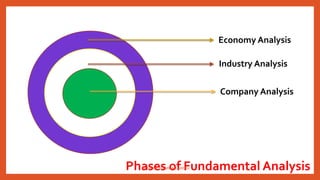
This document discusses the concepts and process of fundamental analysis for making investment decisions. It explains that fundamental analysis examines the intrinsic value of a company by analyzing the economy, industry, and company. The analysis involves 3 phases - evaluating the economy, industry life cycle stages (pioneering, expansion, stagnation), and company financial ratios to determine if the stock is under or overvalued compared to market price. Making investment decisions requires understanding these fundamental analysis concepts.