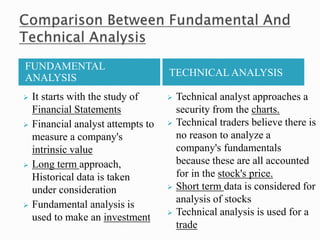
This document discusses various techniques for fundamental analysis of stocks. It describes examining a company's future earnings potential, economic well-being, and impacting factors. The objective is to value stocks compared to their price to determine if they are underpriced or overpriced. Some valuation metrics discussed include earnings per share, price-earnings ratio, dividend payout ratio, and discounted cash flow models. It also covers analyzing the overall economy and industries through factors like GDP, employment, inflation and more. The steps for industry analysis involve studying the industry life cycle and qualitative/quantitative factors. Fundamental analysis is distinguished from technical analysis, which uses historical stock price and volume data to identify trading opportunities.






![ Present value of all future cash flows in the form of dividends
plus the present value of the sale price expected .
P= [D1/(1+r)] + [P1/ (1+r)]
Where,
P = Current price/ market price of the share today
D1 = Dividend expected at the end of one year
r = discount rate/ required rate of return
P1= market price/ expected price of share at the end of year 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/shyamala-traditionalmethodsofsecurityanalysis-141005142803-conversion-gate02/85/Traditional-methods-of-security-analysis-Fundamental-Analysis-8-320.jpg)