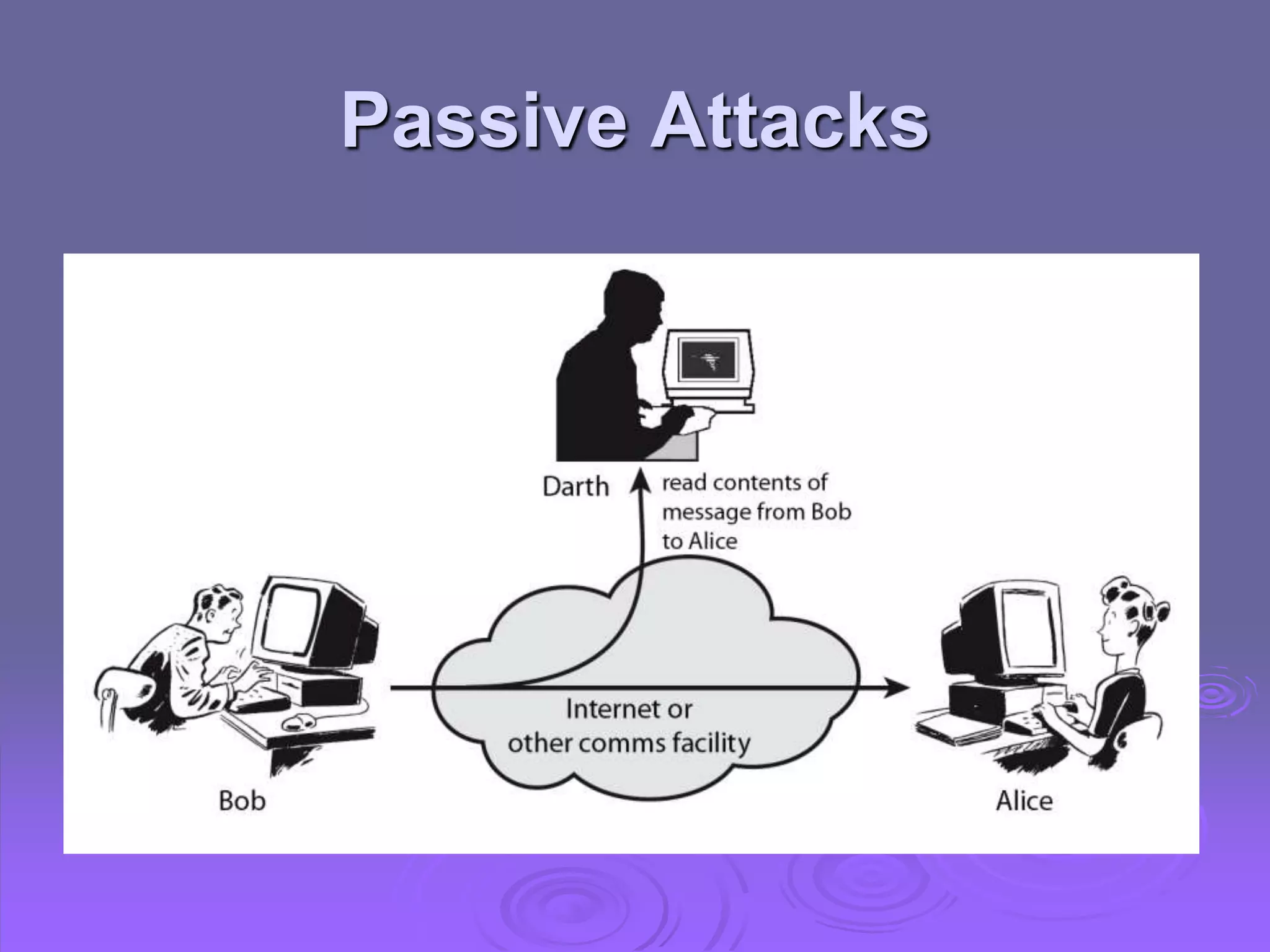
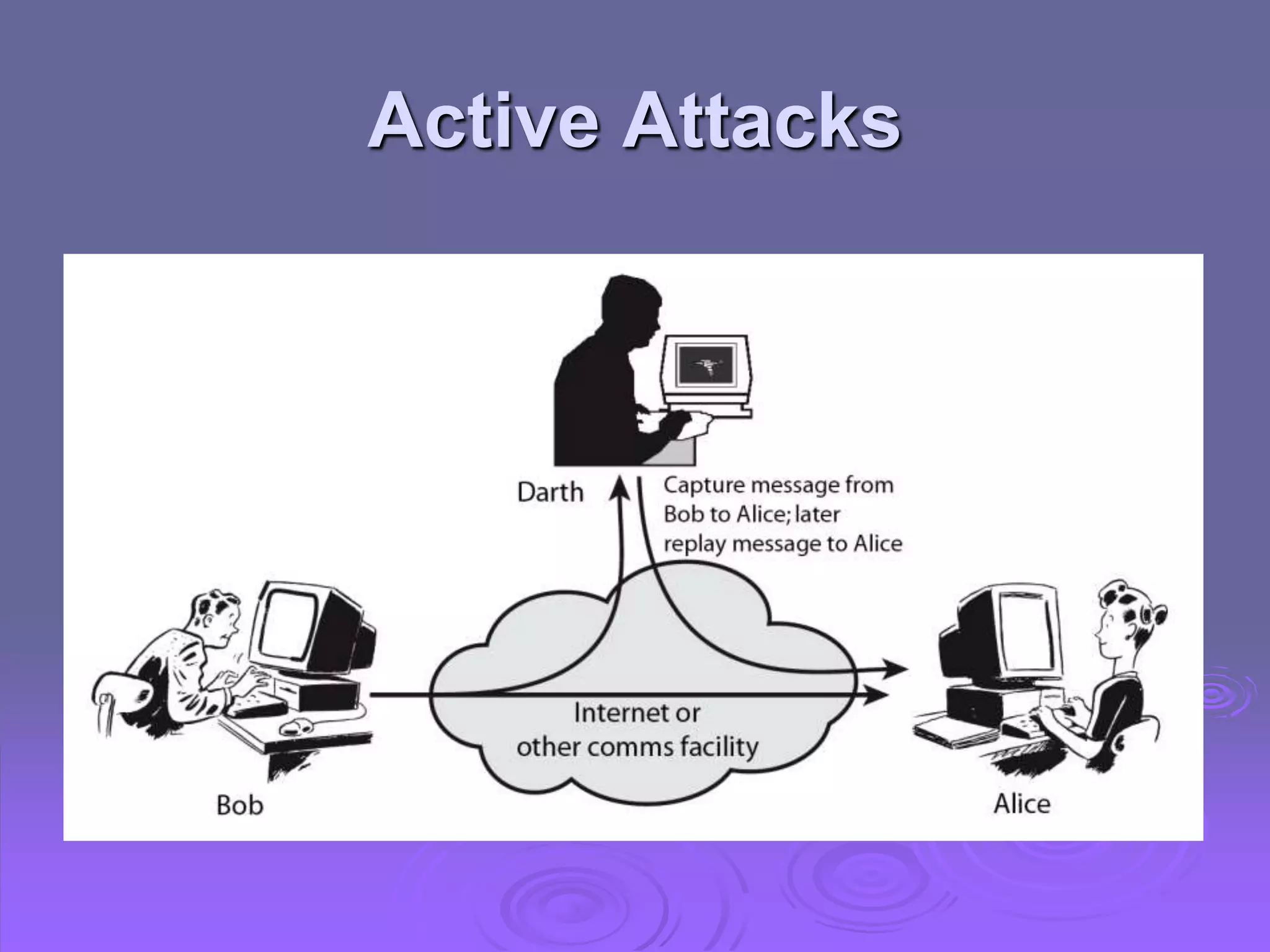
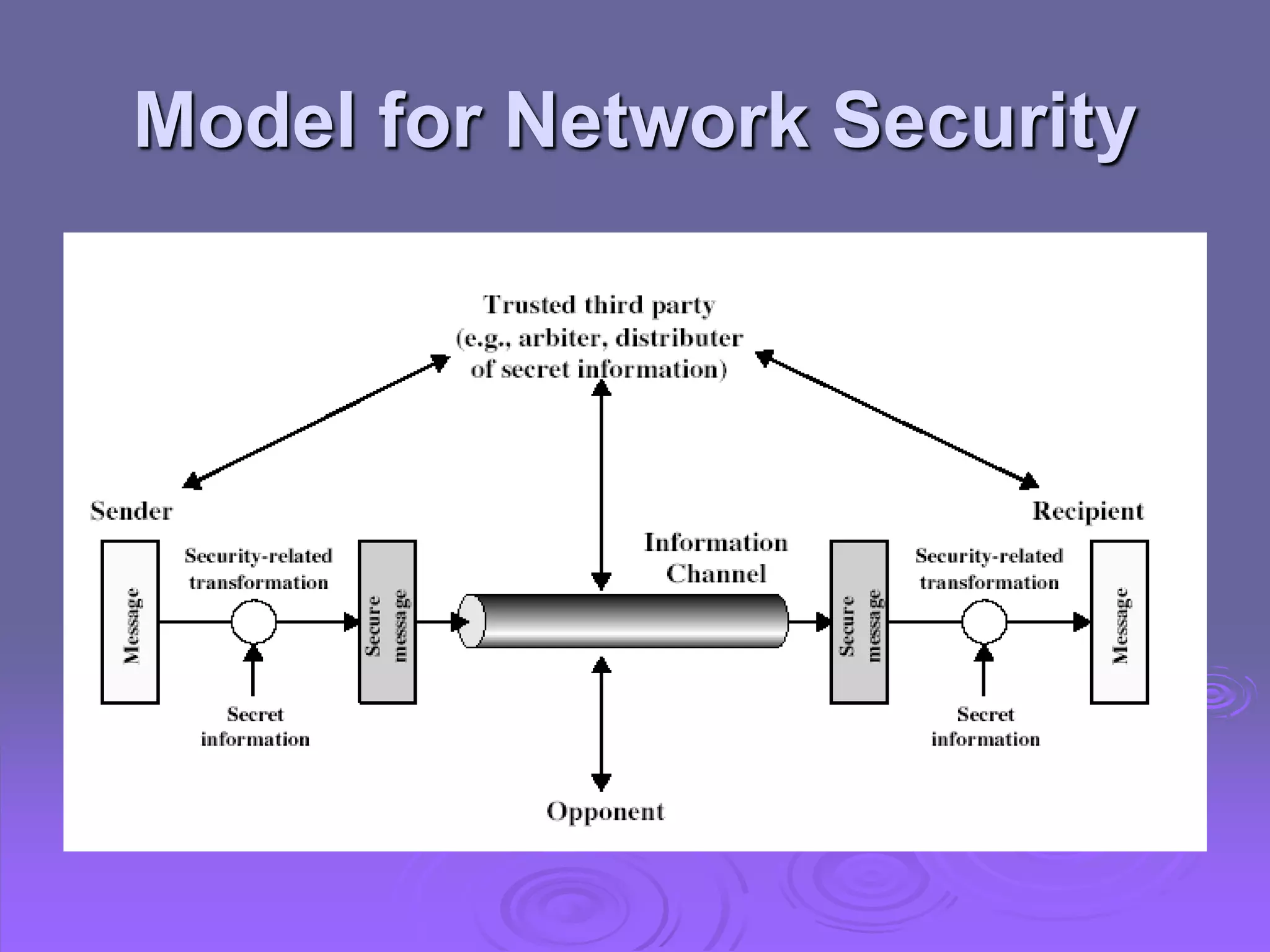
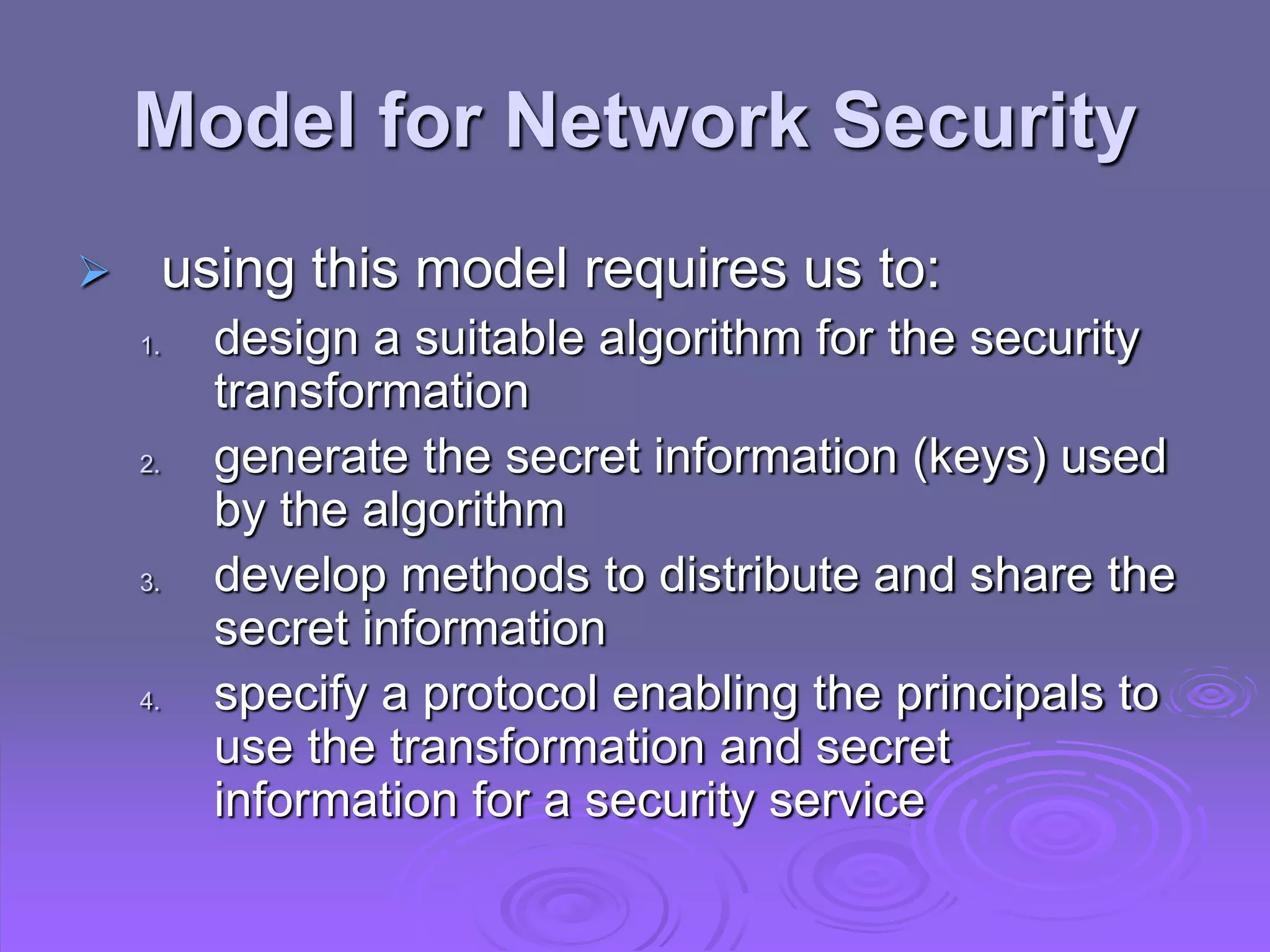
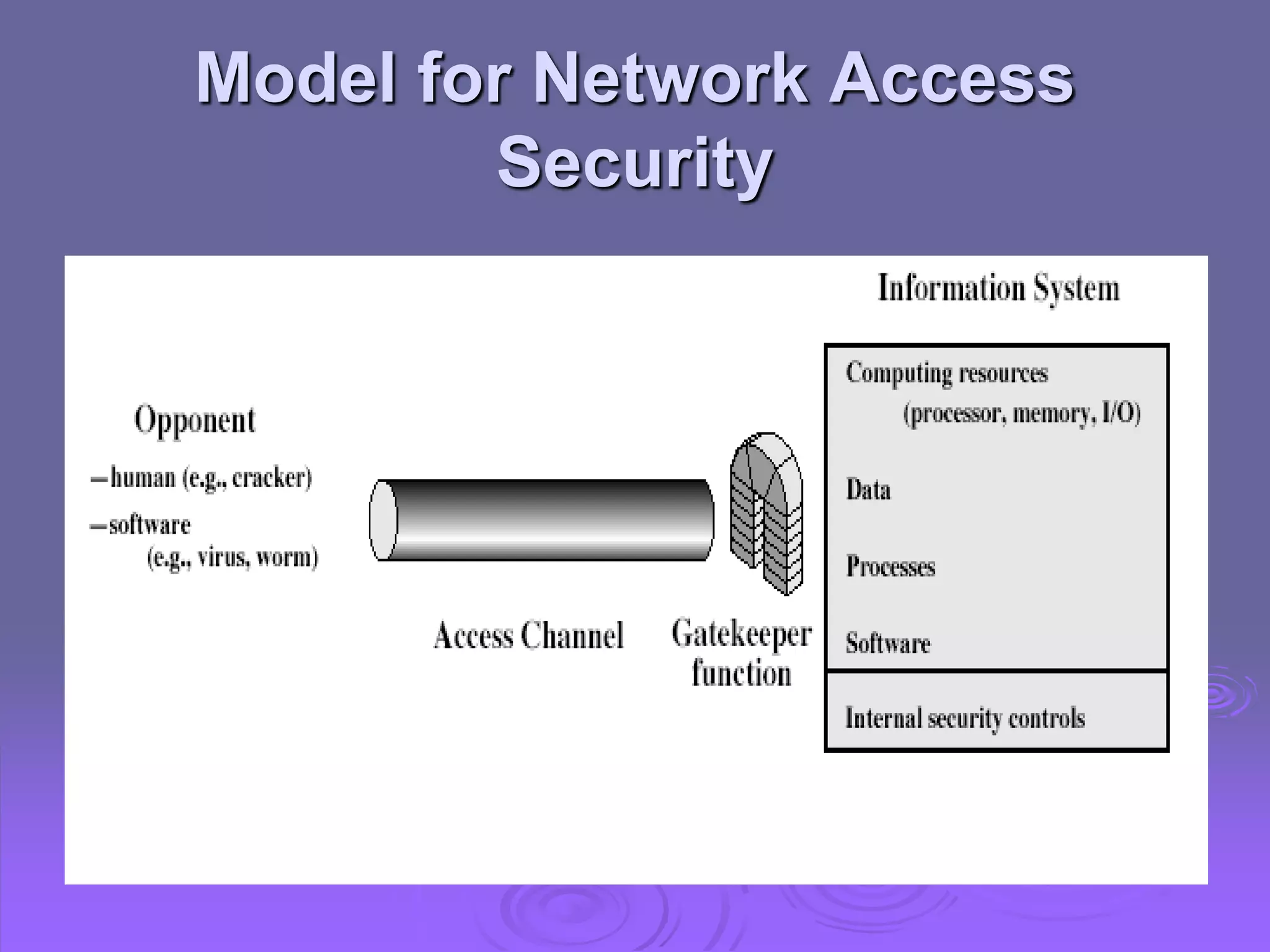
This document discusses cryptography and network security. It defines computer, network, and internet security and outlines the OSI security architecture. It describes security attacks, services, and mechanisms. Specifically, it distinguishes between passive and active attacks and examines authentication, access control, data confidentiality, data integrity, and non-repudiation as security services. Finally, it presents models for providing network and network access security that utilize cryptographic techniques and access controls.