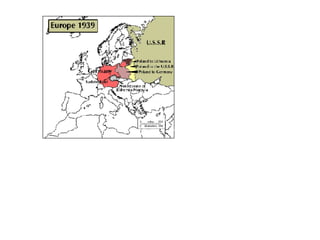
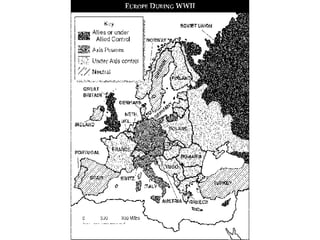
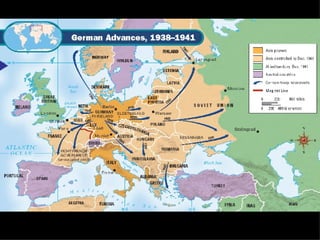
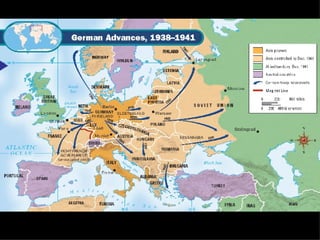
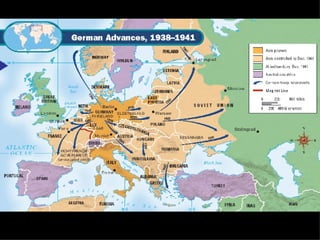
After coming to power, Hitler took several aggressive foreign policy actions which Britain and France failed to stop. He annexed Austria in 1938 and was allowed to take the Sudetenland region of Czechoslovakia under the Munich Agreement, despite promising it would be his last territorial demand. In 1939, Hitler seized the rest of Czechoslovakia. Britain and France had pursued a policy of appeasement but Winston Churchill strongly opposed this, warning that it would lead to war. Germany then invaded Poland using lightning-fast Blitzkrieg tactics, and the war began.









![Winston Churchill on Appeasement “ [W]e have passed an awful milestone in our history. . . . And do not suppose that this is the end. . . . This is only the first sip, the first foretaste of a bitter cup which will be proffered to us year by year unless, by a supreme recovery of moral health and martial vigor, we arise again and take our stand for freedom as in the olden time.” What was appeasement, and why did Churchill oppose it so strongly?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/war-in-europe-1200324986694067-4/85/War-In-Europe-11-320.jpg)









![“ [W]e shall defend our island, whatever the cost may be, we shall fight on the beaches, we shall fight on the landing grounds, we shall fight in the fields and in the streets, we shall fight in the hills; we shall never surrender.” -- Winston Churchill, May 1940](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/war-in-europe-1200324986694067-4/85/War-In-Europe-24-320.jpg)