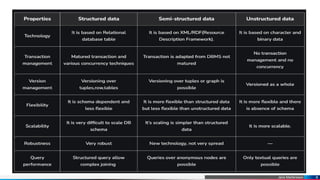
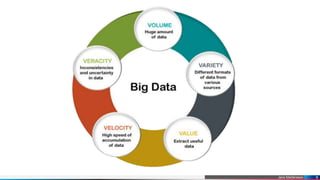
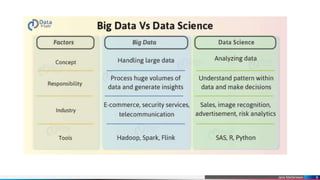
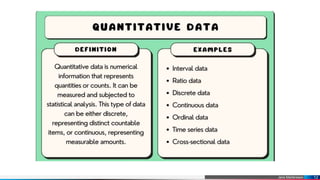
Data science is a multidisciplinary field focused on extracting meaningful insights from structured and unstructured data using scientific methods, mathematics, and technology. It encompasses various types of data, including structured, semi-structured, and unstructured, with an emphasis on the significance of big data for organizations in making data-driven decisions. Data scientists play a key role by analyzing large data sets to provide actionable insights that facilitate business growth.