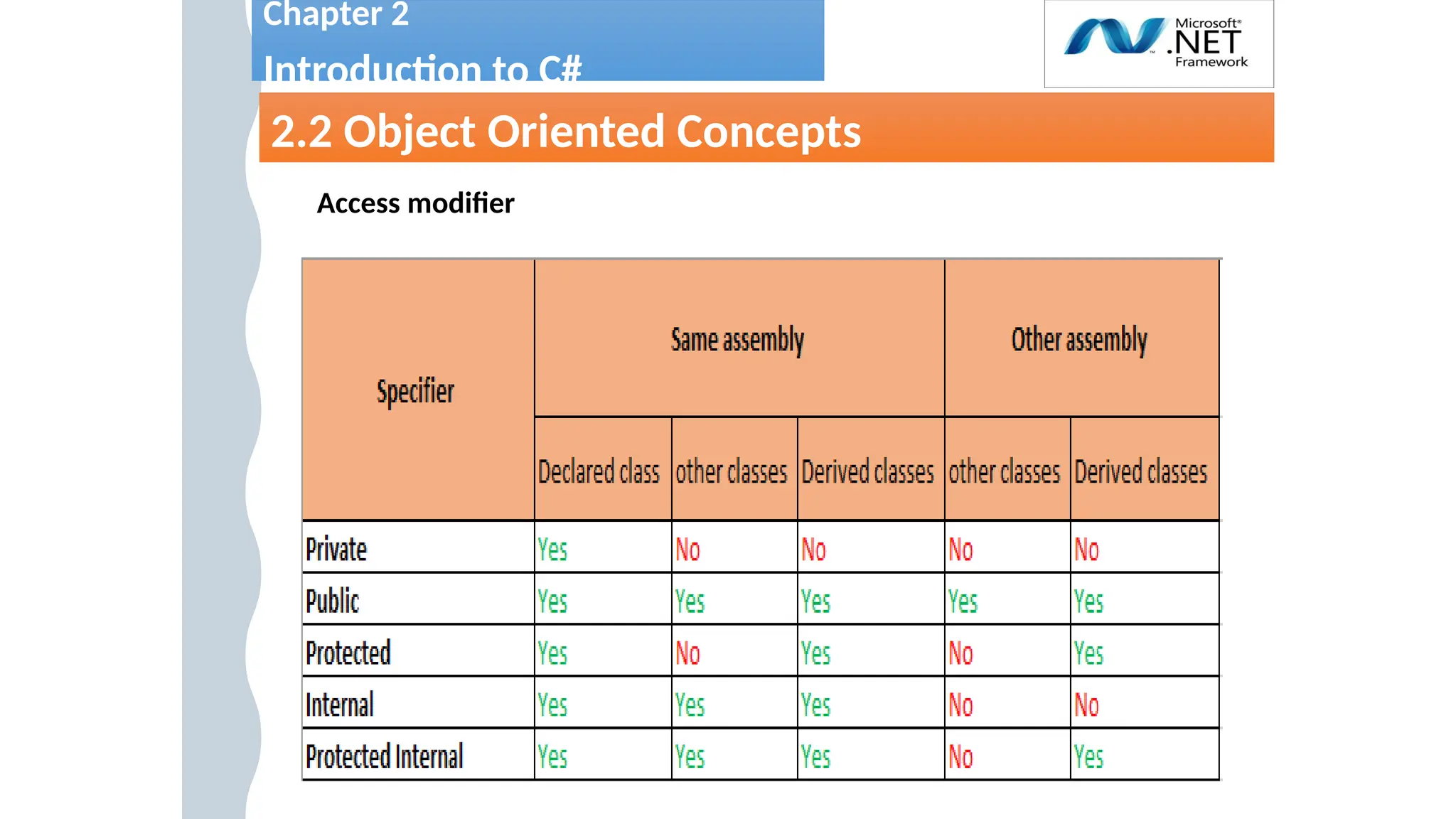
This document provides a comprehensive overview of object-oriented concepts in C#, including defining classes, access modifiers, inheritance, abstraction, polymorphism, and encapsulation. Key principles such as constructors, function overloading, and method overriding are explained with examples. It serves as a foundational guide for understanding OOP in C#.