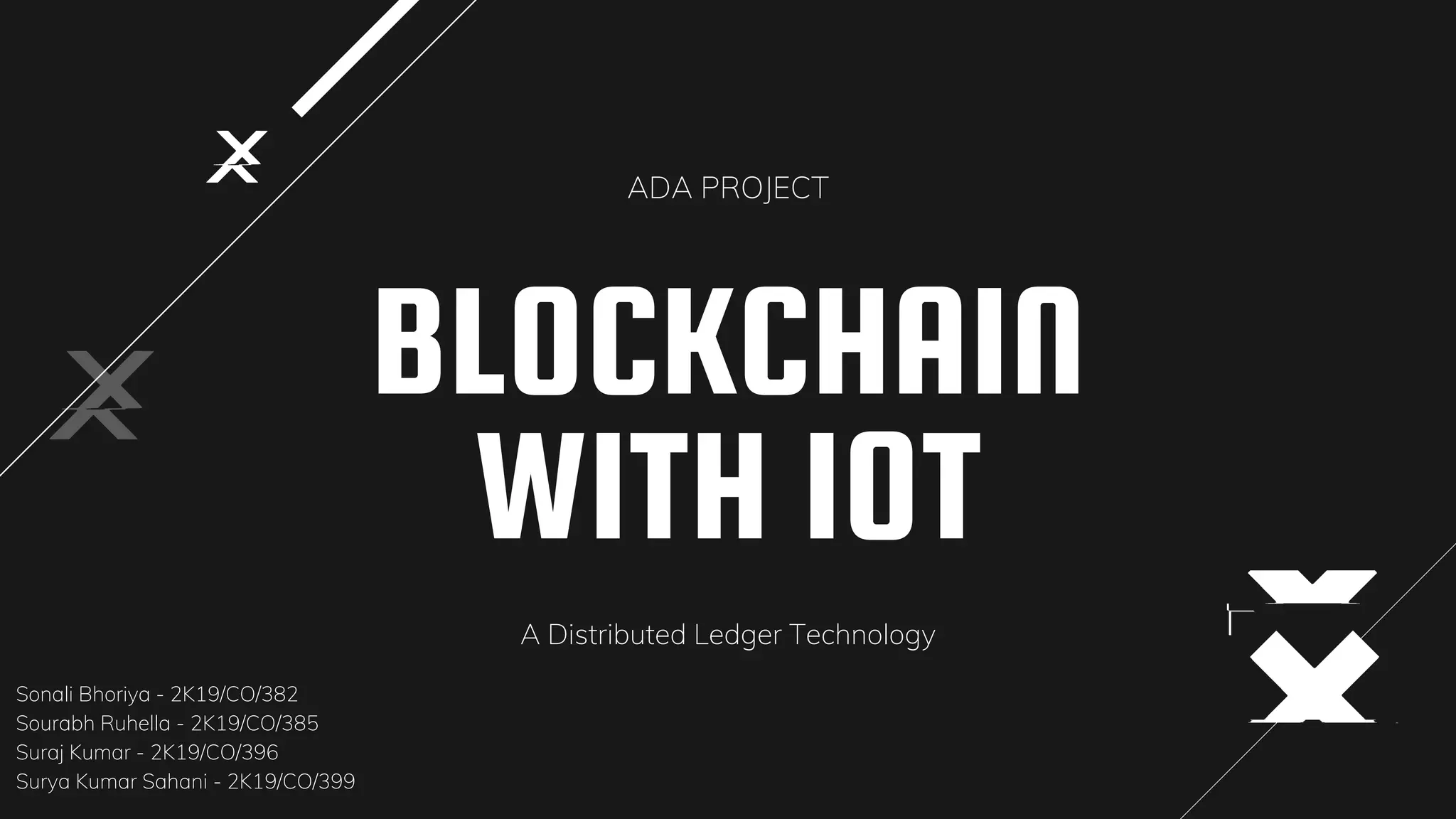
Blockchain and IoT convergence has potential benefits across many industries. IBM is working on extending private blockchains to cognitive IoT solutions. Blockchain can improve IoT features and cost efficiency through smart contracts that automatically execute transactions. However, challenges remain regarding technology, business models, legal issues, and developing agreements between many ecosystem actors. Future applications may involve peer-to-peer IoT device interactions using blockchain for security and transactions without centralized authorities.