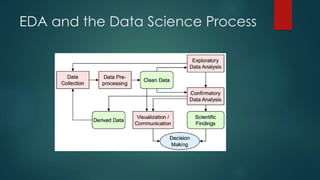
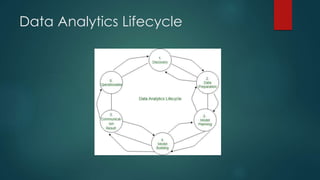
Data science is an interdisciplinary field focused on extracting insights from both structured and unstructured data using methods from statistics, computer science, and machine learning. It follows a lifecycle that includes data capture, maintenance, processing, communication, and analysis, and is essential for businesses to navigate the vast amounts of data generated daily. Key roles include data analyst, data scientist, and machine learning engineer, with skills ranging from technical abilities like programming and statistical analysis to non-technical skills like critical thinking and effective communication.