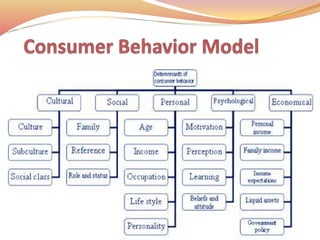
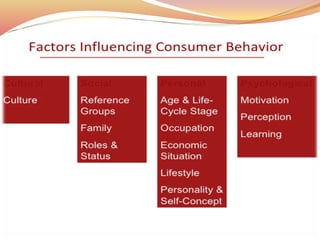
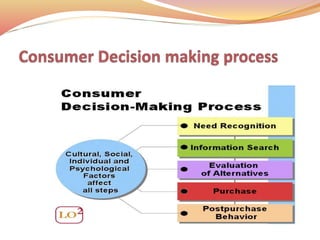
Consumer behavior examines how individuals or groups select and interact with products and services to fulfill their needs, impacting both consumers and society. It differentiates between customers, who purchase, and consumers, who use the products, and discusses various perspectives in consumer research including behavioral, cognitive, and personality traits. The study emphasizes the importance of understanding these behaviors to enhance marketing strategies, especially in a rapidly changing and competitive marketplace.