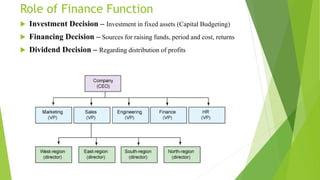
The case study on Unilever Limited highlights the transformation of its finance function, evolving from a traditional approach focusing solely on fund procurement to a modern strategy that encompasses fund allocation and strategic partnership with the CEO. Despite challenges in 2014, Unilever demonstrated resilience with competitive sales growth and improved core operating margins, while also emphasizing risk management and treasury functions to optimize financial resources and minimize risks. Key initiatives include the development of a Global Finance Excellence Center and innovative asset allocation models to navigate economic pressures.