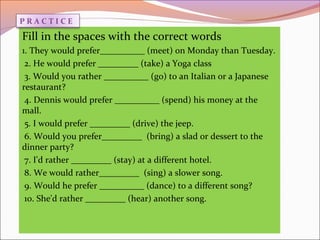
This document provides a summary of English language learning materials for the February-June 2016 semester. It covers units 7 and 8, focusing on passive verbs with prepositions, would rather/would prefer structures, and using gerunds with "by" to describe how to do things. Explanations, examples, exercises and a bibliography are provided to help students practice these grammar points and vocabulary through visual examples. The goal is for students to develop their English skills through interactive situations.











![Infinitive clauses and phrases
Structure the sentences as follows:
(A way/ Two Ways) + infinitive + is/are + infinitive
One thing+ to do about it+ is+ to talk to the company’s management
Another way+ to stop them+ is +to get a TV station to run a story
The best ways+ to fight HIV / AIDS +are +to do more research and educate
people.
An infinitive is part of the subordinate clauses which are named after the form of
the verb . TO-INFINITIVE CLAUSE:
You must book early [to secure a seat]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/diapositivasinglesiiisec3-160419140229/85/Unidad-8-Ingles-III-12-320.jpg)