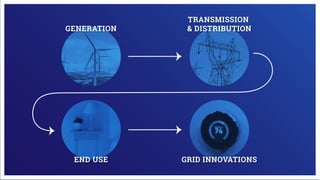
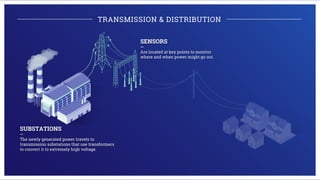
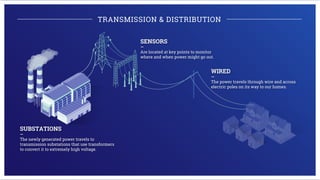
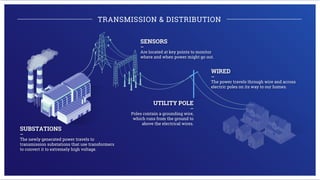
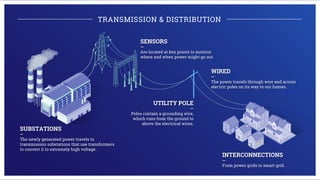
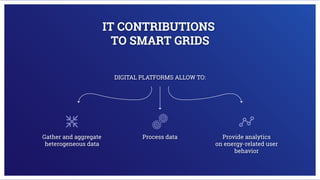
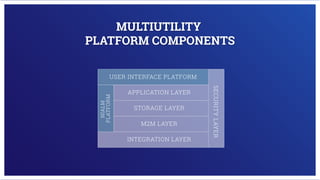
Electricity is generated at power plants through various methods like fossil fuels, wind, solar, water, and nuclear energy. It is then sent through high voltage transmission lines to substations where the voltage is reduced before being distributed through wires on utility poles to homes and businesses. Advanced technologies are improving the grid through microgrids, energy storage, smart meters, and digital platforms that allow for better monitoring, analytics, and innovative consumer services.