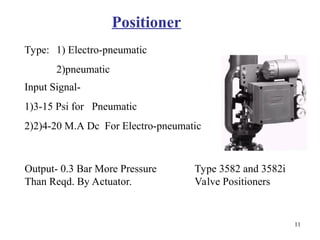
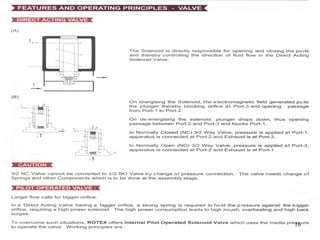
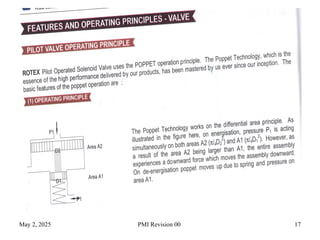
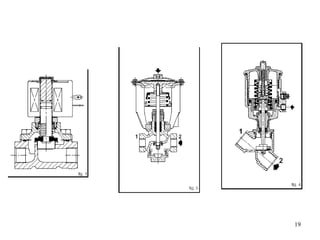
Pneumatic actuators are devices that use compressed air to produce mechanical motion. They play a key role in automation systems across a variety of industries due to their reliability, simplicity, and power. Here's a breakdown of the principles and applications of pneumatic actuators:
Principles of Pneumatic Actuators
Basic Operation:
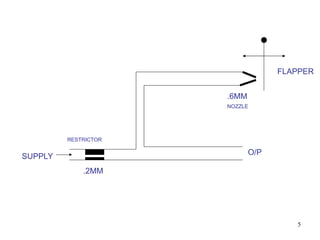
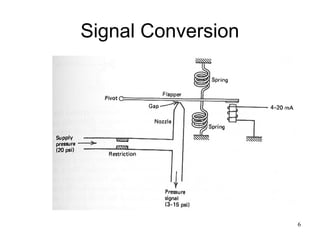
Pneumatic actuators work by converting the energy from compressed air into mechanical movement. When air is supplied to one side of the actuator, it creates pressure that moves a piston or diaphragm, which then produces linear or rotary motion.
Types of Pneumatic Actuators:
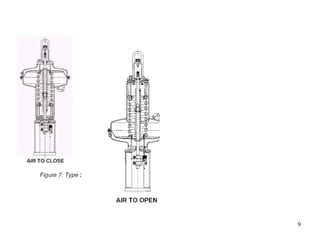
Linear Pneumatic Actuators: These actuators generate straight-line motion (e.g., pushing or pulling). The most common design is the cylinder, where a piston moves inside a tube.
Rotary Pneumatic Actuators: These actuators generate rotary motion, turning a shaft through a 90° or full 360° rotation. They are often used in valve control or in applications requiring rotational movement.
Key Components:
Cylinder/Tubing: The body of the actuator that holds the piston and provides a space for the air to move.
Piston: The part that moves under the influence of compressed air, creating force.
Valves: Control the direction, speed, and pressure of the compressed air entering the actuator.
Seals: Prevent air leakage and ensure efficient operation.
Types of Motion:
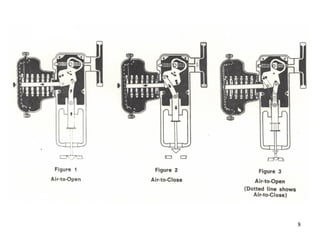
Single-Acting Actuators: These actuators use compressed air to move the piston in one direction, and a spring returns it to its initial position.
Double-Acting Actuators: These actuators use compressed air to move the piston in both directions, providing more control over motion.
Applications of Pneumatic Actuators
Pneumatic actuators are widely used across various industries for tasks requiring controlled, repeatable, and reliable motion.
Manufacturing and Automation:
Used for robotic arms, conveyor systems, and material handling.
Operate machine tools, presses, and clamping systems.
Automotive Industry:
Control doors, windows, and seat adjustments.
Operate valves and other fluid control systems.
HVAC Systems:
Used to control dampers and valves for air distribution and temperature regulation.
Food and Beverage Industry:
Pneumatic actuators help in packaging, filling, and labeling machines.
Used in food processing systems for precise control of valves.
Oil and Gas:
Pneumatic actuators are used for valve control in pipelines and rigs, where they operate remotely under harsh conditions.
Medical Devices:
Used in equipment like dental chairs and patient beds where precise movement is required.
Agriculture:
Pneumatic actuators are used in automated systems for planting, harvesting, and irrigation control.
Advantages of Pneumatic Actuators
High Speed: Pneumatic actuators offer quick response times and fast movement.
Simplicity: They are easy to install, operate, and maintain.
Force-to-Weight Ratio: Pneumatic actuators provide high force in relation to their size.