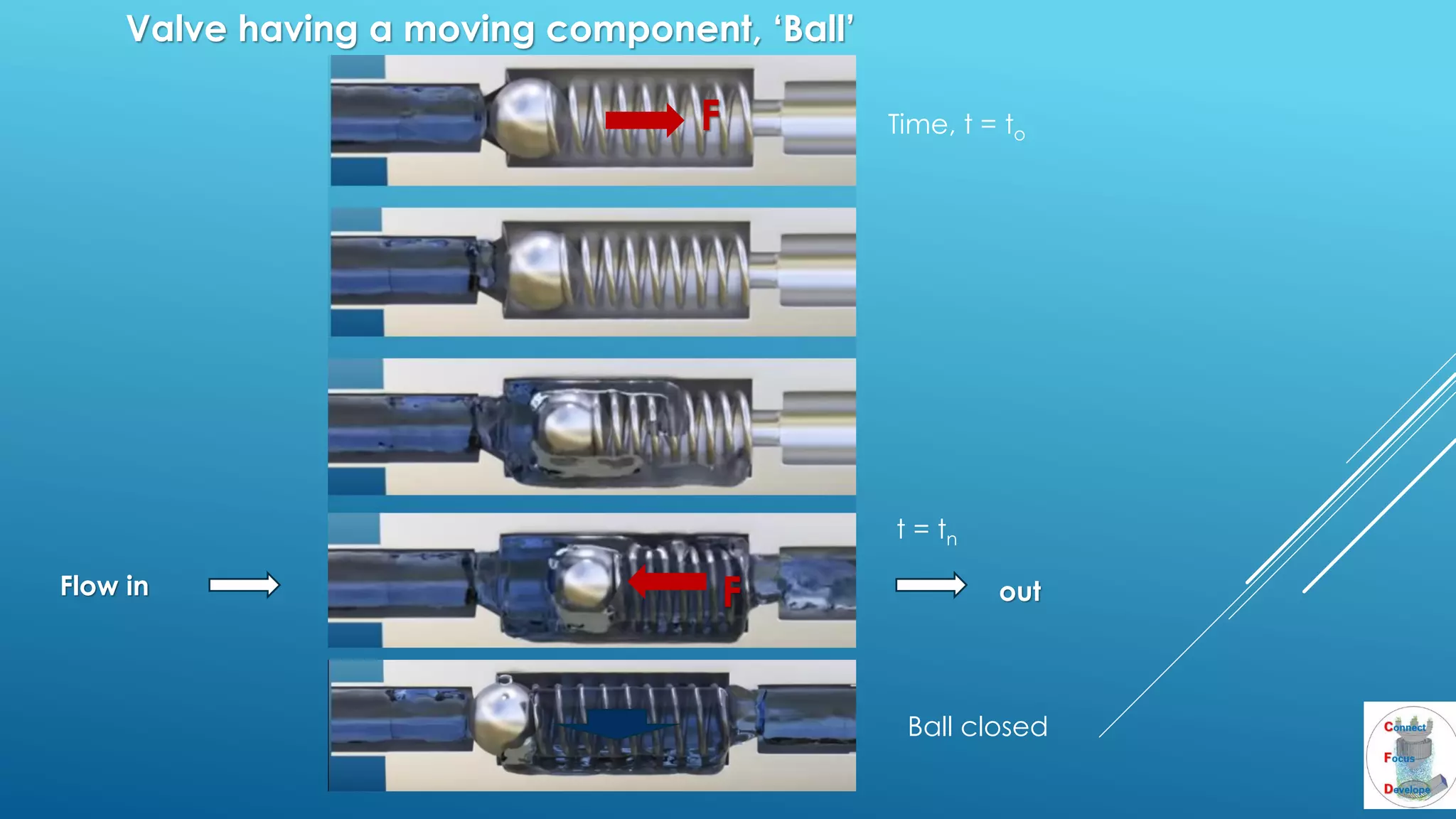
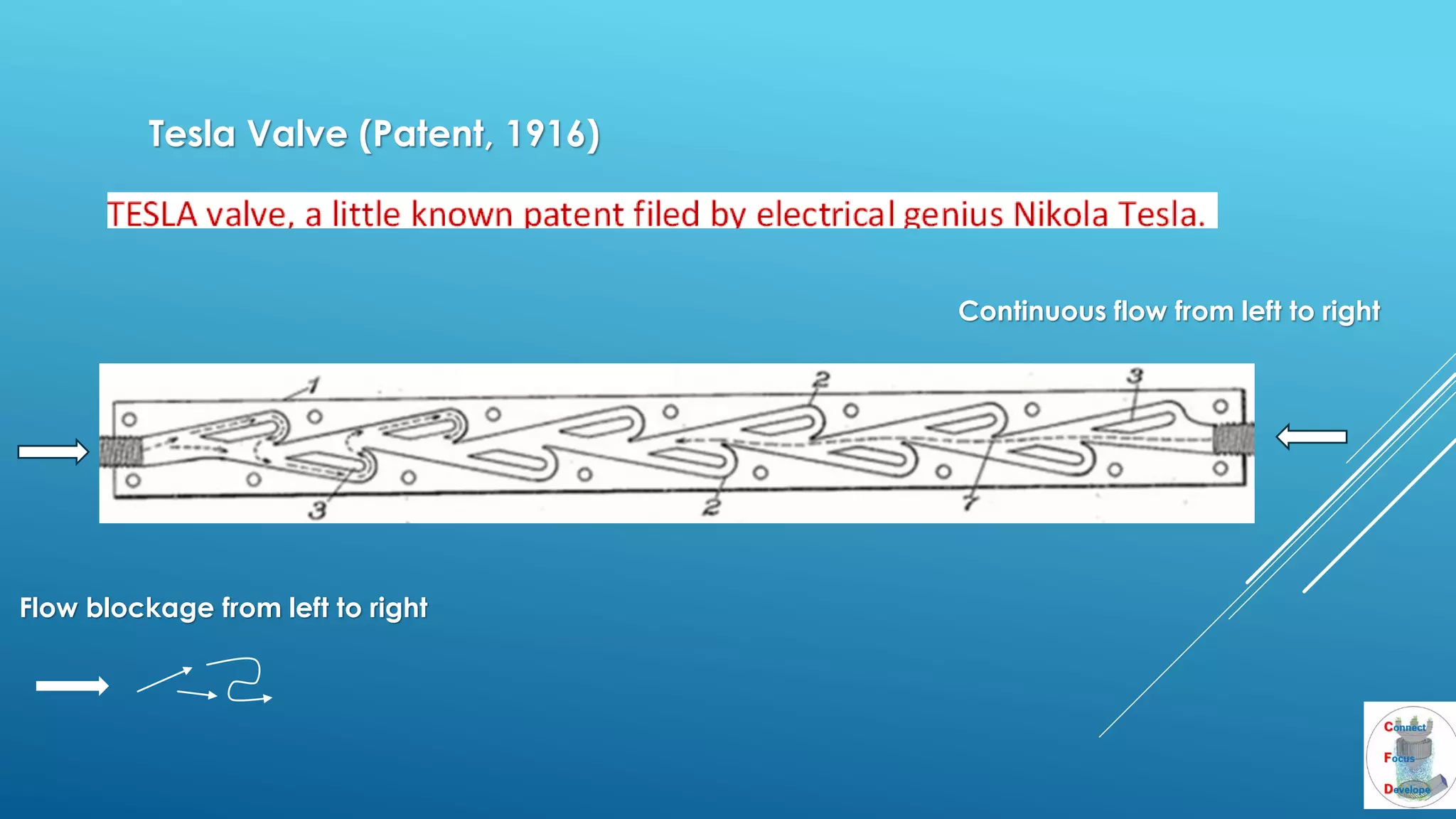
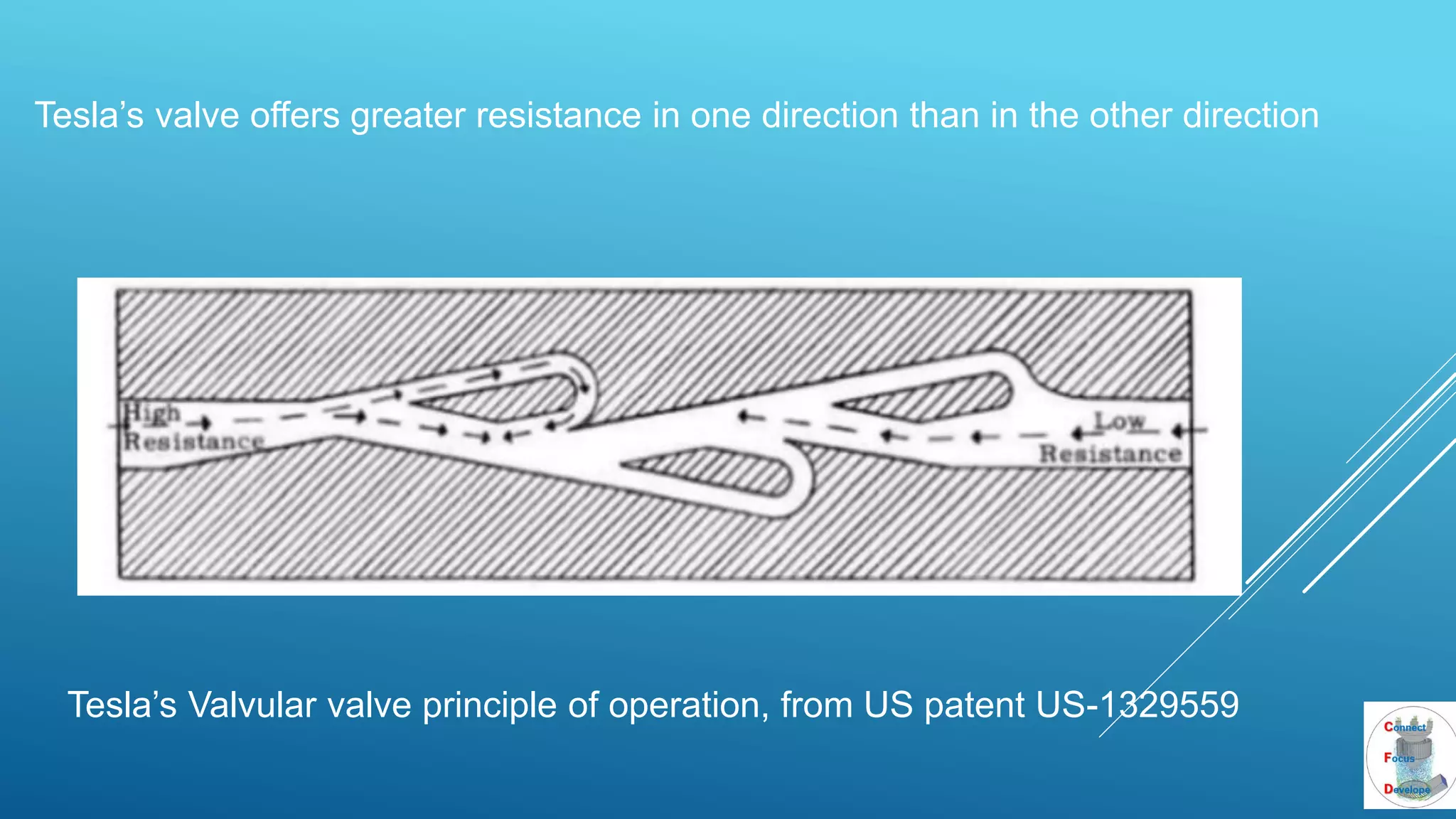
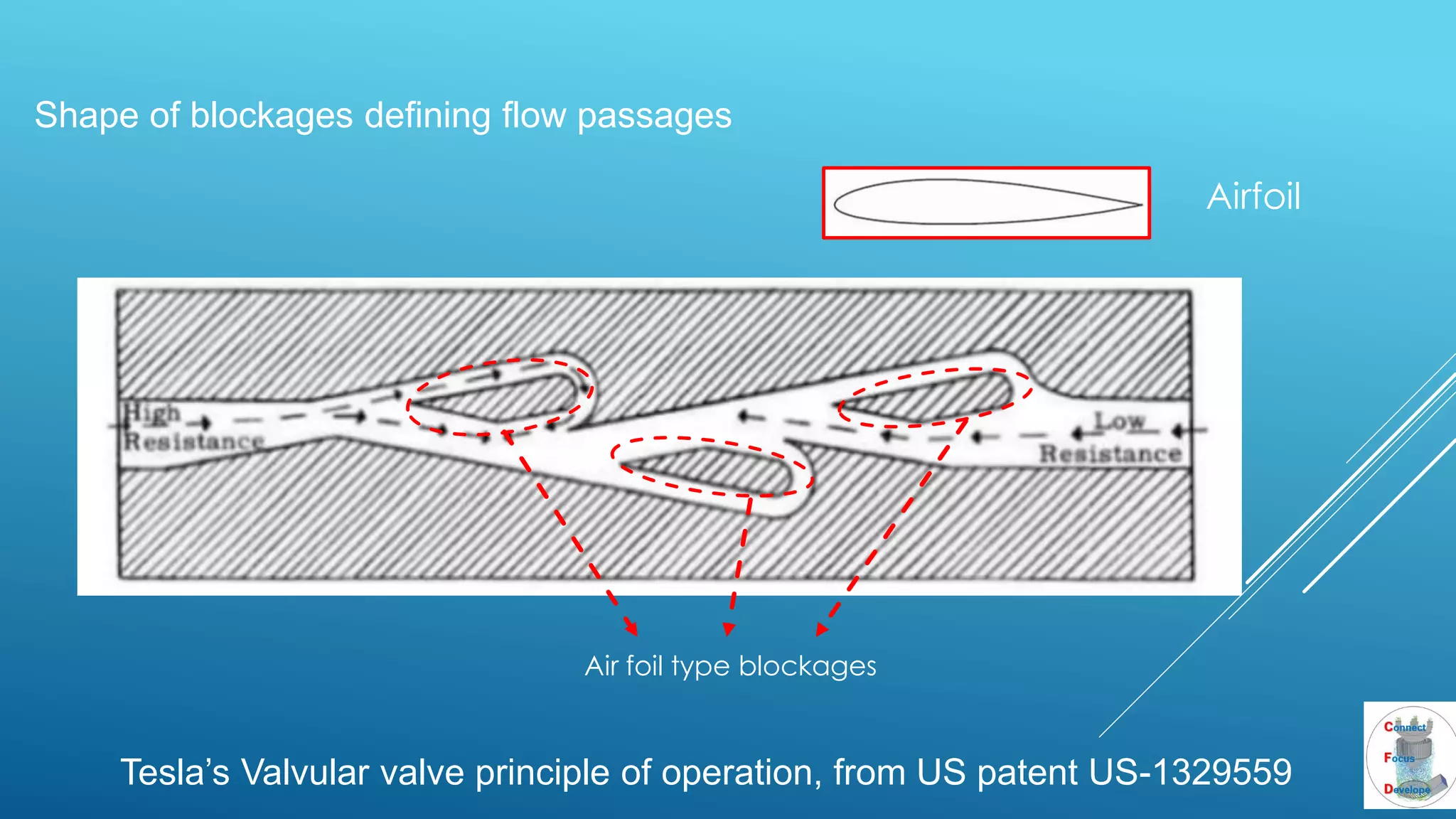
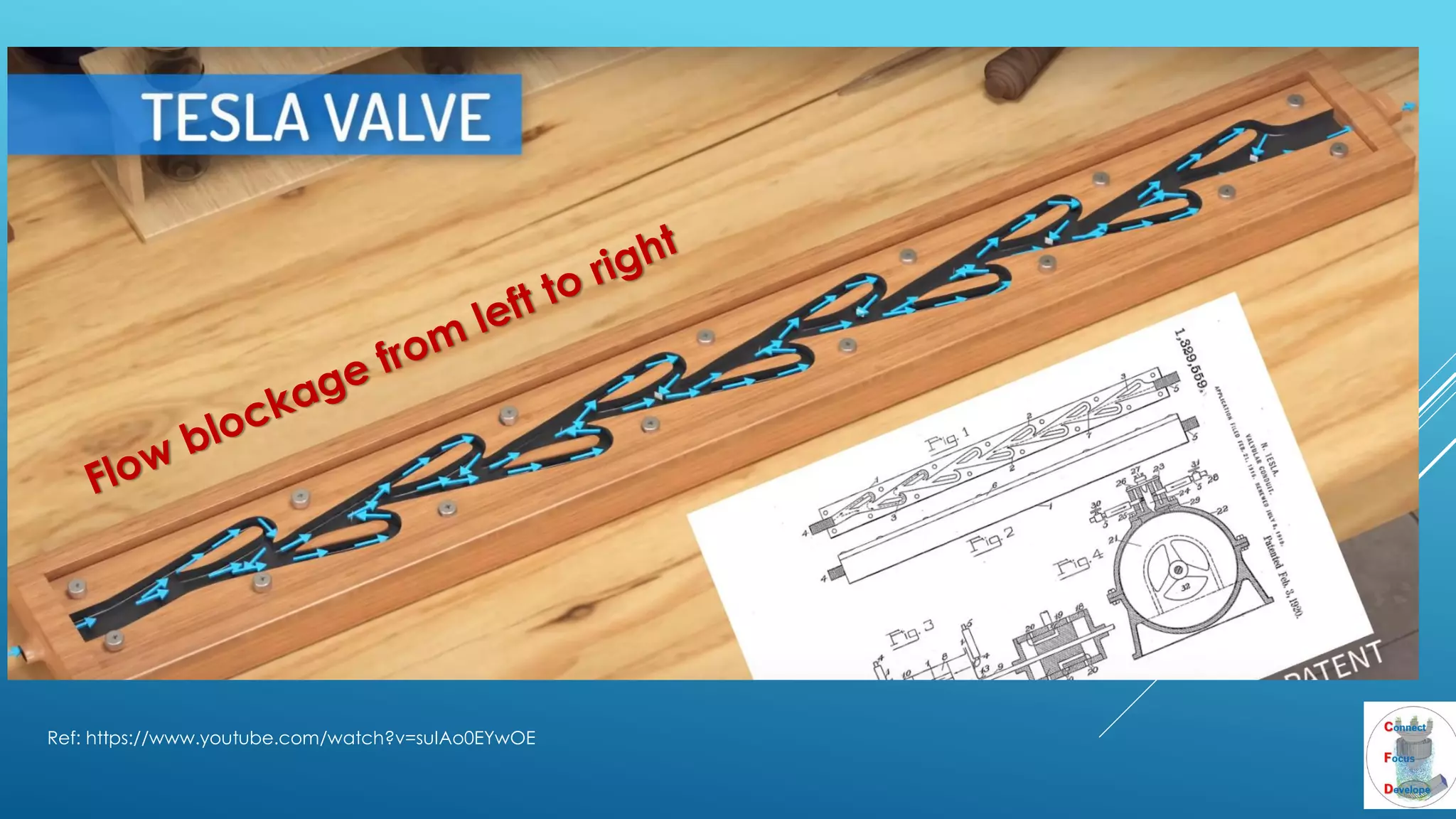
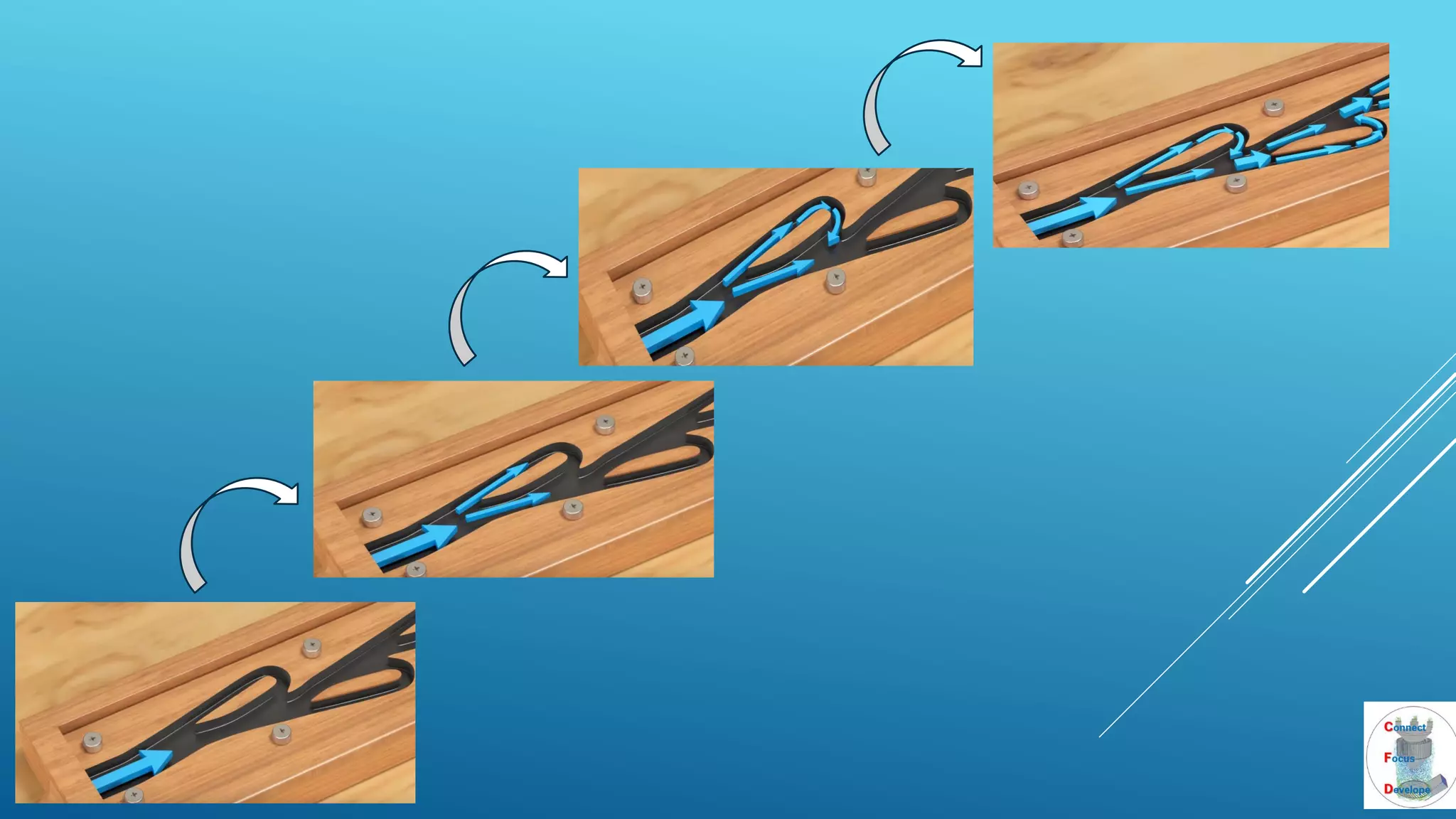
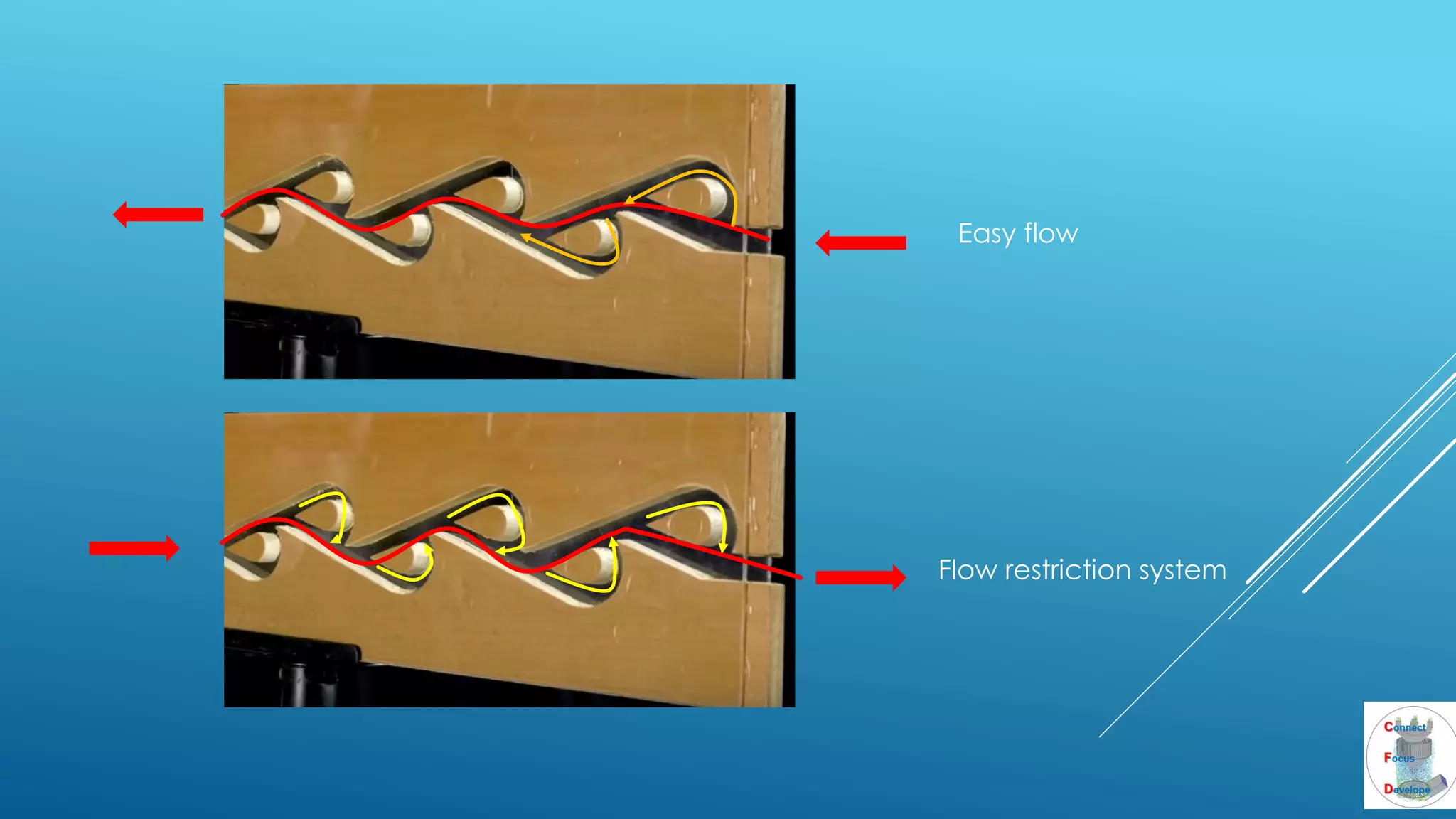
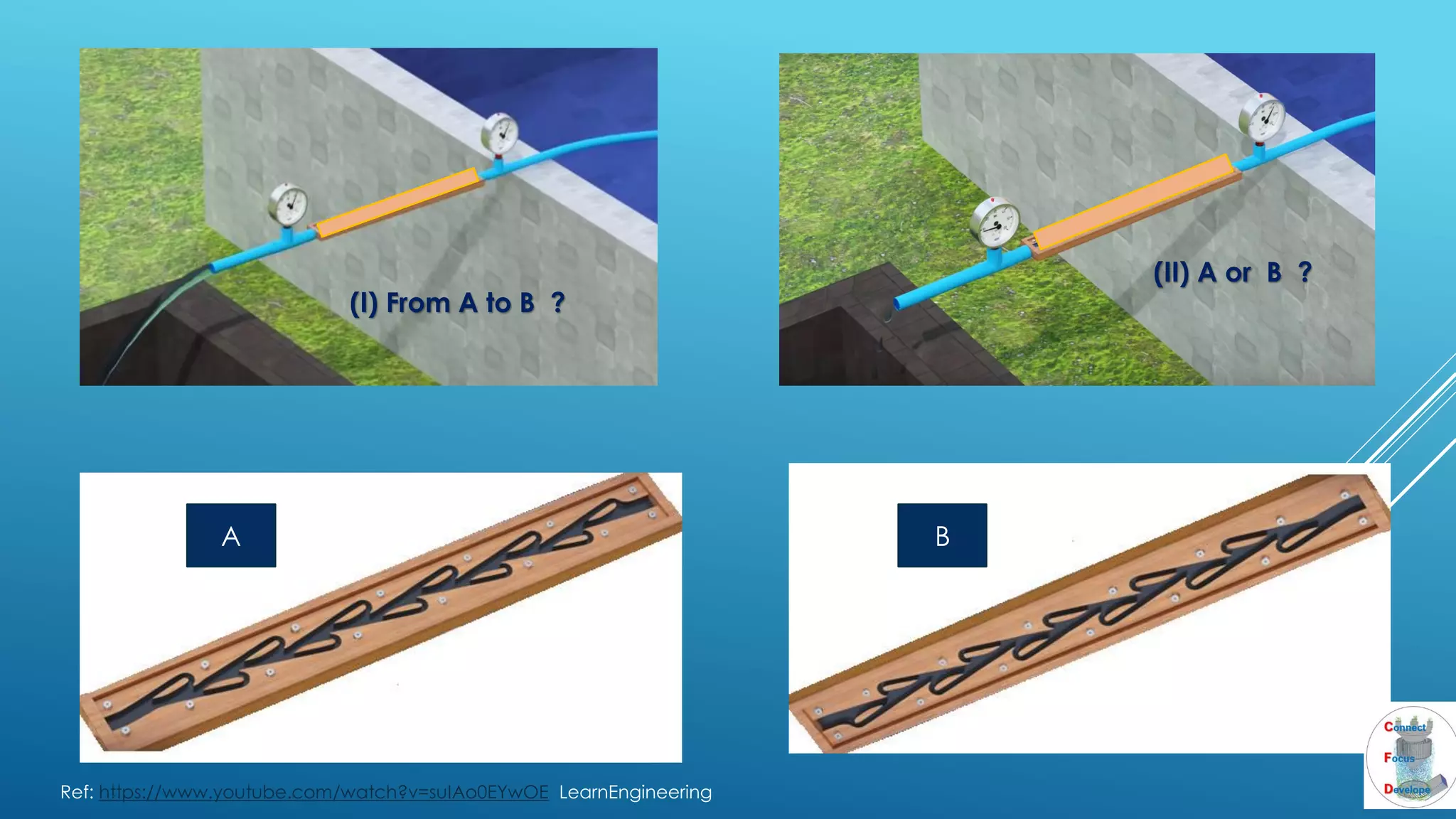
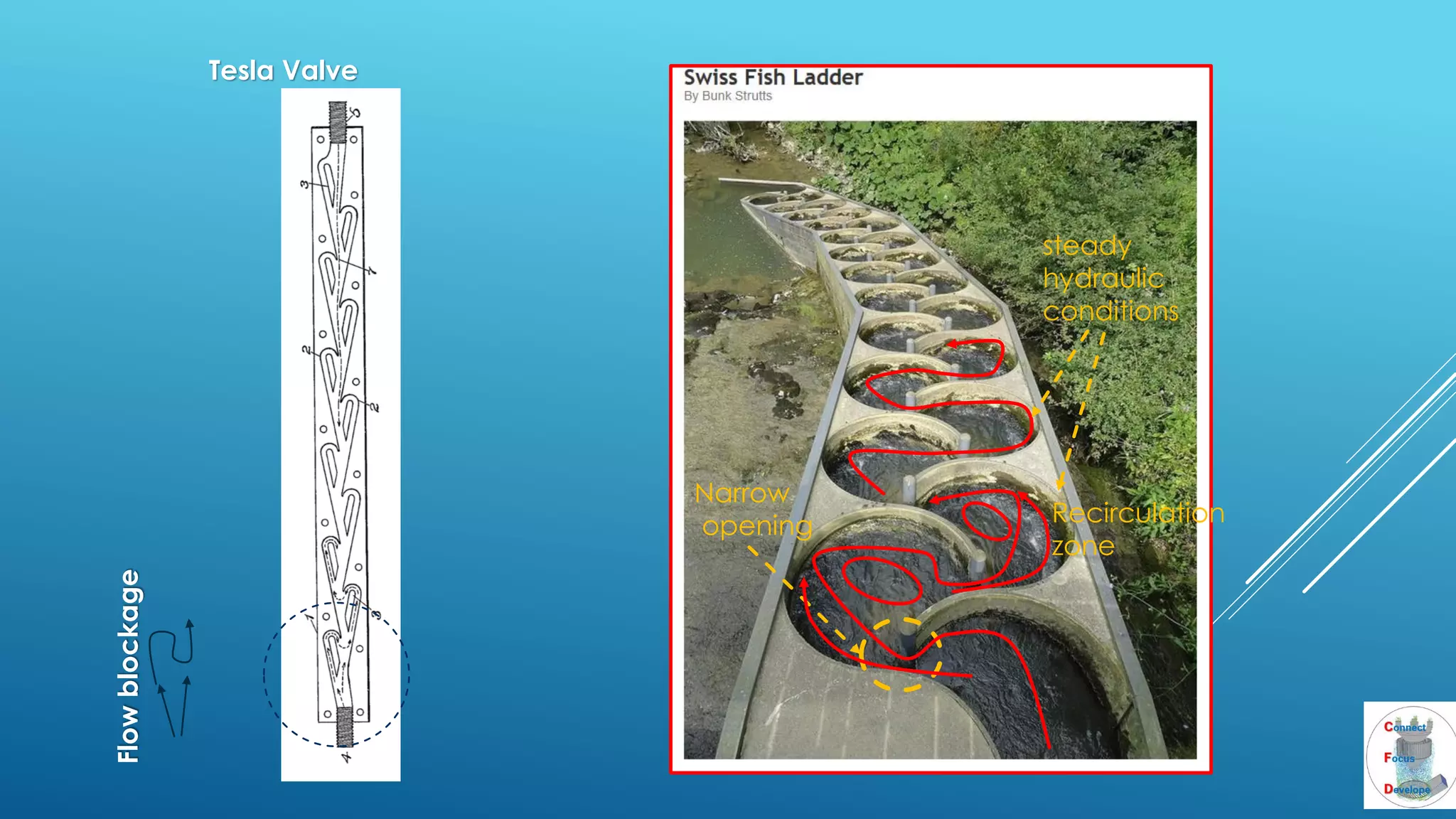
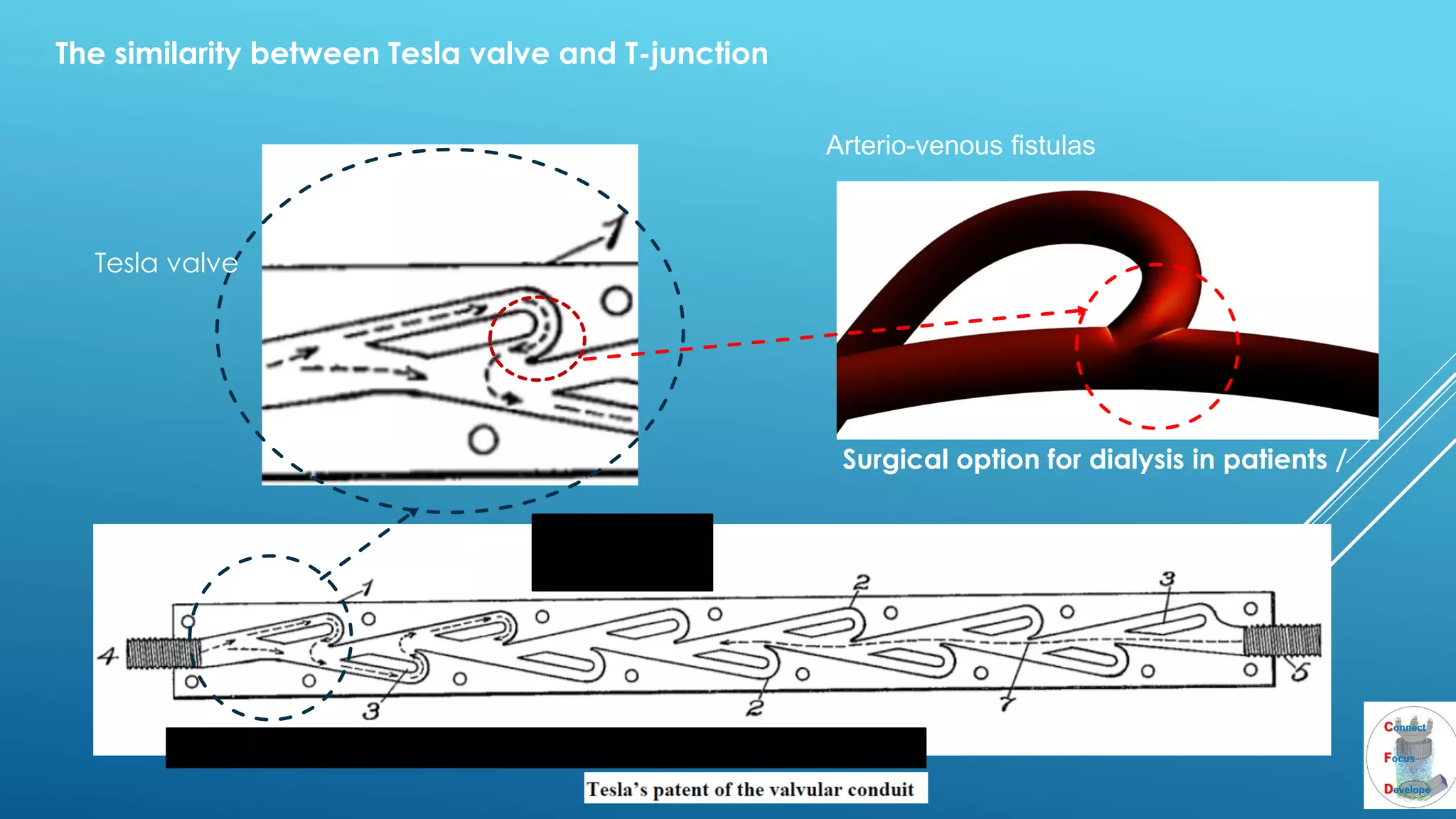
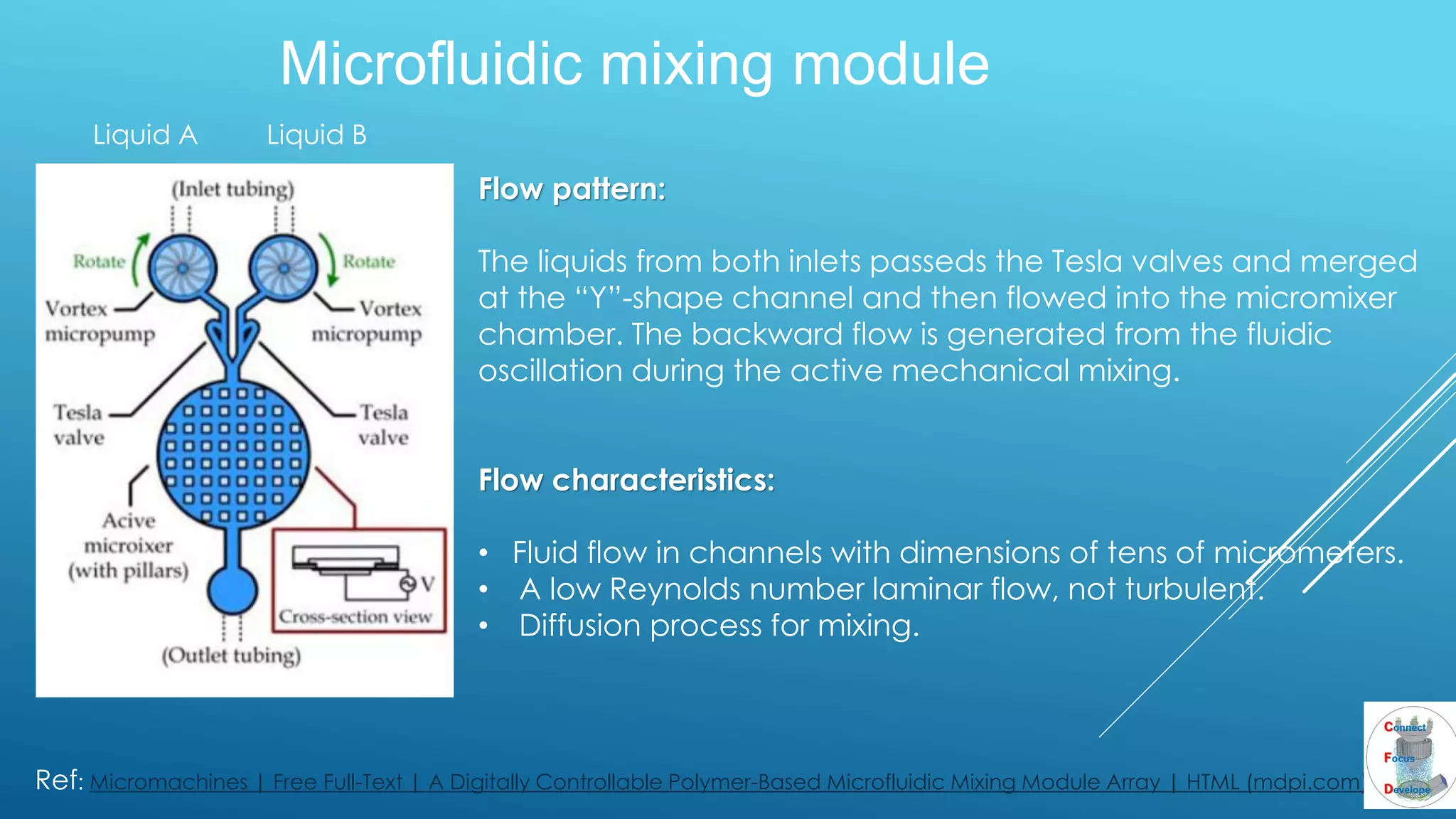
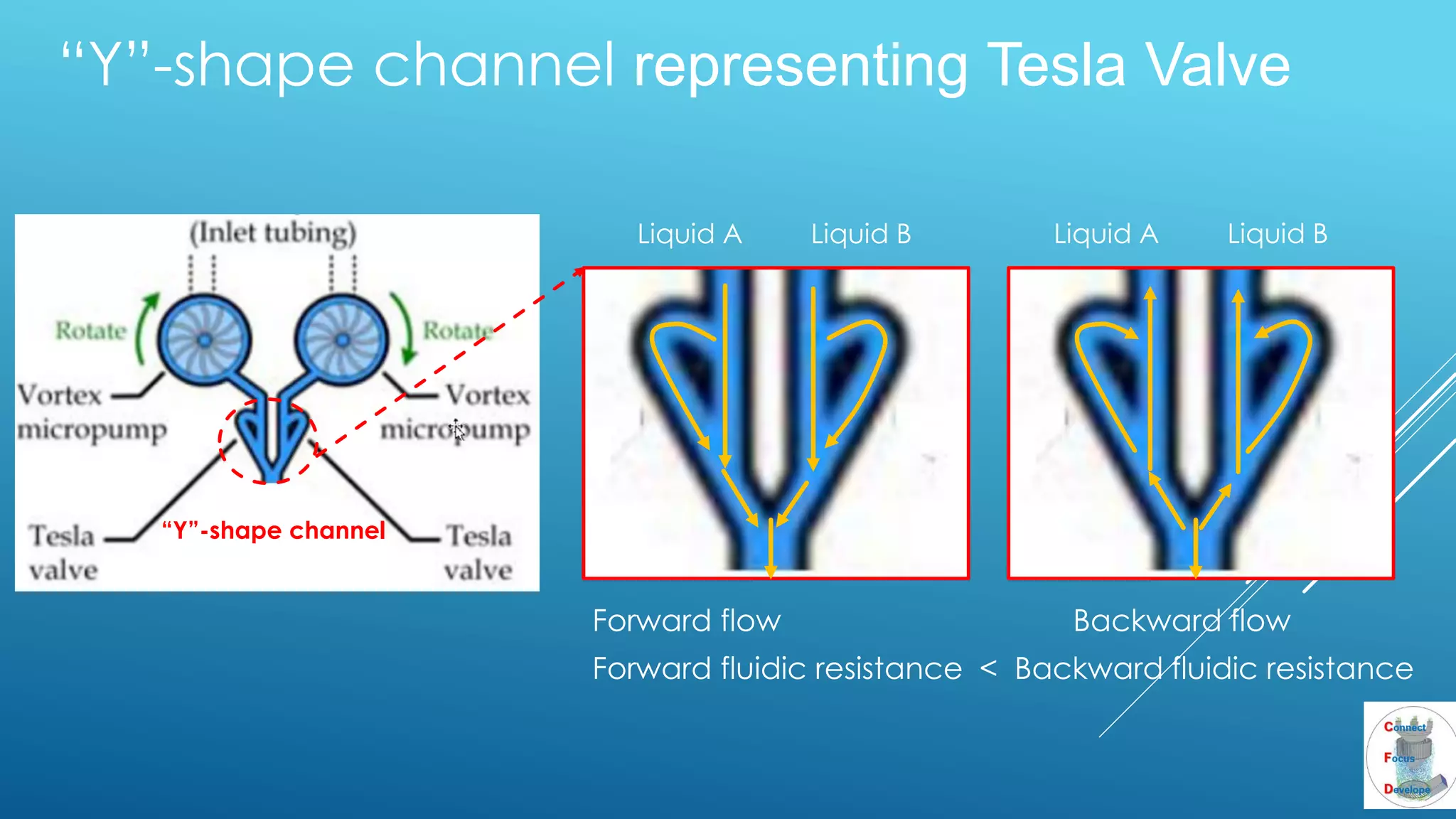
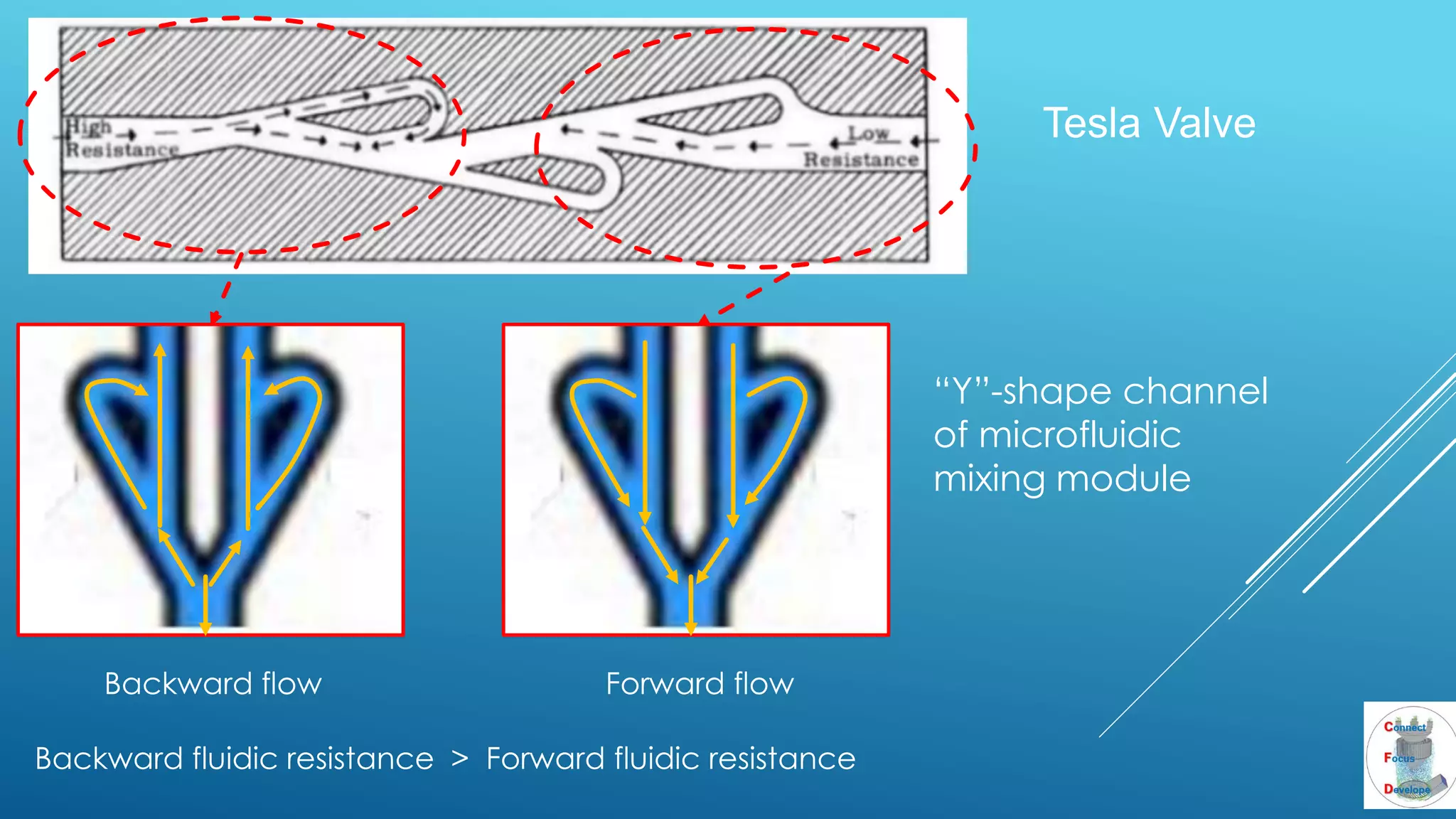
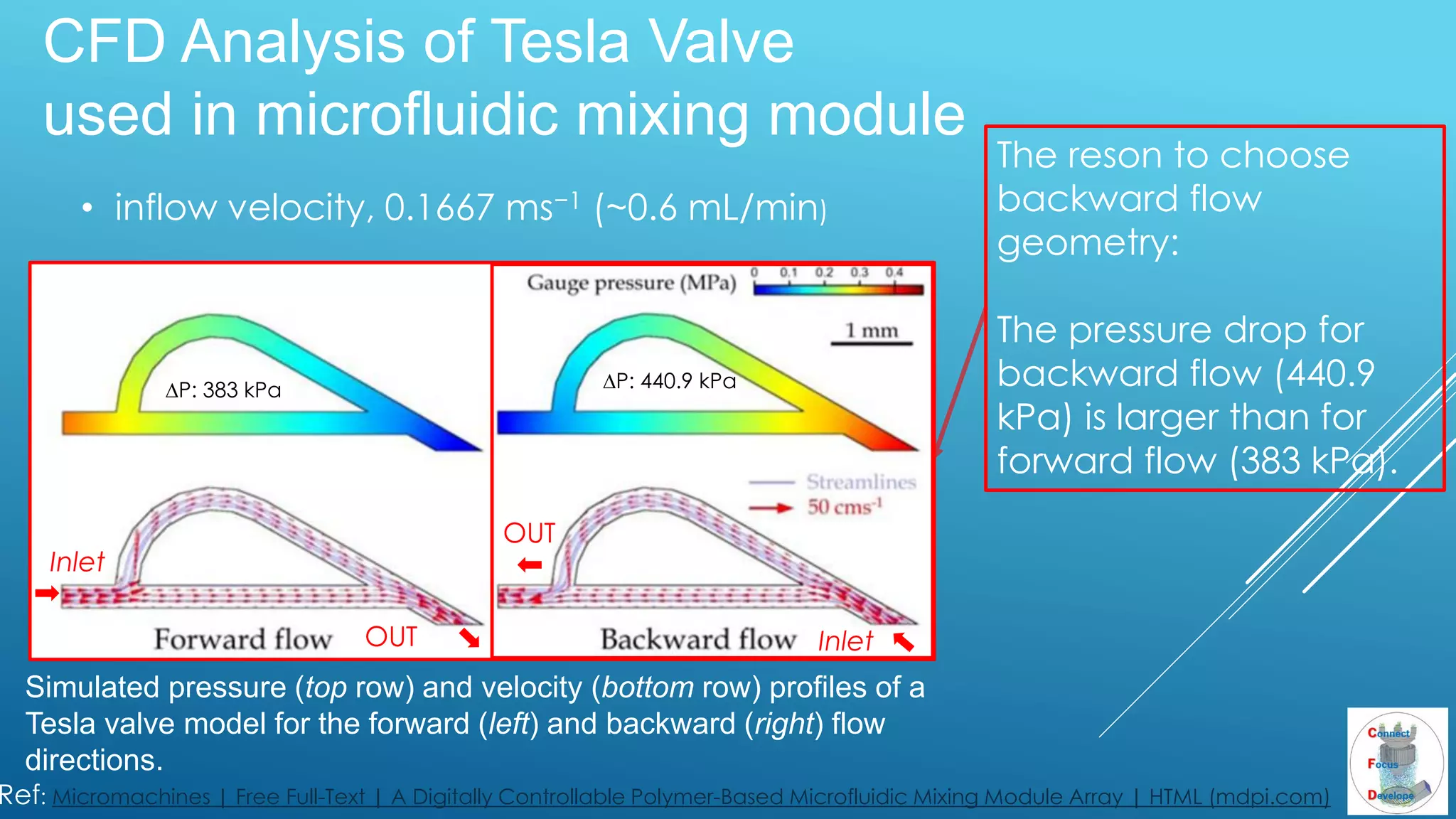
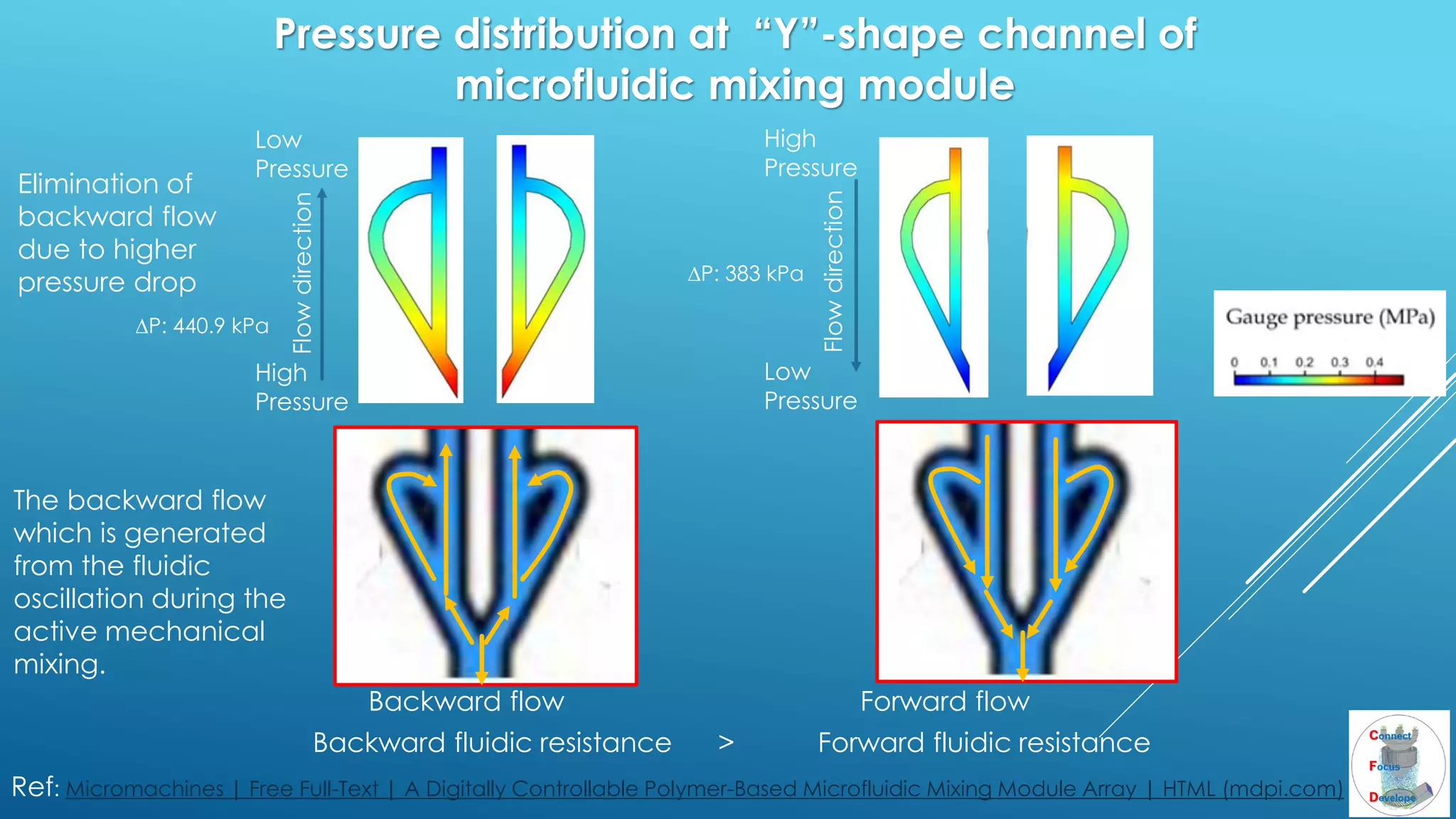
The document outlines the principles and applications of the Tesla valve, highlighting its unique feature of functioning without moving components, unlike traditional valves. It discusses various uses including fish ladders, medical applications such as t-junctions for dialysis, and microfluidic mixing modules that utilize Tesla valves to manage flow and prevent backward flow. The analysis emphasizes the valve's design for improving fluid dynamics in various engineering contexts.