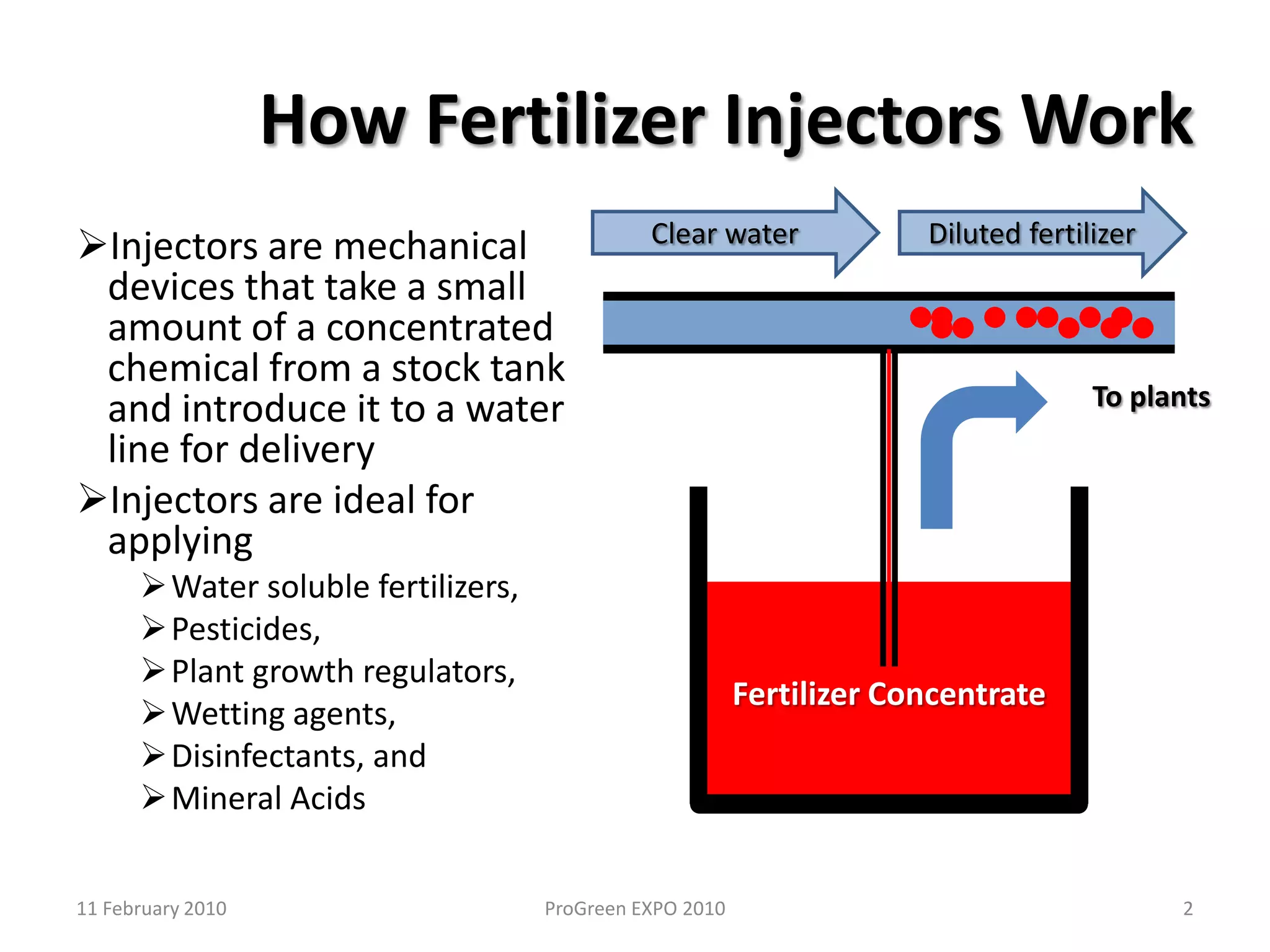
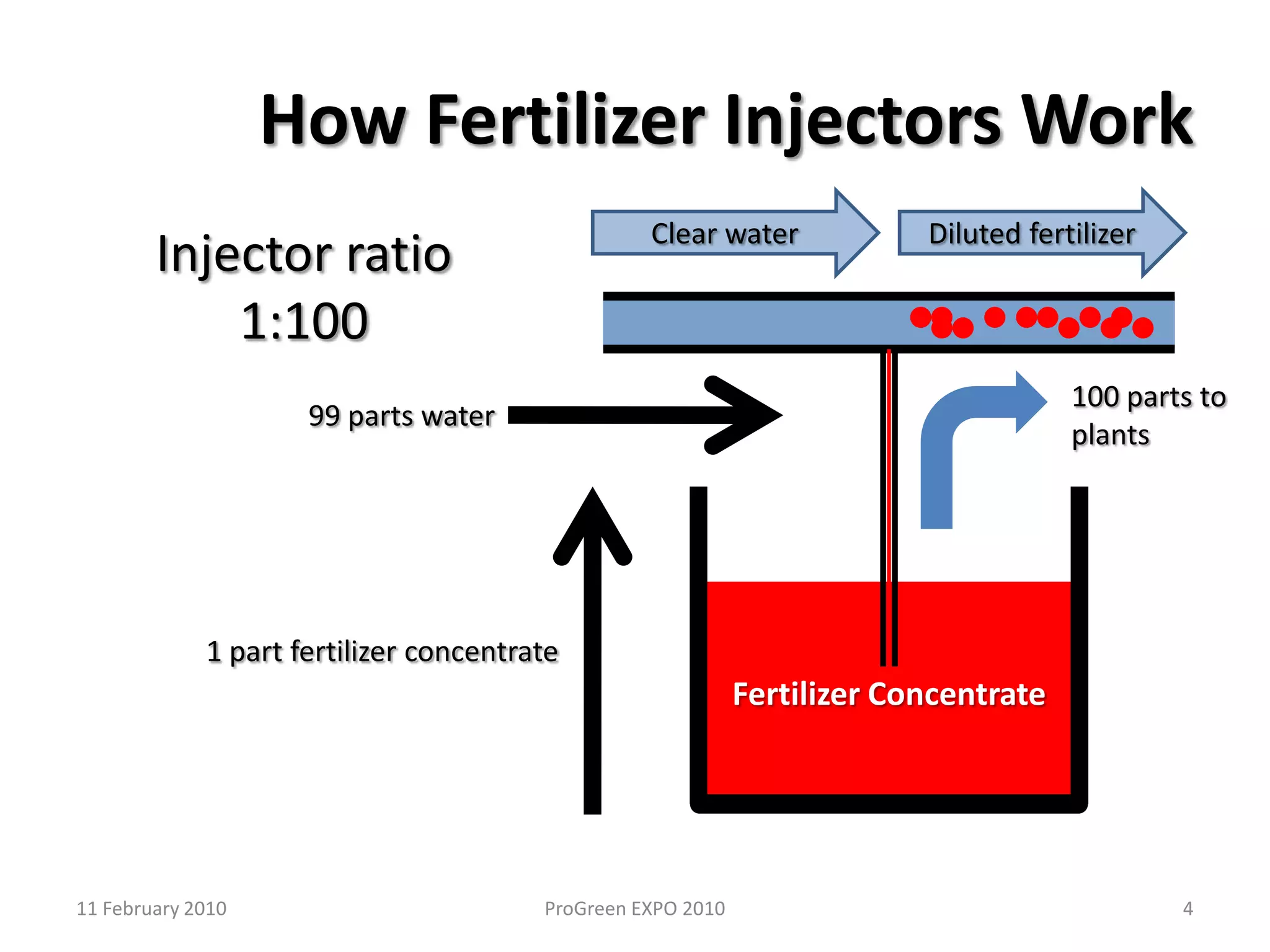
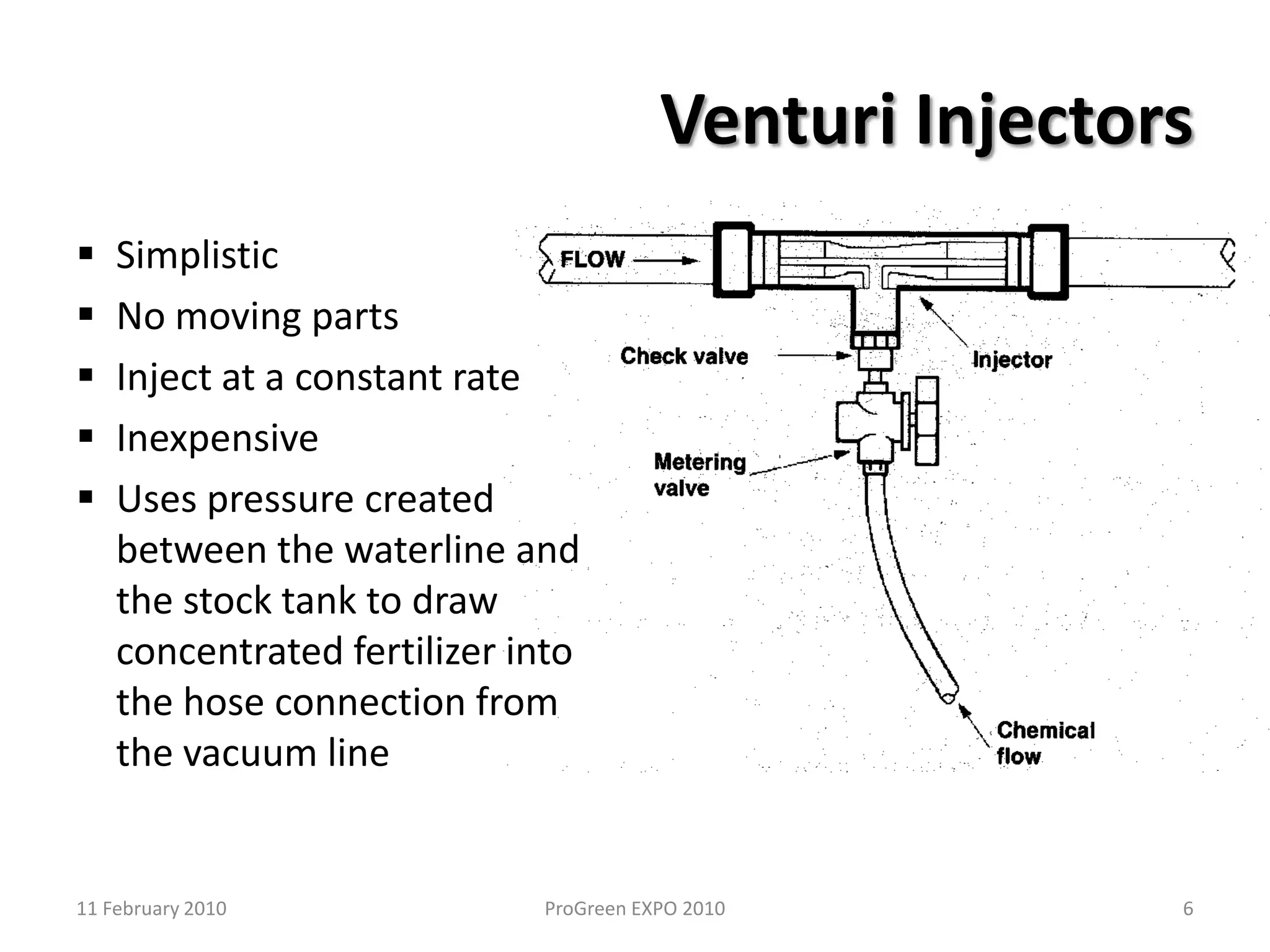
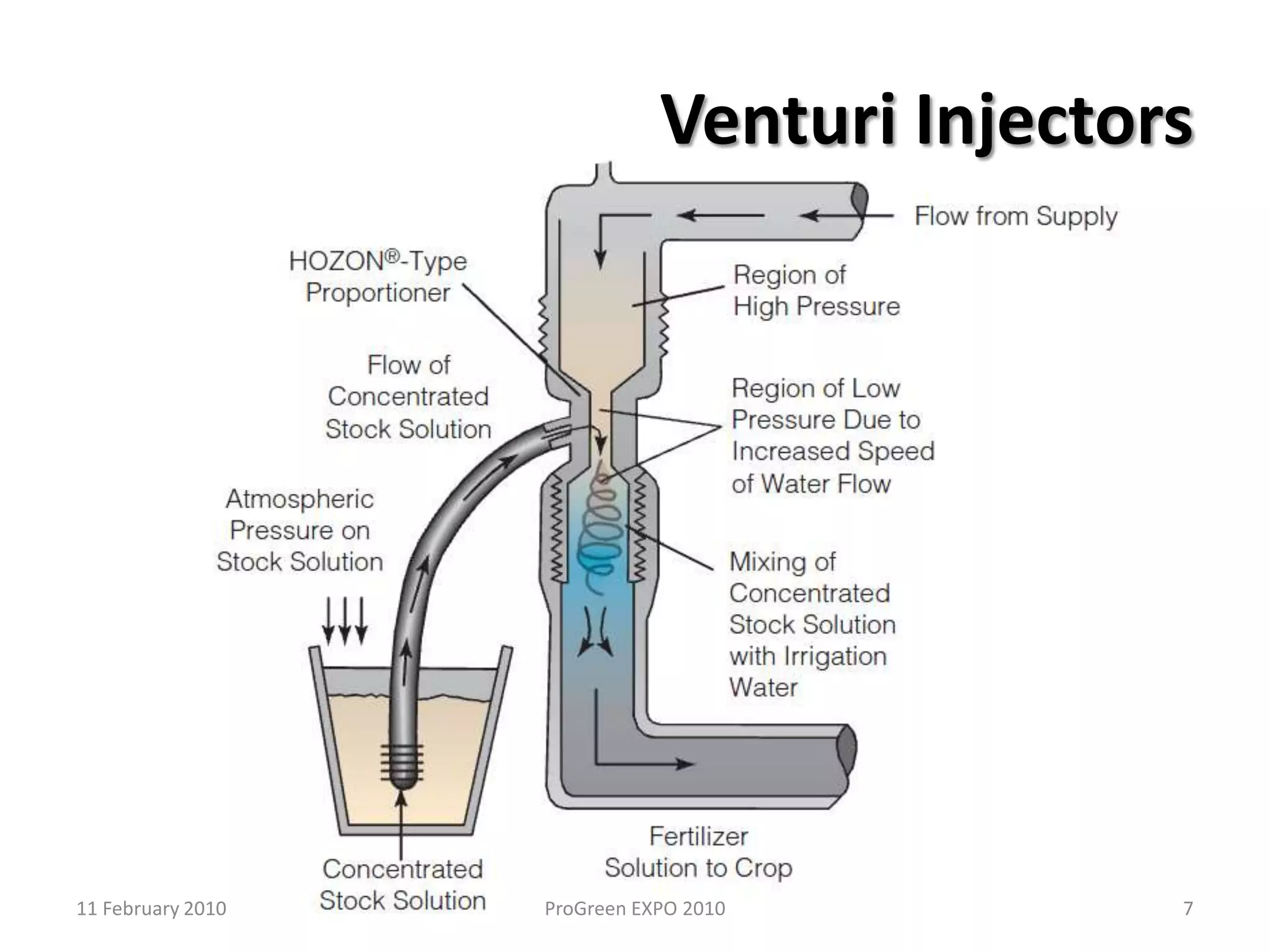
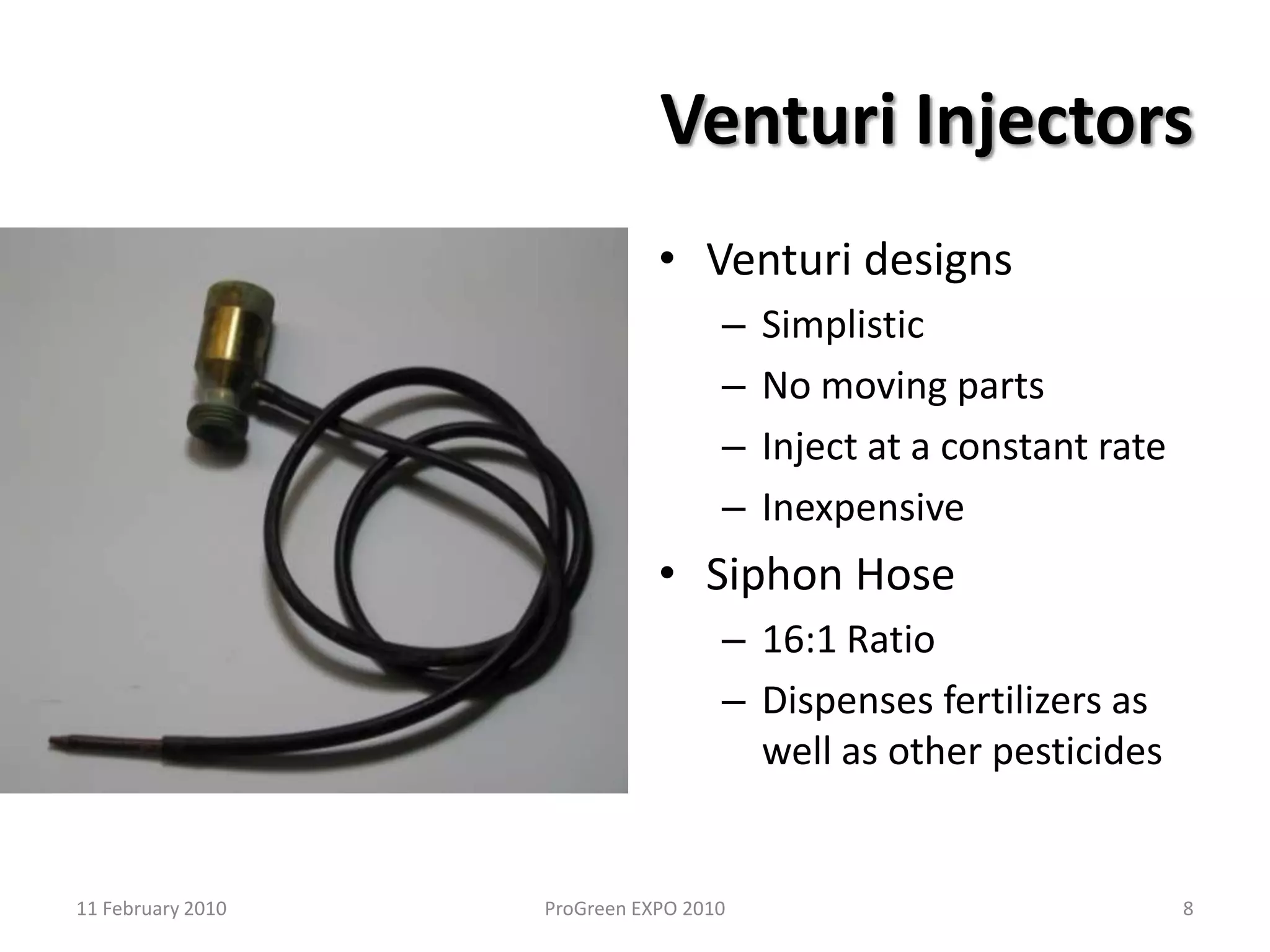
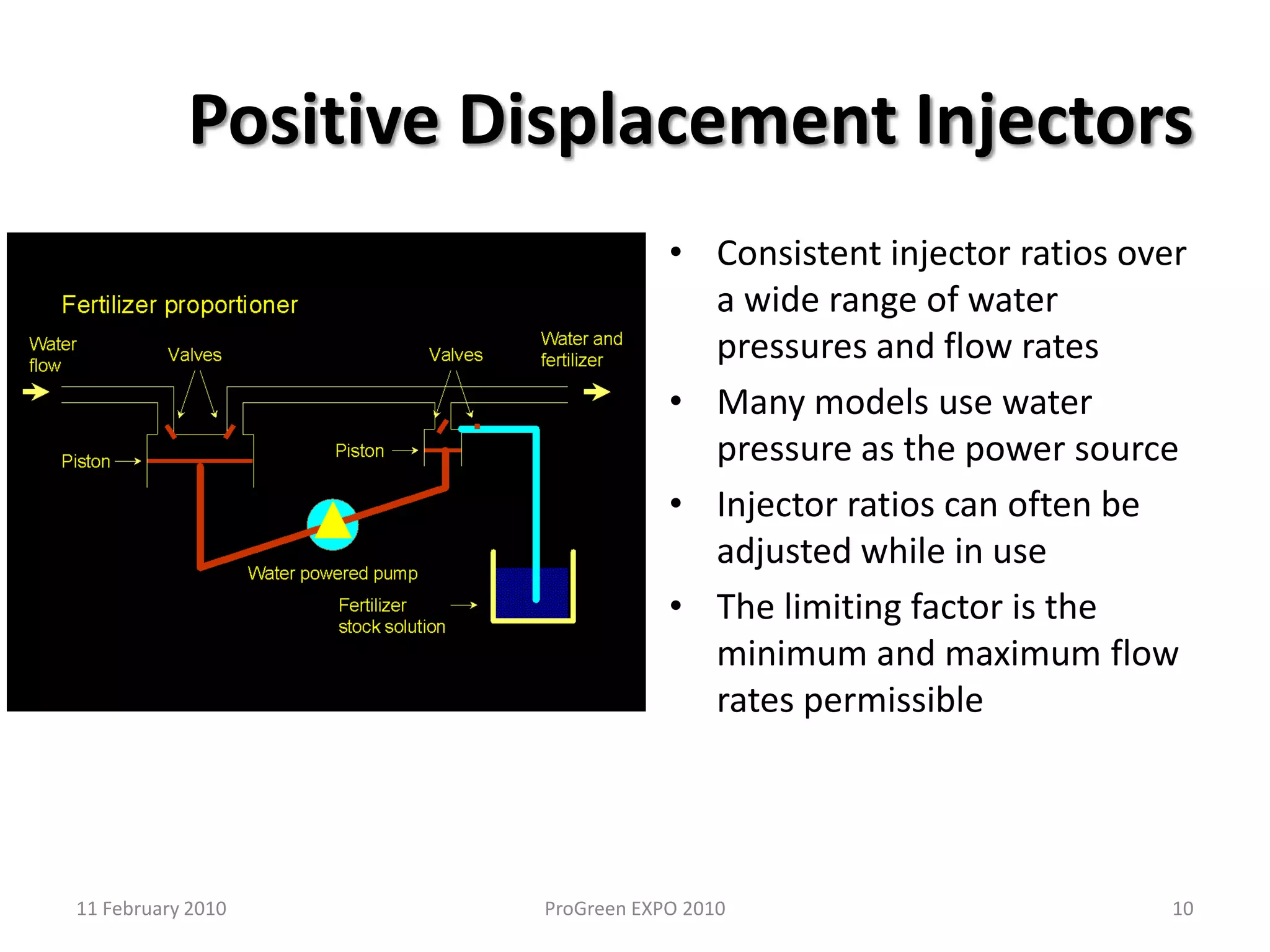
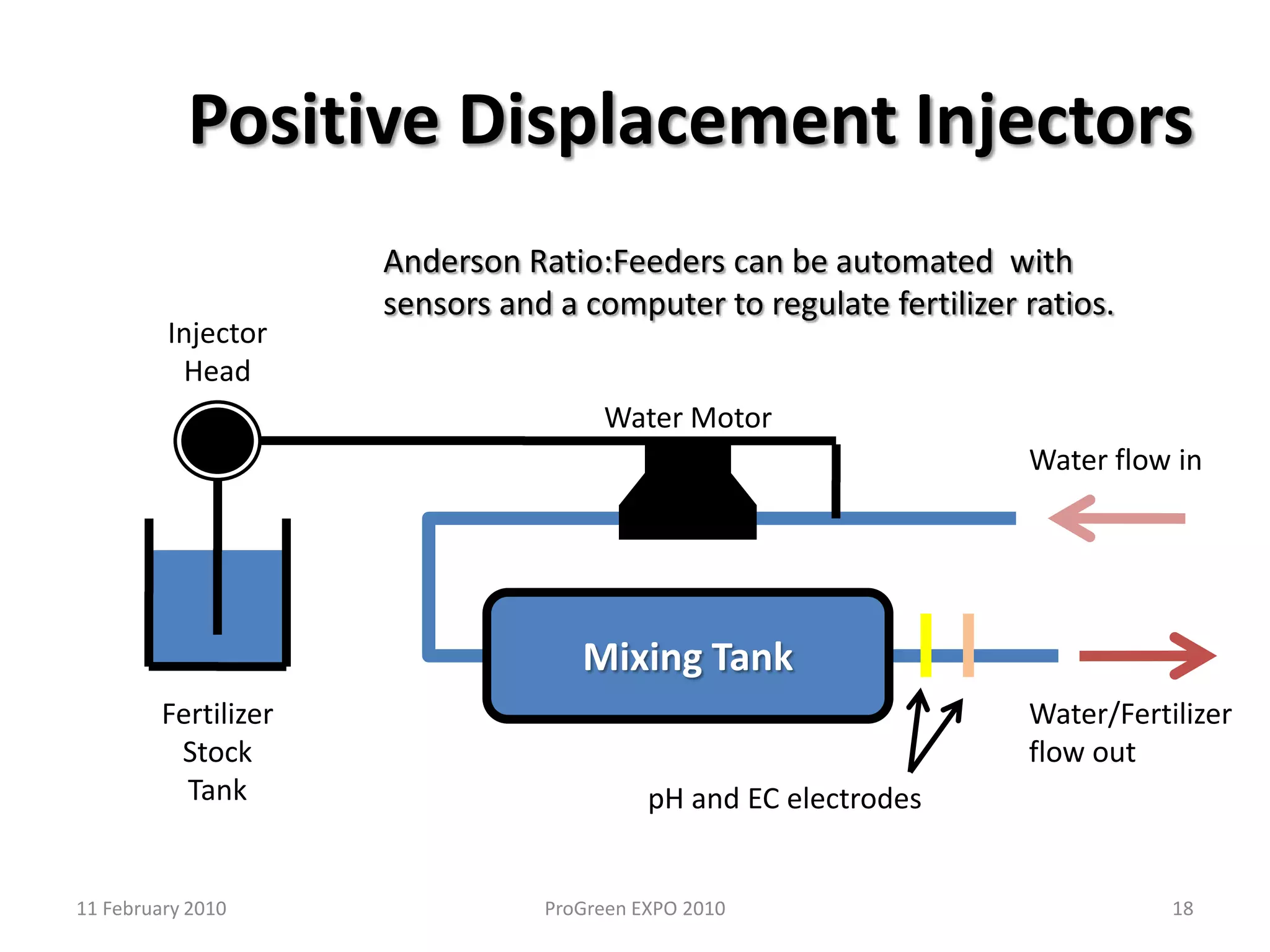
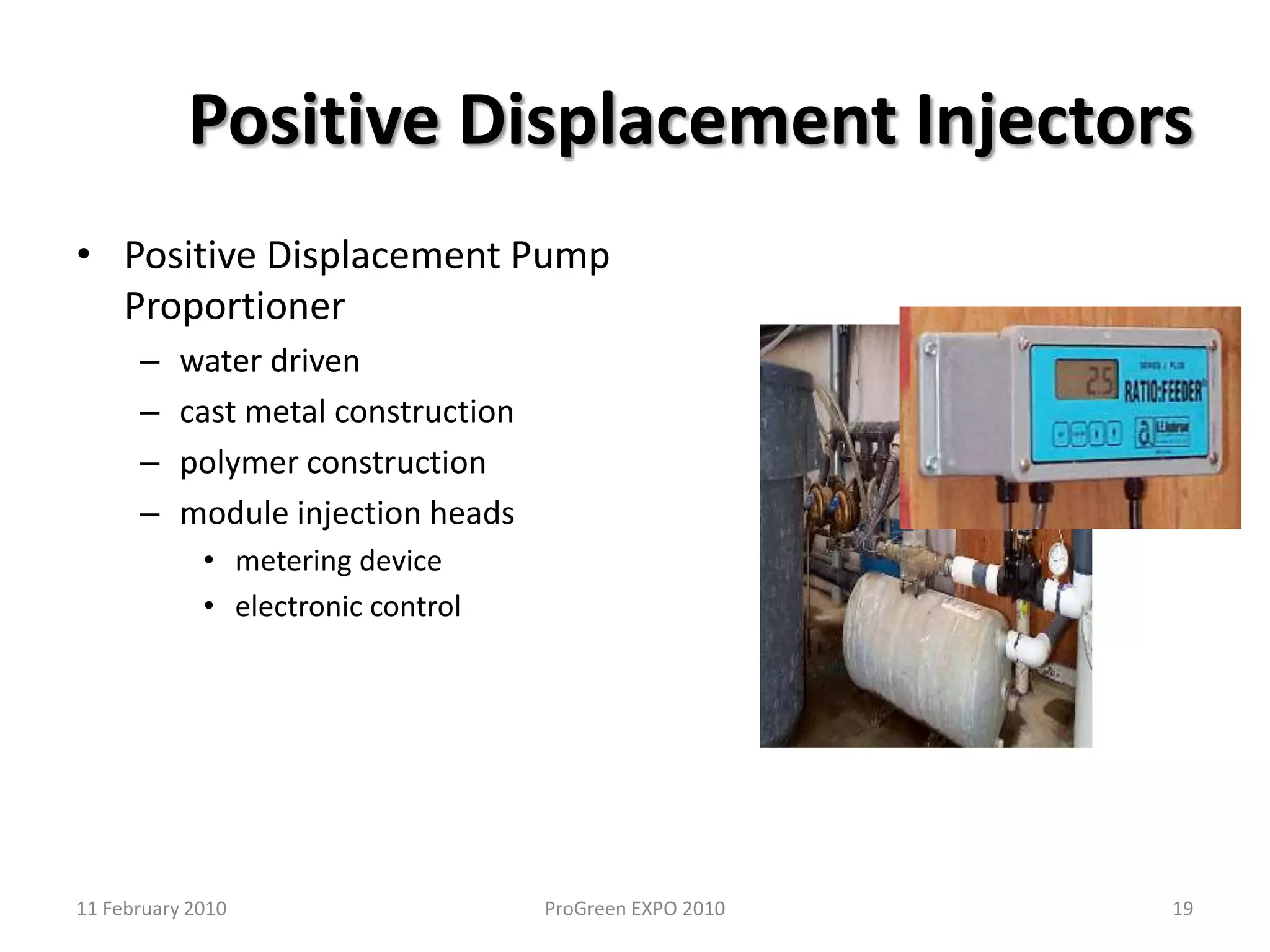
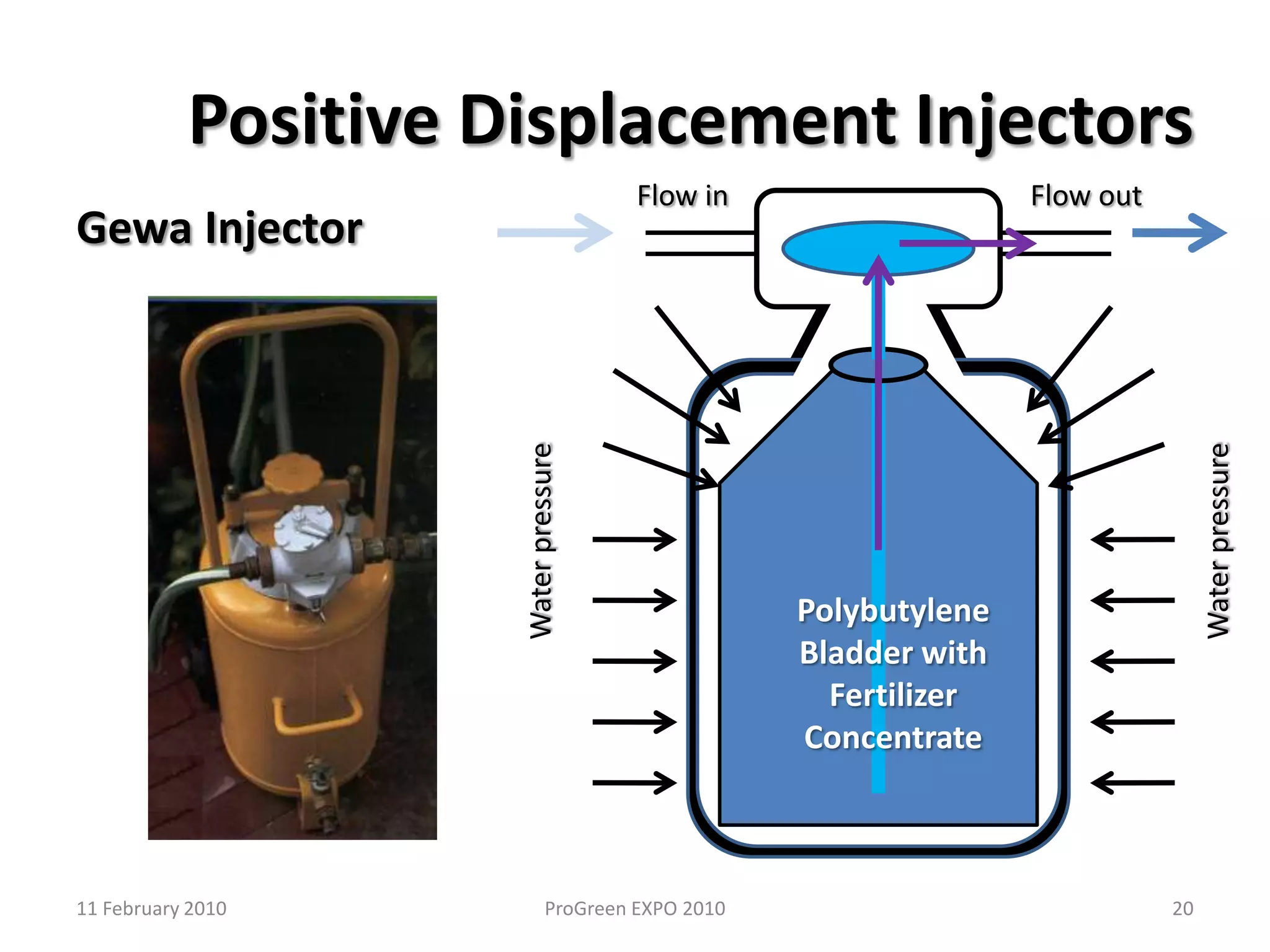
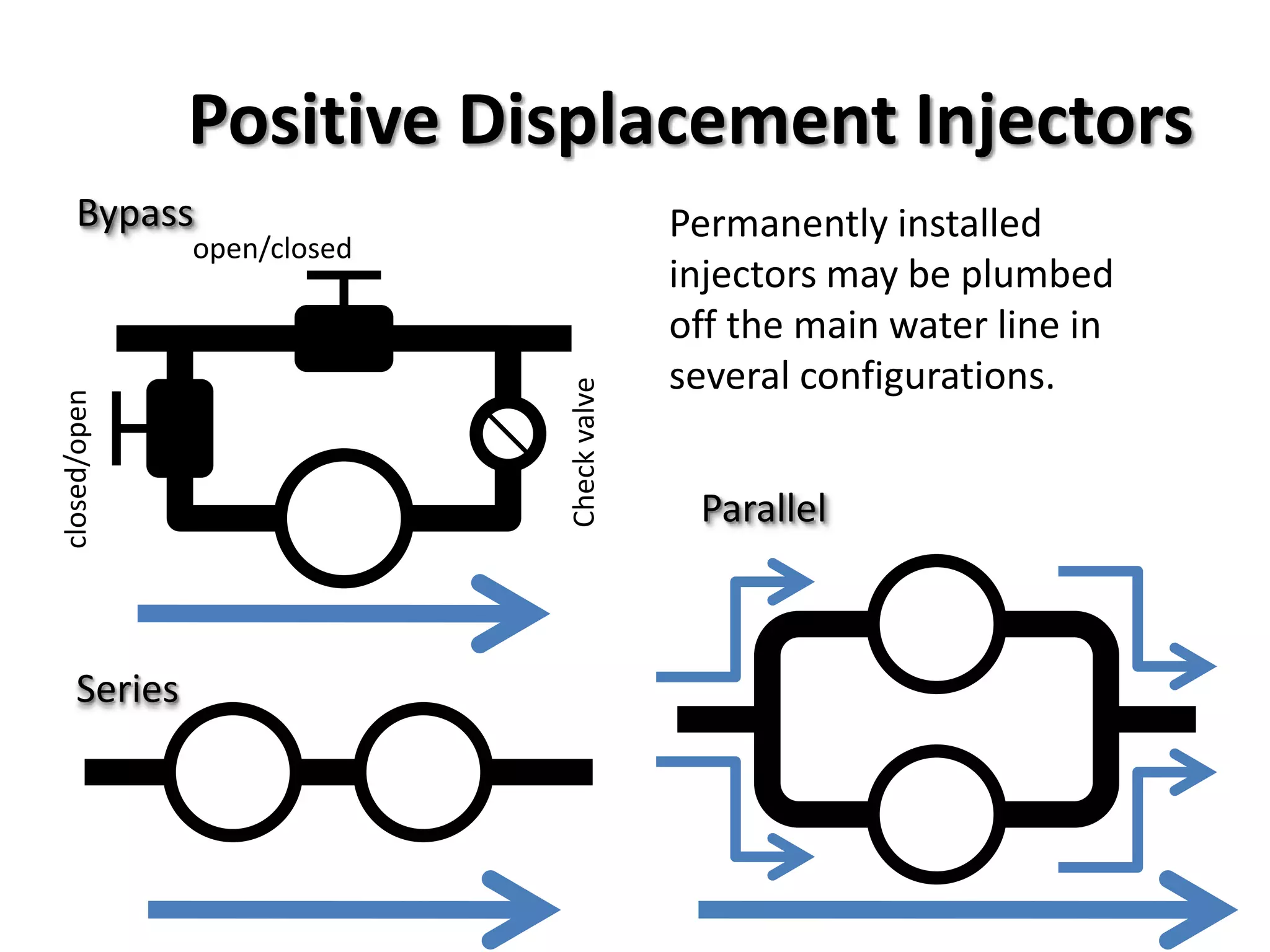
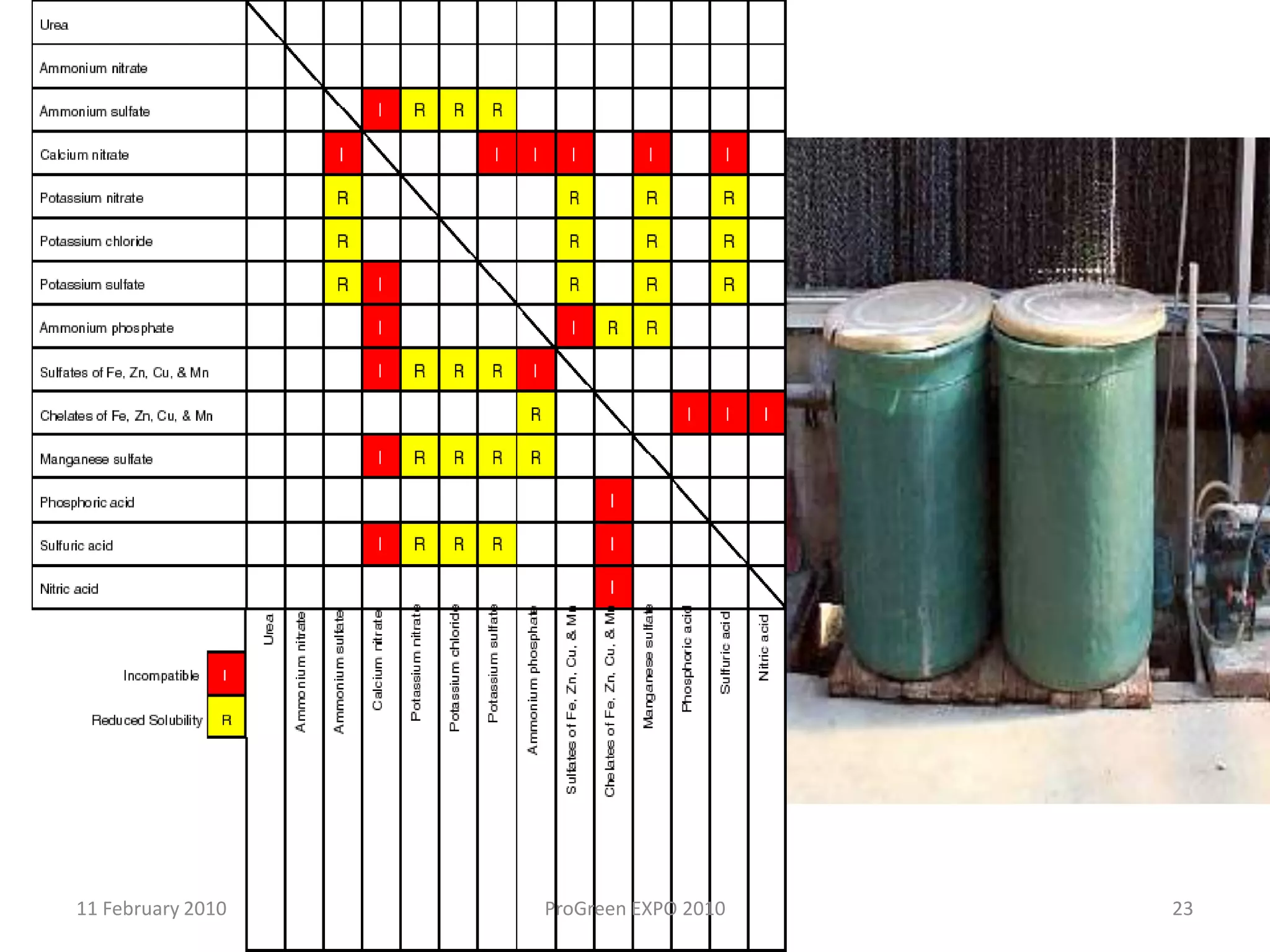
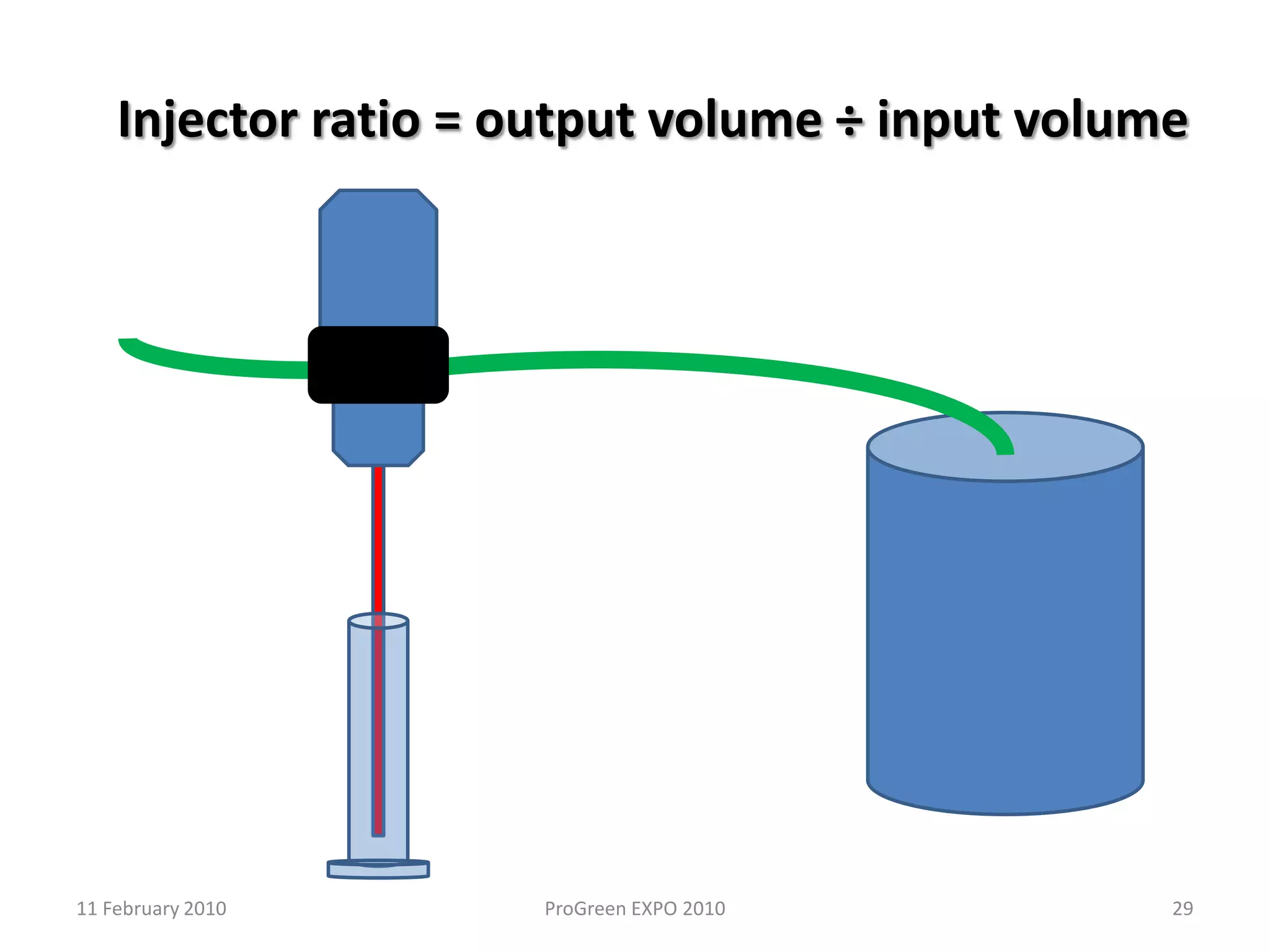
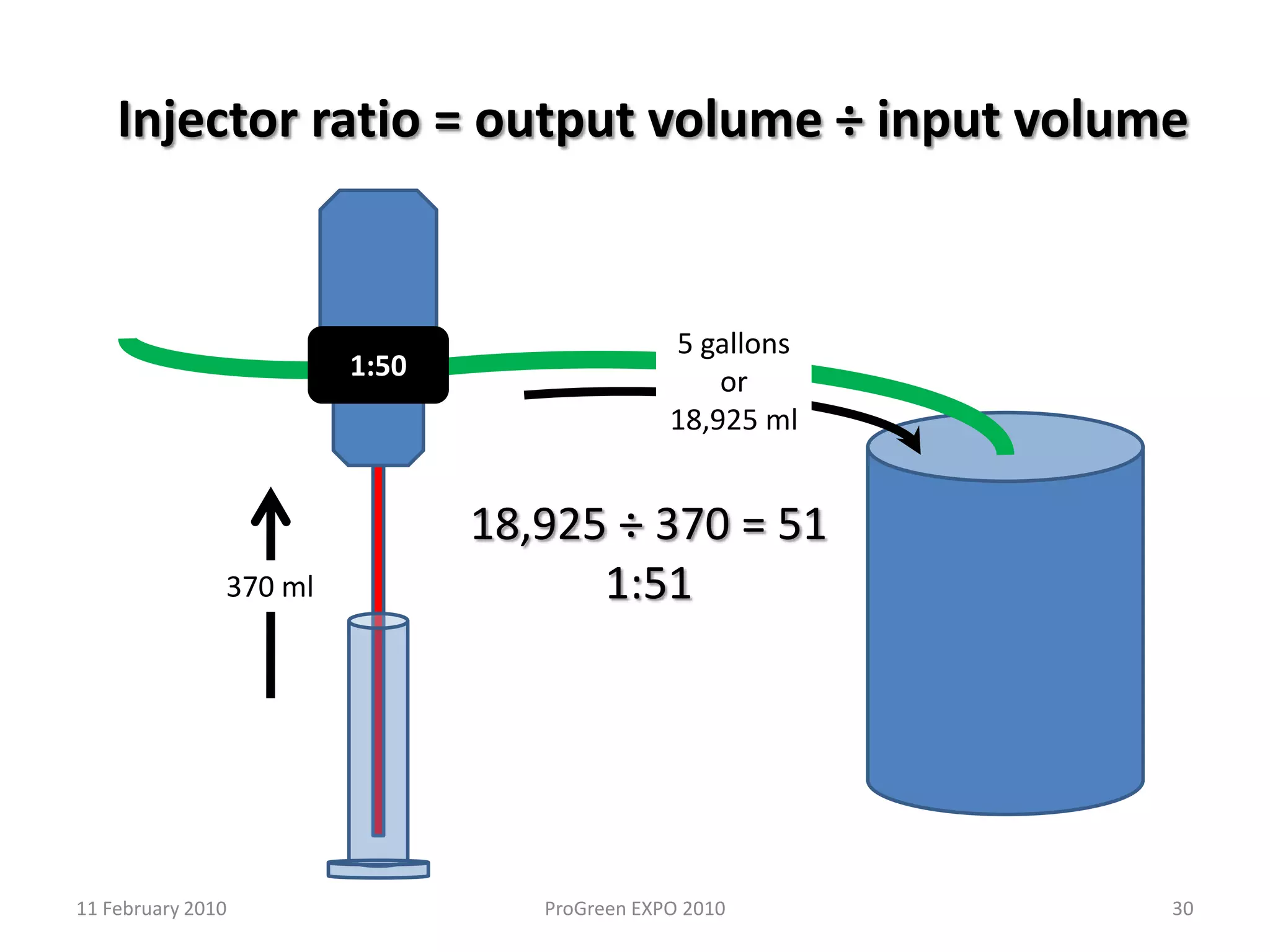
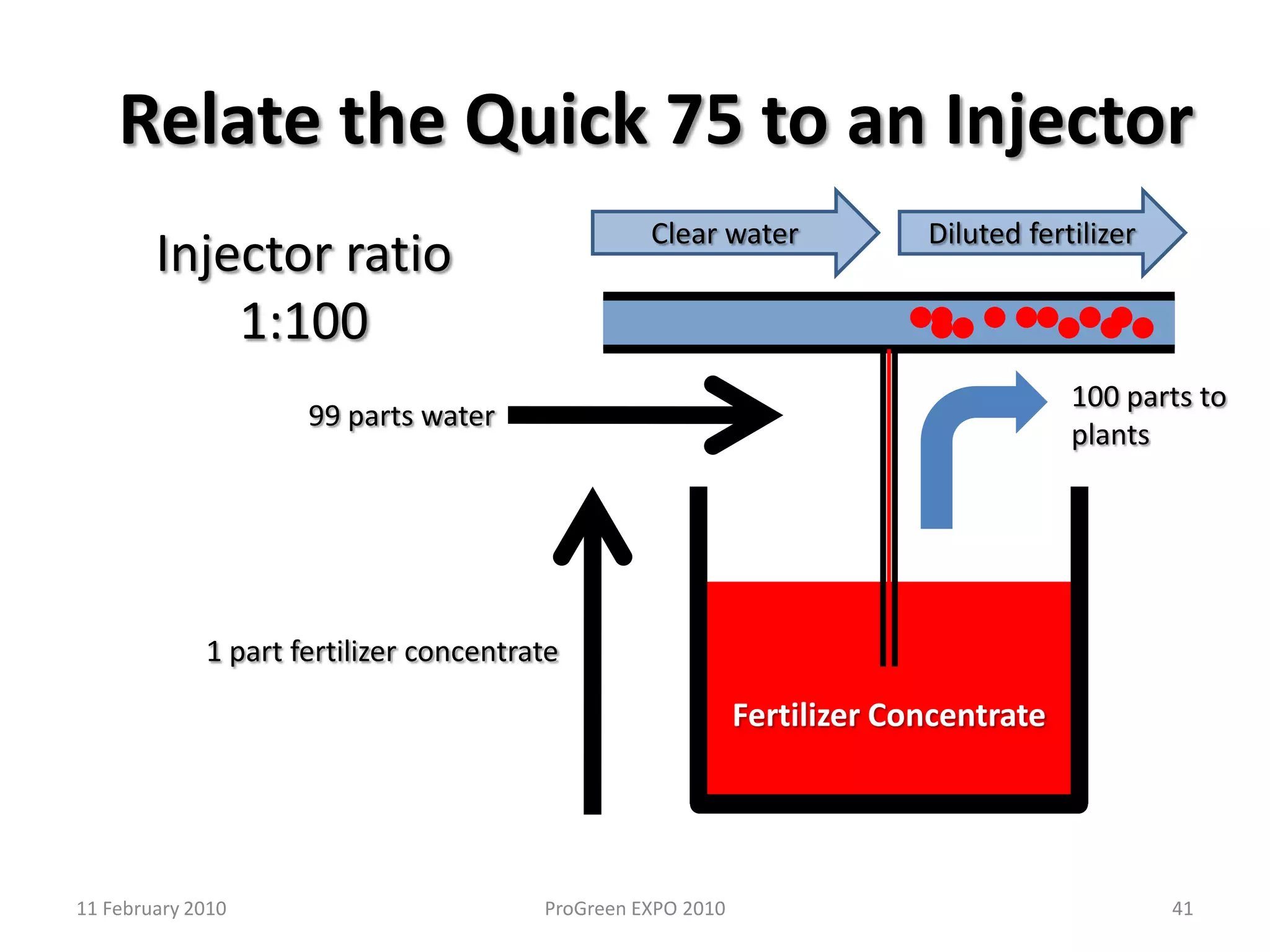
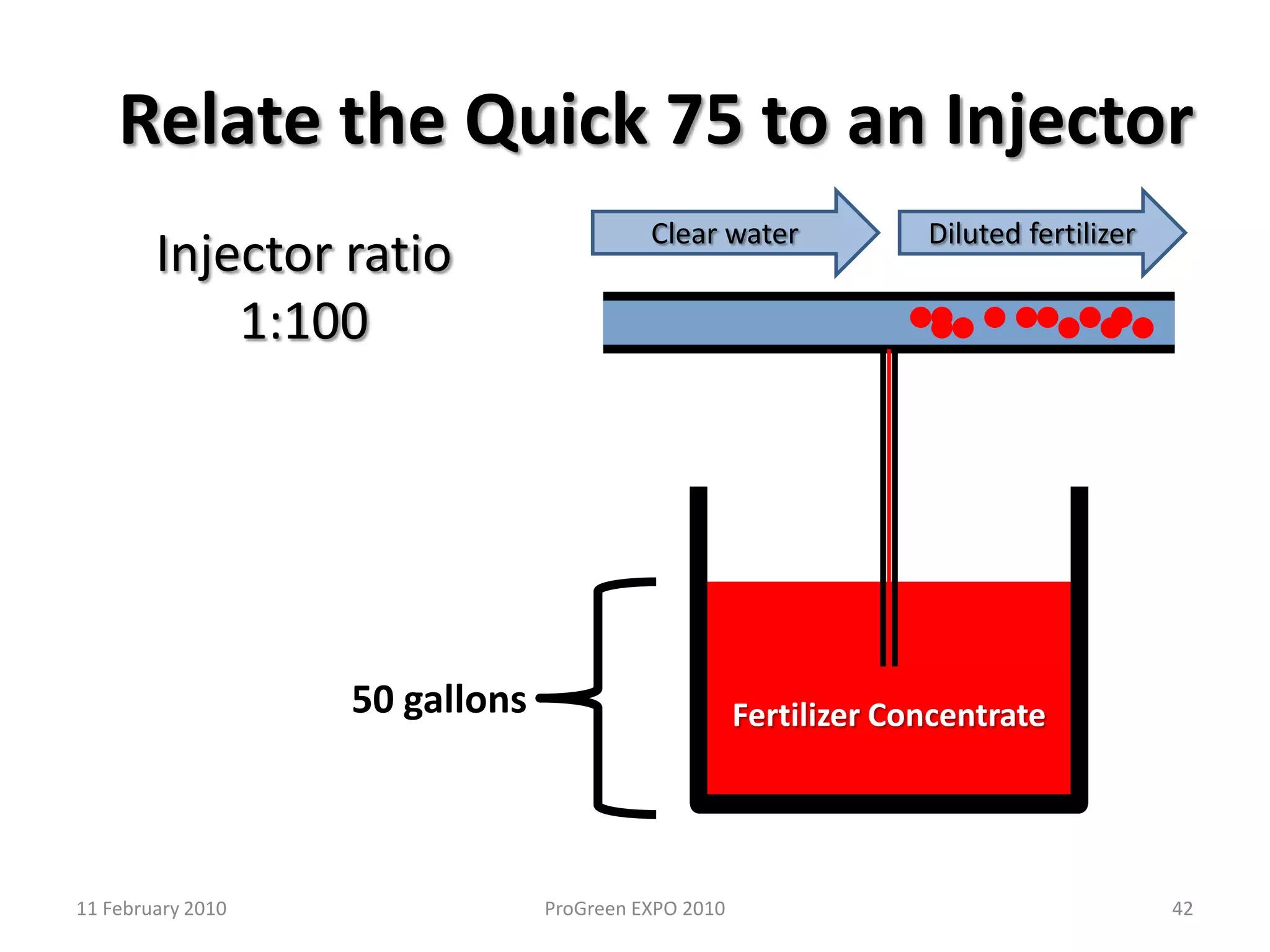
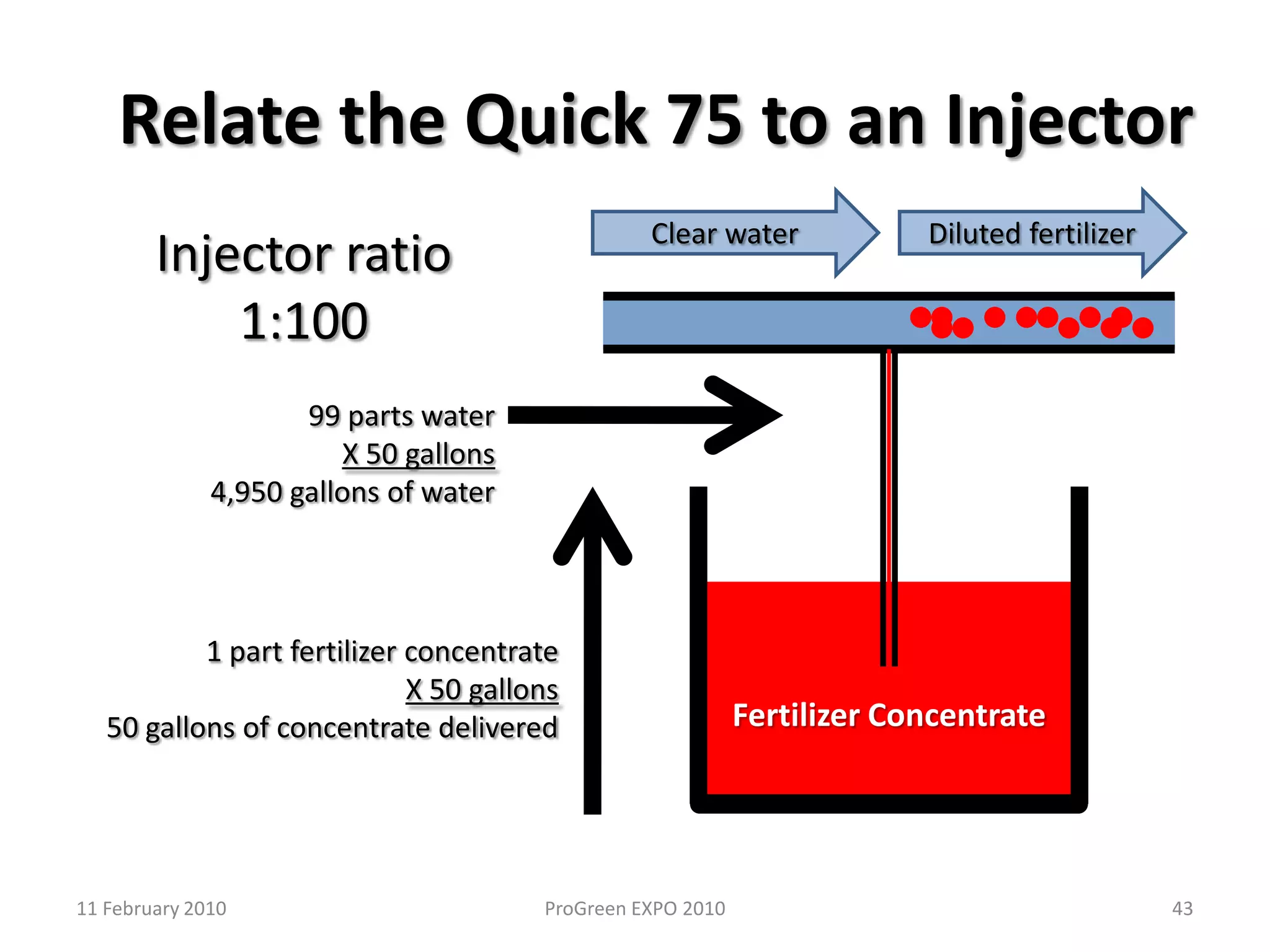
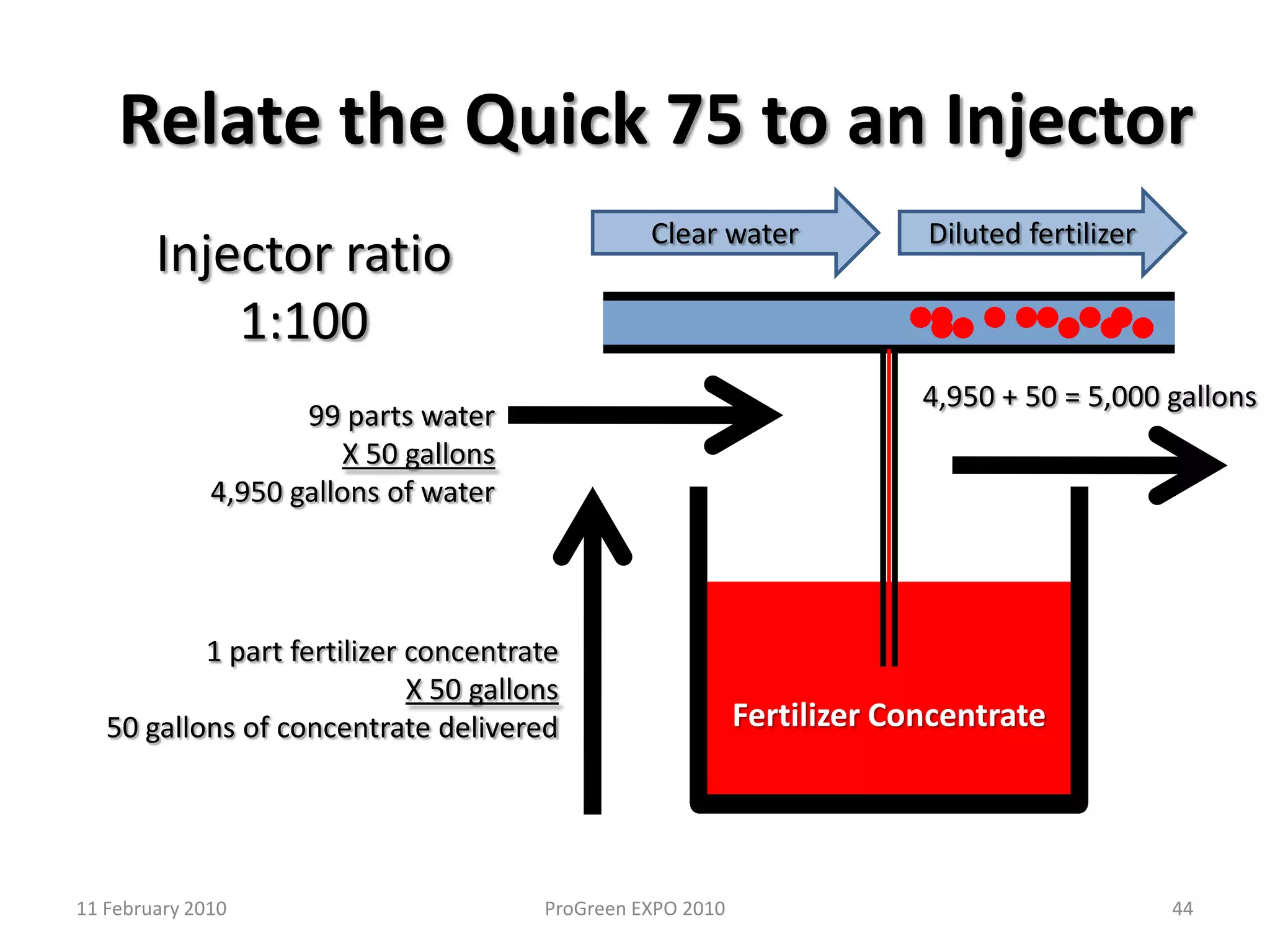
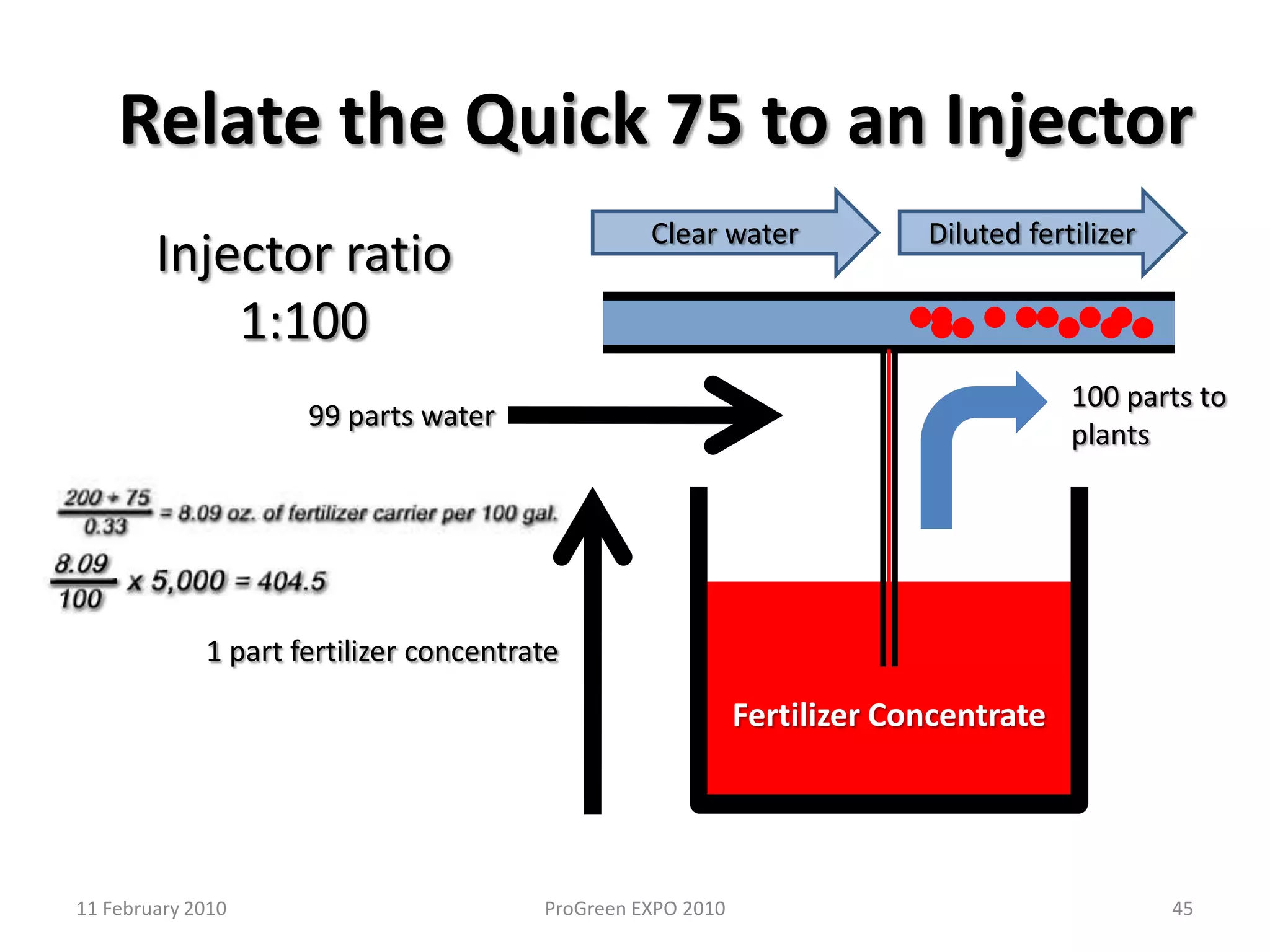
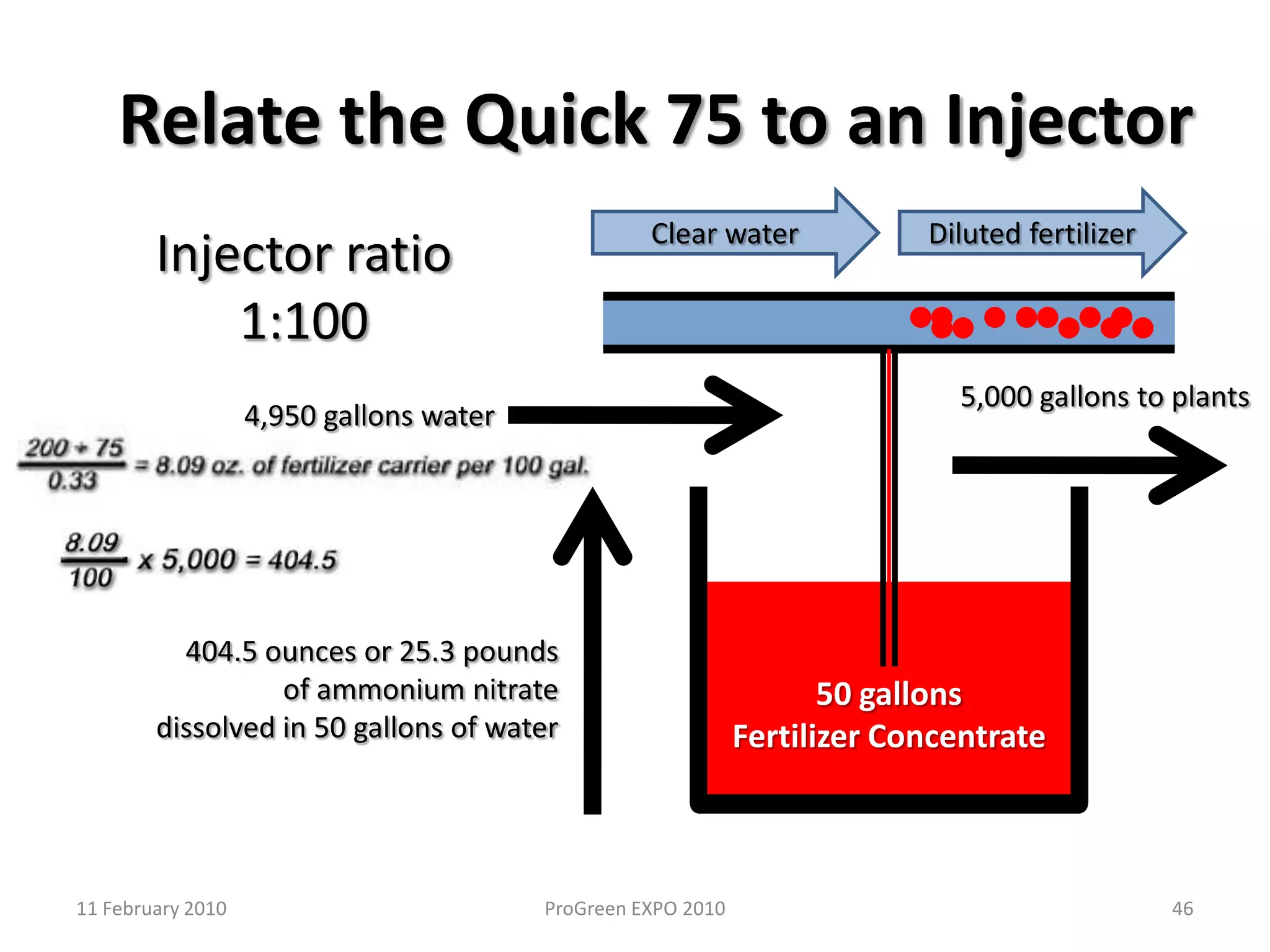
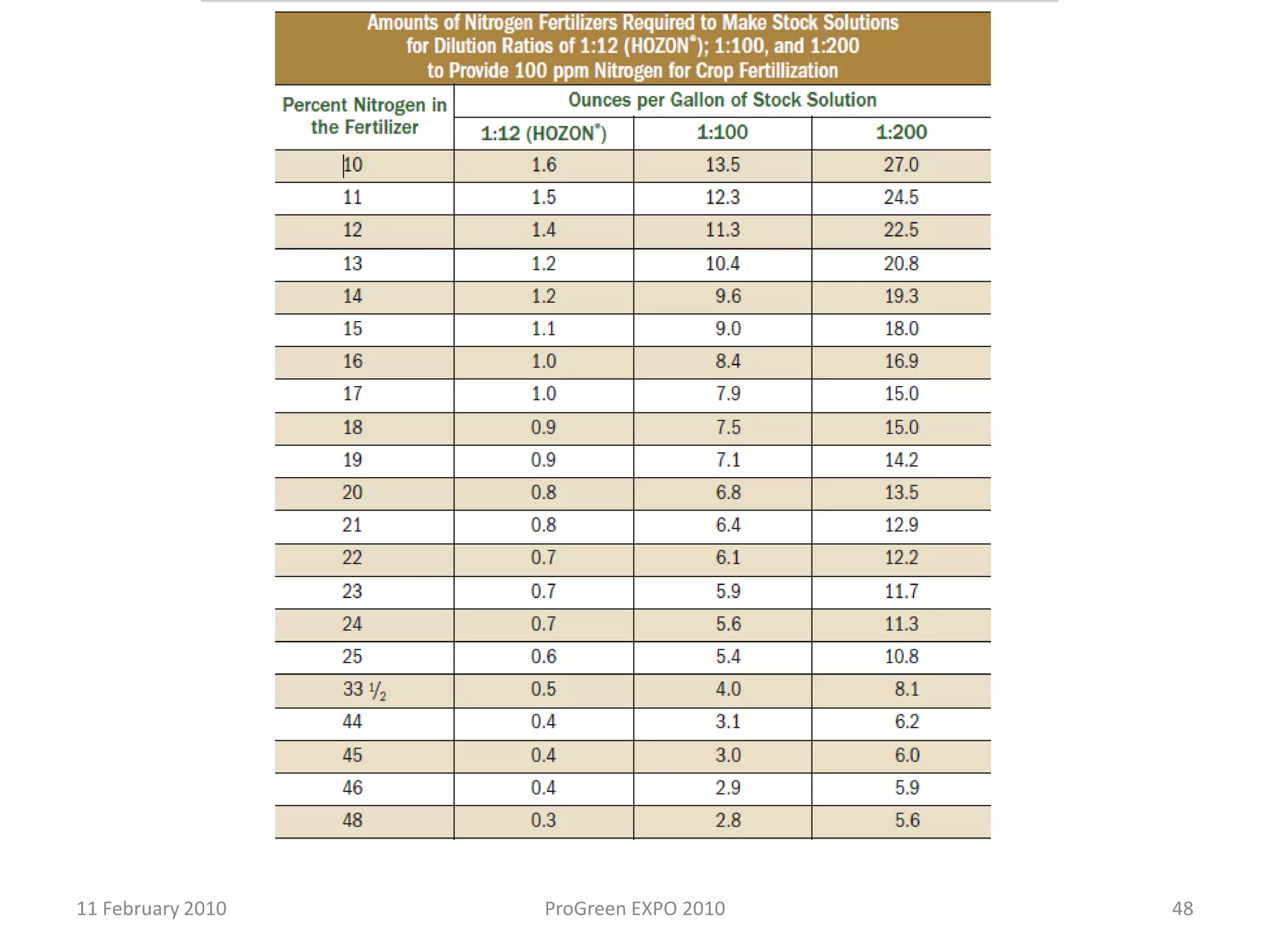
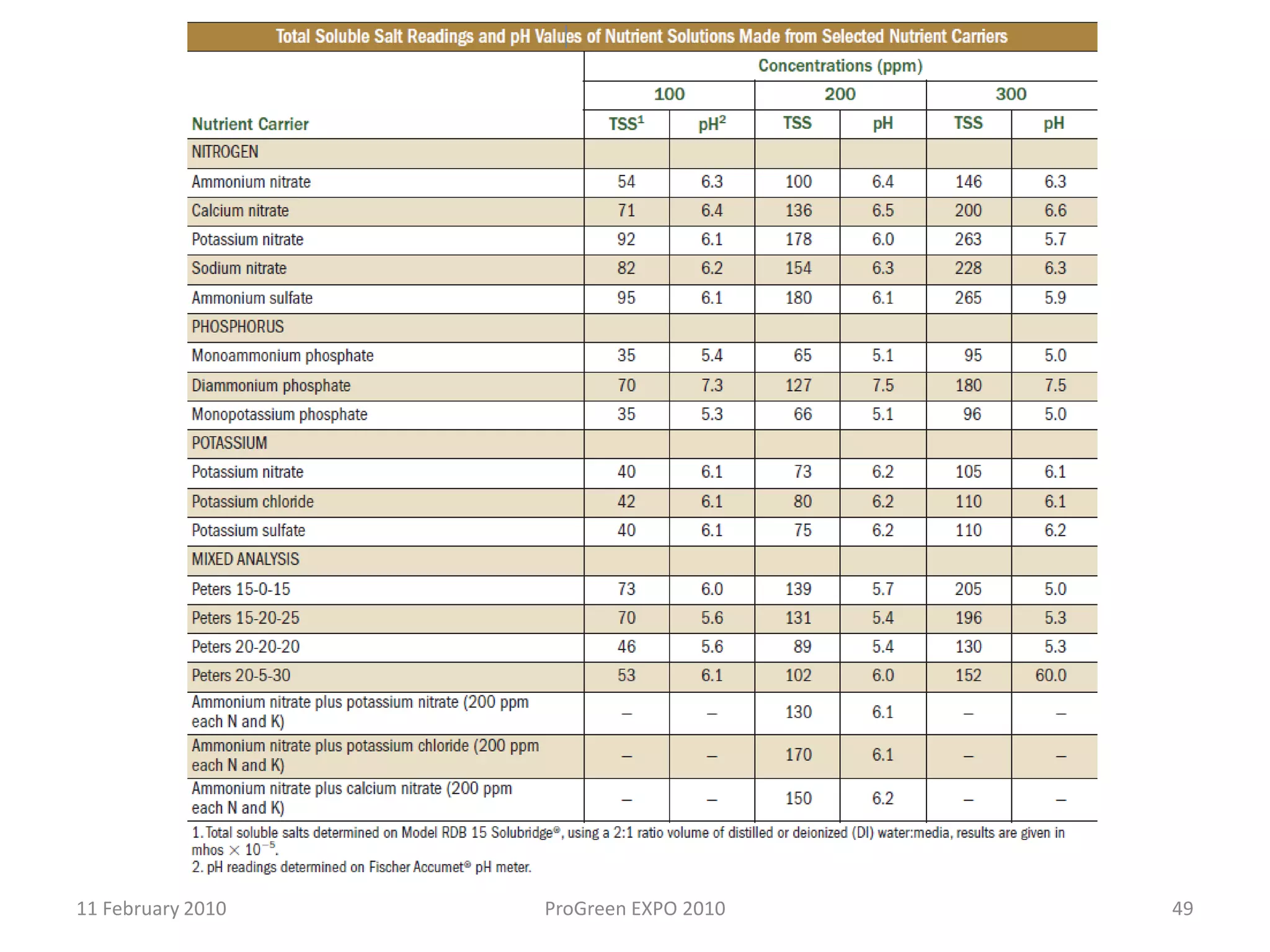
The document discusses how fertilizer injectors work to dilute concentrated fertilizer solutions. It explains that injectors introduce a small amount of concentrate from a stock tank into a water line. Different types of injectors include venturi and positive displacement injectors. Venturi injectors have no moving parts while positive displacement injectors can adjust ratios. The document provides examples of calculating fertilizer ratios and parts per million concentrations.