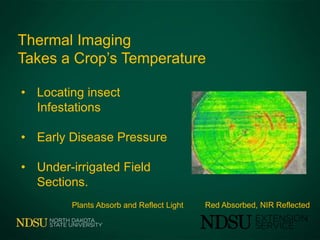
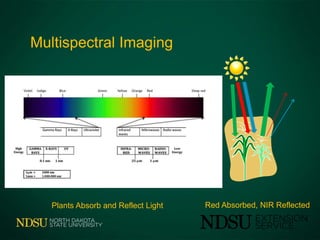
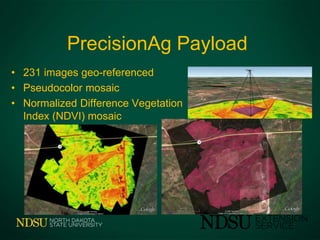
The document discusses the use of unmanned aircraft systems (UAS) in agriculture. UAS, also known as drones, are small, remote-controlled or autonomous aircraft that can be equipped with cameras and sensors. The FAA has designated several test sites across the U.S. to help develop regulations and standards for integrating UAS into national airspace safely. Current UAS applications in agriculture include monitoring and imaging crops, livestock, and rangeland. However, privacy and regulation issues still need to be addressed as UAS usage expands.