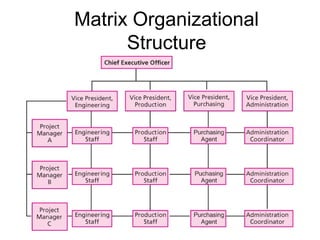
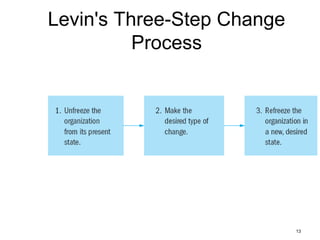
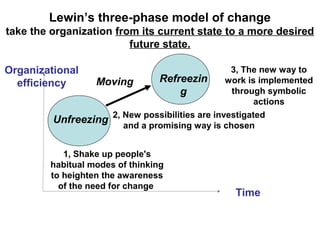
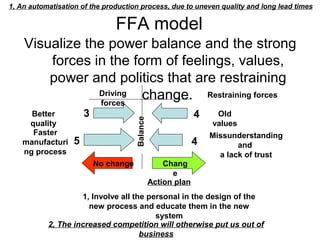
This document discusses types of organizational power and structure. It describes five types of power: legitimate, coercive, reward, expert, and referent power. It also discusses matrix and boundaryless organizational structures. The matrix structure combines functional and product departmentalization. Boundaryless organizations eliminate vertical boundaries through cross-functional teams and lateral job rotations. Virtual organizations are highly centralized and outsource major functions. Finally, it summarizes Lewin's three-step change model of unfreezing, changing, and refreezing an organization.