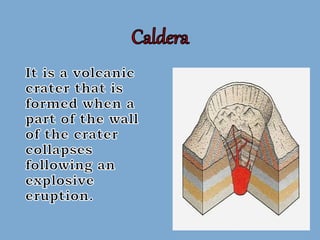
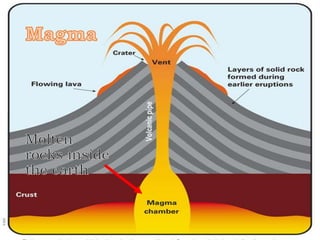
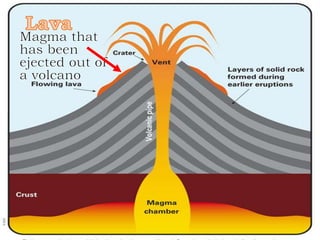
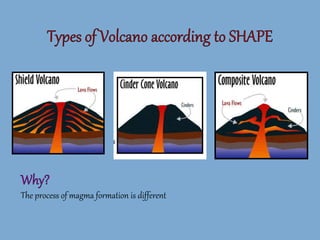
The document discusses the four main types of volcanoes: shield volcanoes like Mauna Loa which are broad dome shaped structures formed by fluid lava flows; cinder cone volcanoes like Paricutin which are steep sloped and formed from ejected rock and ash fragments; stratovolcanoes which are large cone shaped volcanoes formed by layers of hardened lava and ash like Mount Fuji; and calderas which are cauldron shaped volcanic depressions formed by collapse after a very large eruption. It also describes pyroclastic flows, tephra, and phreatic eruptions.