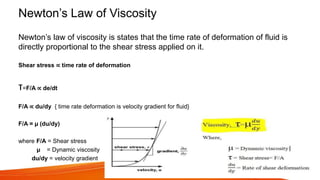
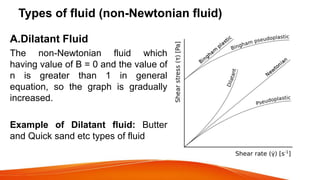
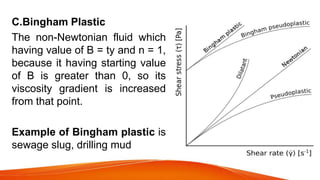
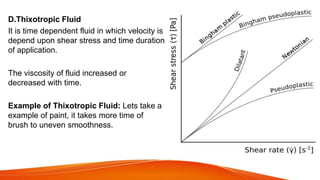
This document defines different types of fluids and their properties. It begins by defining an ideal fluid and real fluid, then discusses Newton's law of viscosity. Newtonian fluids obey this law, having constant viscosity, while non-Newtonian fluids do not. Four types of non-Newtonian fluids are described: dilatant fluids increase in viscosity with stress; pseudoplastic fluids decrease in viscosity with stress; Bingham plastics have a yield stress; and thixotropic fluids' viscosity depends on time under stress. Examples are given for each fluid type.