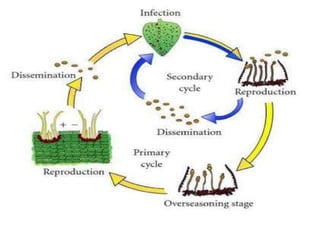
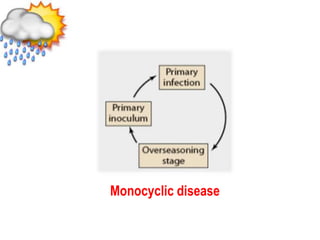
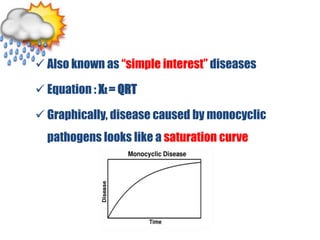
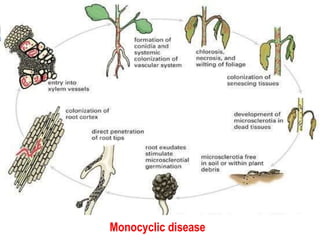
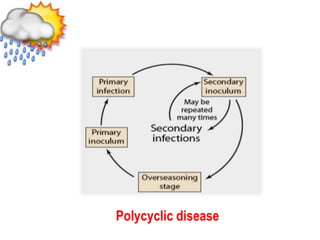
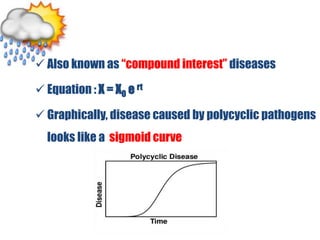
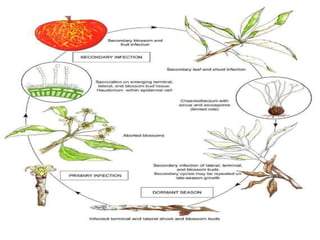
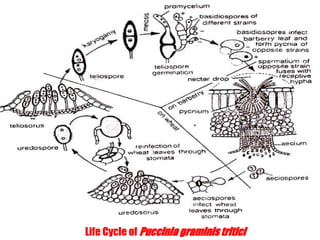
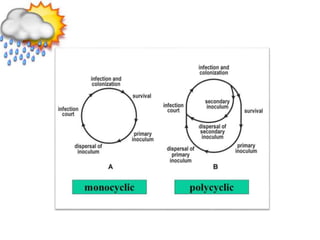
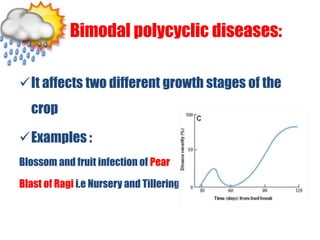
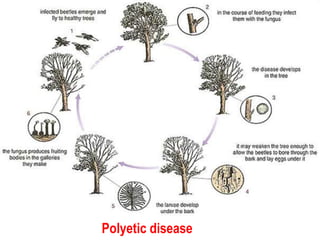
This document discusses types of plant disease epidemics. It defines an epidemic as a disease occurring year after year at a moderate to severe level or an increase in disease within a population. Epidemiology is the study of disease in populations. The main types of epidemics discussed are monocyclic, polycyclic, and polyetic. Monocyclic diseases have one infection cycle per season, while polycyclic diseases can have multiple cycles from secondary infections. Polyetic diseases take multiple years to produce inoculum and may not cause new infections every year. Examples of each type are provided.