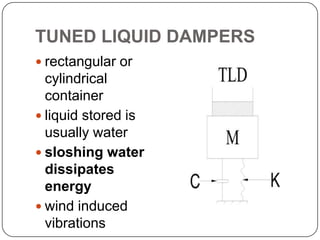
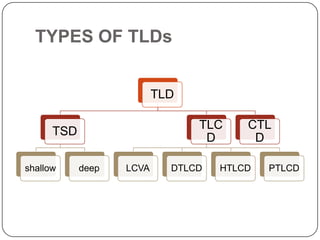
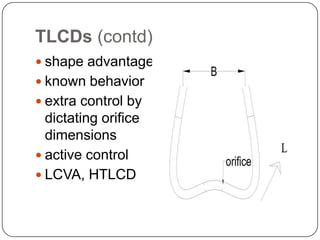
This document discusses different methods for providing lateral load resistance in structures, including structural modifications, aerodynamic modifications, base isolation, and damping sources. It focuses on tuned liquid dampers, which use sloshing liquid in a container to dissipate vibrational energy. Tuned liquid dampers can be tuned to the natural frequency of a structure by adjusting their dimensions and work through sloshing of liquid in rectangular or cylindrical containers, usually filled with water. They provide effective damping against wind and earthquake vibrations at low cost and maintenance.