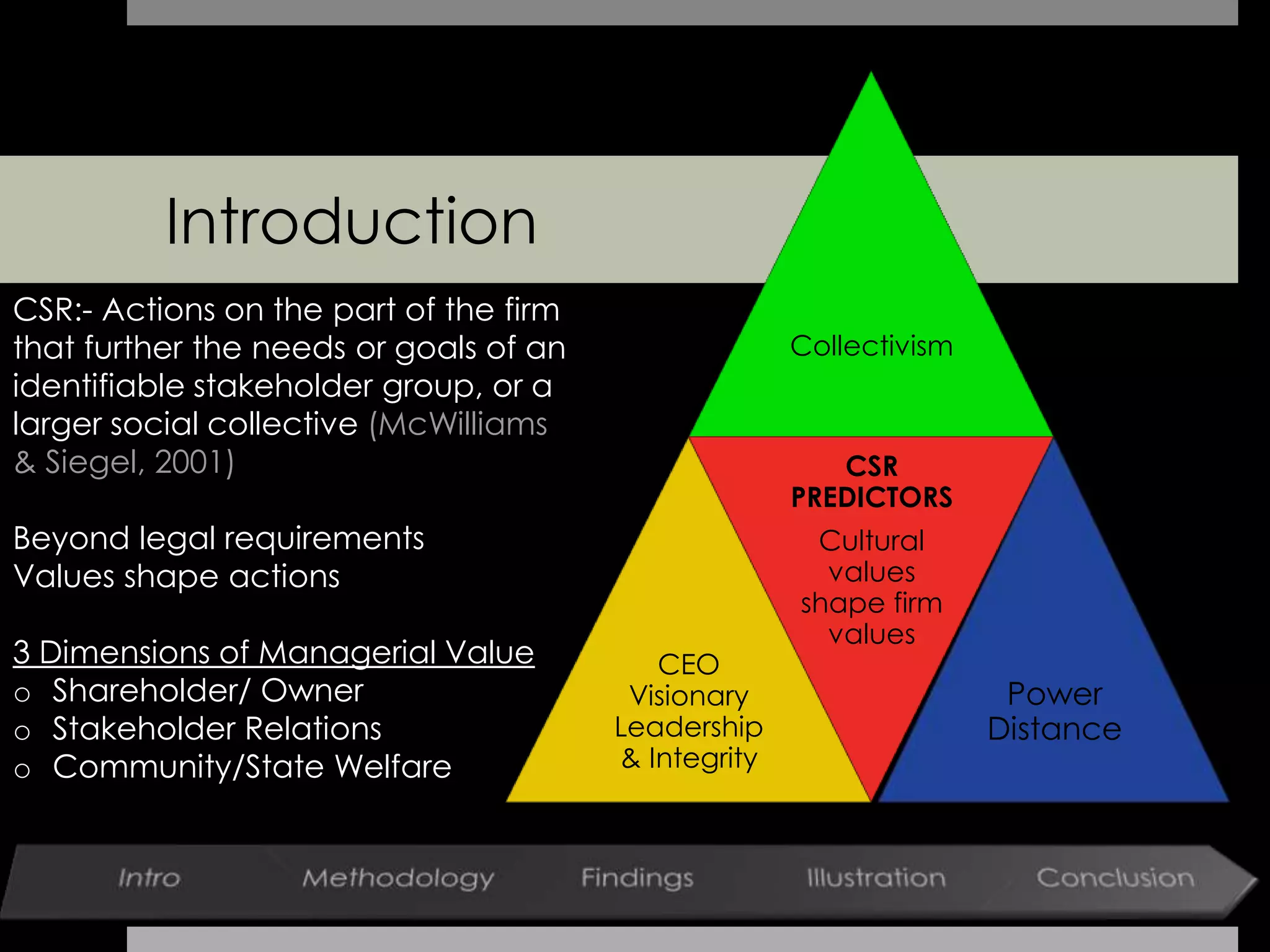
This document summarizes a study examining the relationship between cultural factors and corporate social responsibility (CSR). The study analyzed data from over 40 firms in 15 countries. It found that CSR is a multidimensional concept consisting of concern for shareholders, stakeholders, and community. Cultural values like collectivism and power distance influenced managers' priorities among these three CSR dimensions. Specifically, collectivist cultures prioritized more aspects of CSR, while high power distance cultures valued CSR less. Additionally, visionary leadership within organizations was found to positively influence managers' views on shareholder and stakeholder CSR. The study concluded that cultural, demographic, and leadership factors are important determinants of how managers approach CSR internationally.