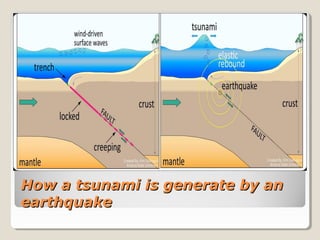
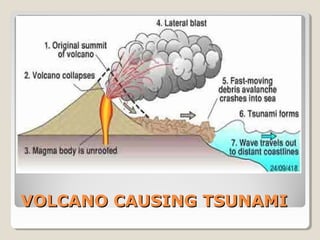
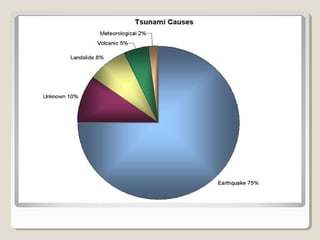
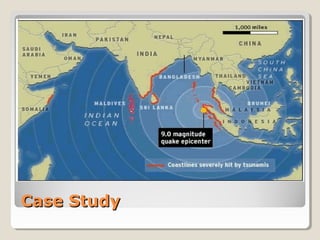
Tsunamis are a series of huge waves caused by undersea disturbances like earthquakes or volcanic eruptions. They are generated by the sudden displacement of water and can cause devastating damage when they reach land. The 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami was triggered by a massive 9.0 magnitude earthquake off the coast of Sumatra, Indonesia. It affected over 12 countries across South and Southeast Asia, causing over 160,000 deaths and widespread destruction of property. The tsunami highlighted the massive scale of relief efforts needed in the aftermath of such a disaster.