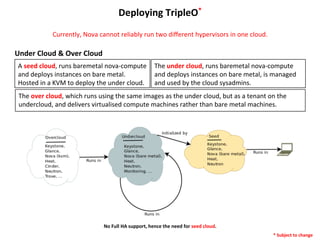
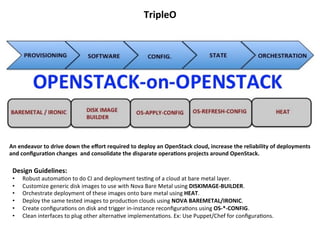
TripleO is an OpenStack project that aims to deploy OpenStack using OpenStack. It provides automation to deploy and test OpenStack clouds at the bare metal layer using tools like Heat, Diskimage-Builder, and Ironic. TripleO designs robust gold images to deploy consistently tested and reliable OpenStack environments, reducing costs of operations and maintenance through continuous integration and deployment techniques. By deploying OpenStack on bare metal with tools like Ironic, TripleO can reliably install and upgrade OpenStack clouds.








![Sample
HOT
parameters:!
InstanceType:!
type: string!
description: Instance type to create!
default: m1.small!
hidden: False!
constraints:!
allowed_values {m1.tiny, m1.small, m1.large}!
resources:!
MyInstance:!
type: OS::Nova::Server!
properties:!
KeyName: { get_param: KeyName }!
ImageId: { get_param: ImageId }!
InstanceType: { get_param: InstanceType }!
outputs:!
InstanceIP:!
description: The IP address of the instance!
value: {get_attr: [MyInstance, PublicIP] }!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/openstacktripleo-131203111059-phpapp01/85/TripleO-16-320.jpg)