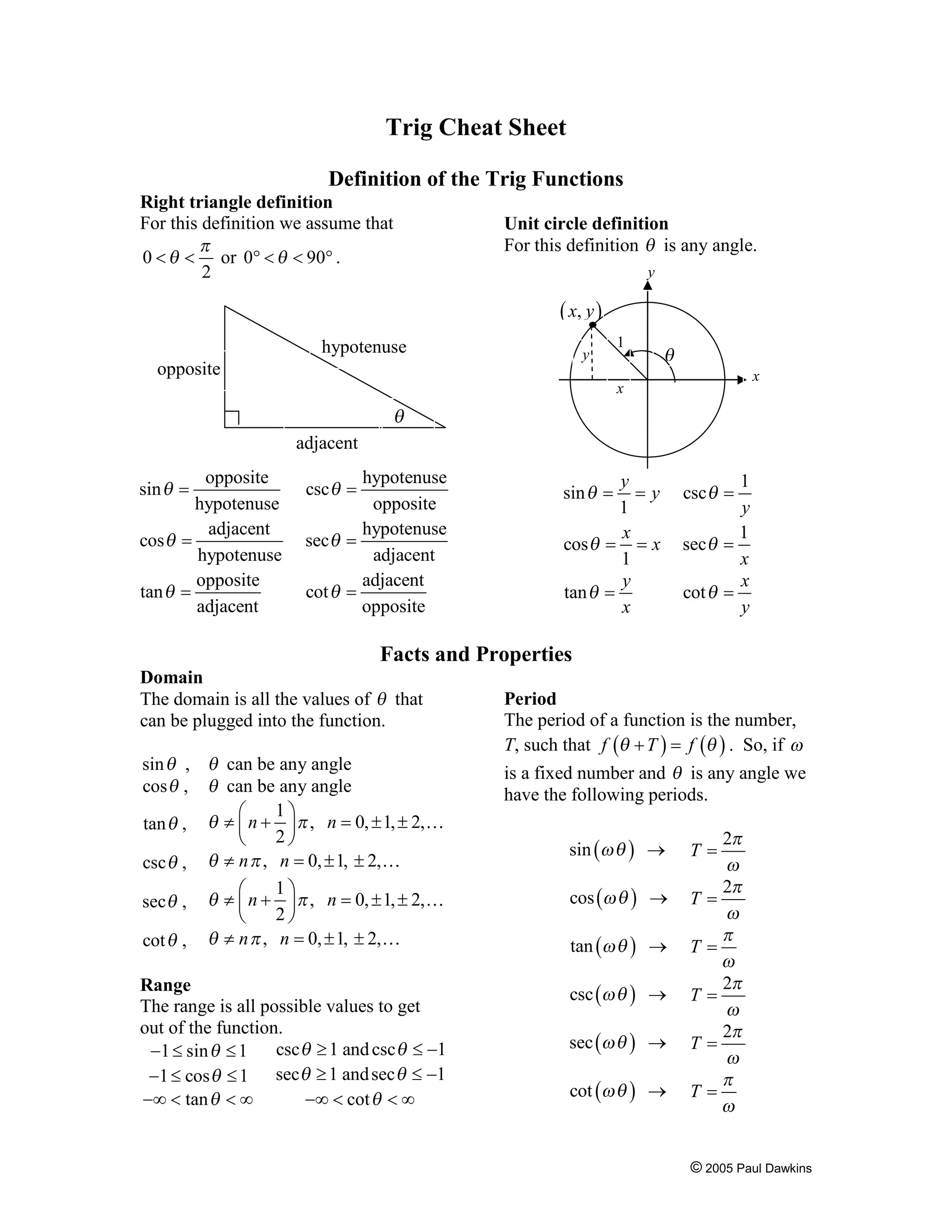
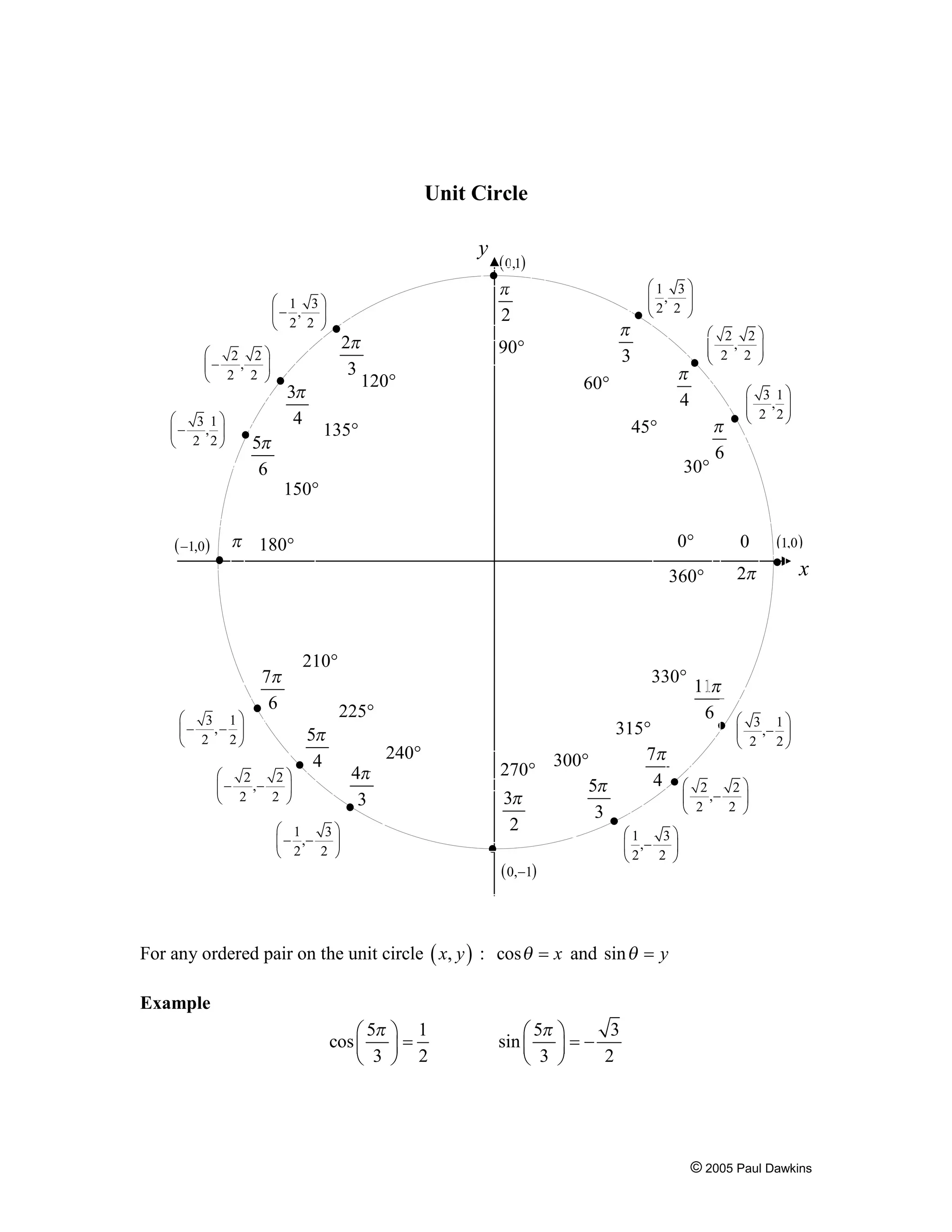
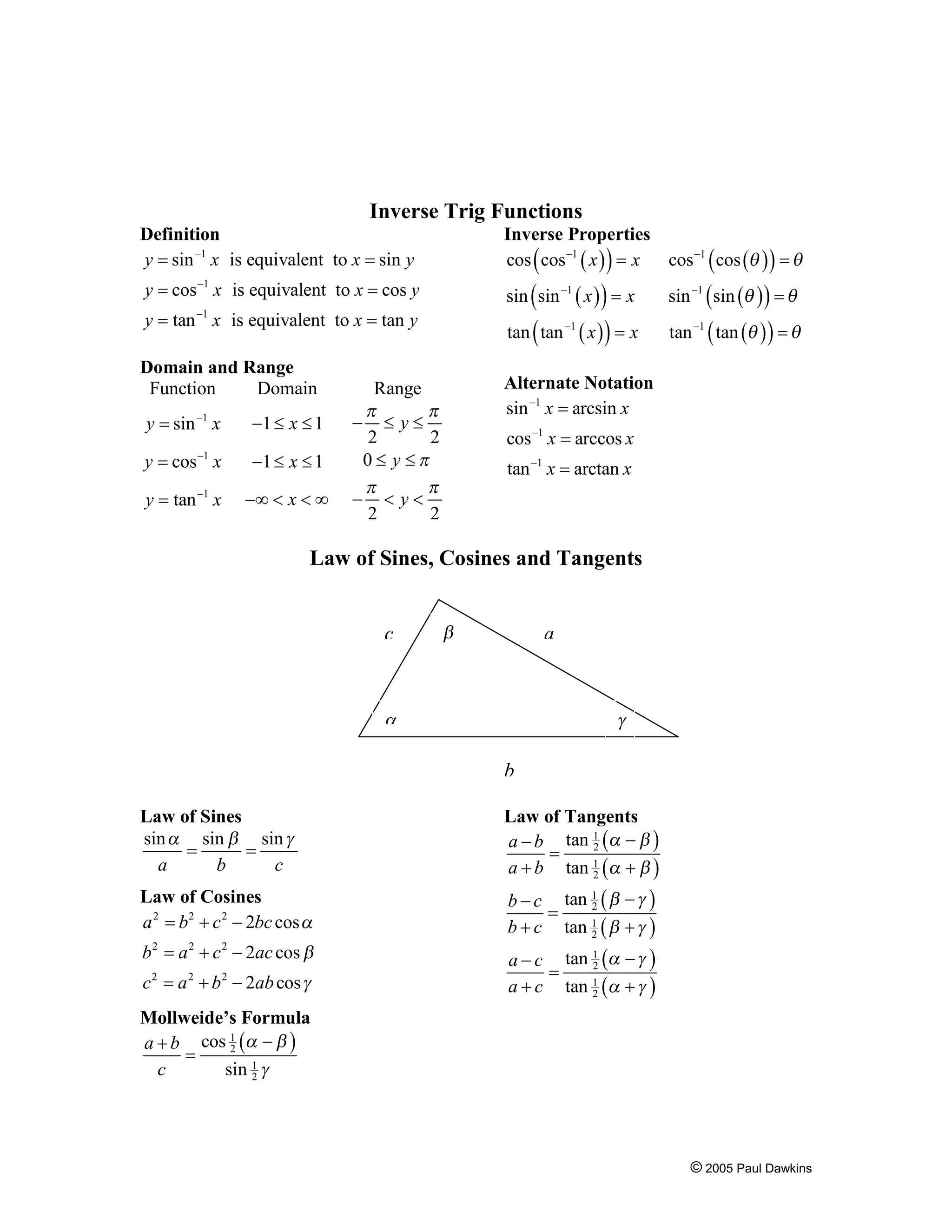
This document provides definitions and formulas for trigonometric functions. It defines the trig functions using right triangles and the unit circle. It lists important properties like domain, range, period, and formulas for sums, differences, inverses, and the laws of sines, cosines, and tangents.