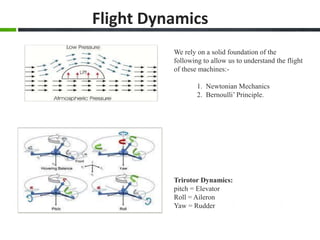
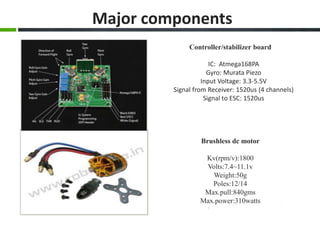
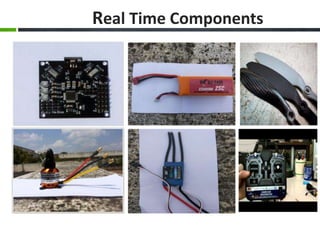
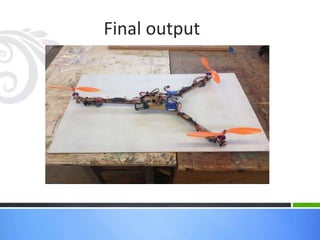
This document provides an overview of the design and fabrication of a tricopter drone. It describes the motivation to build the tricopter with a low budget and light weight. The key components of the tricopter include three brushless motors, an Atmega168PA controller board, receiver, batteries, and a glass fiber frame. Challenges in the design included balancing the tricopter and integrating the gyroscope and accelerometer. Testing involved mechanical design, propeller selection, electrical connections, and programming the controller board. The conclusion discusses potential applications in military, industrial, and commercial uses if further funding and experimental analysis are conducted.