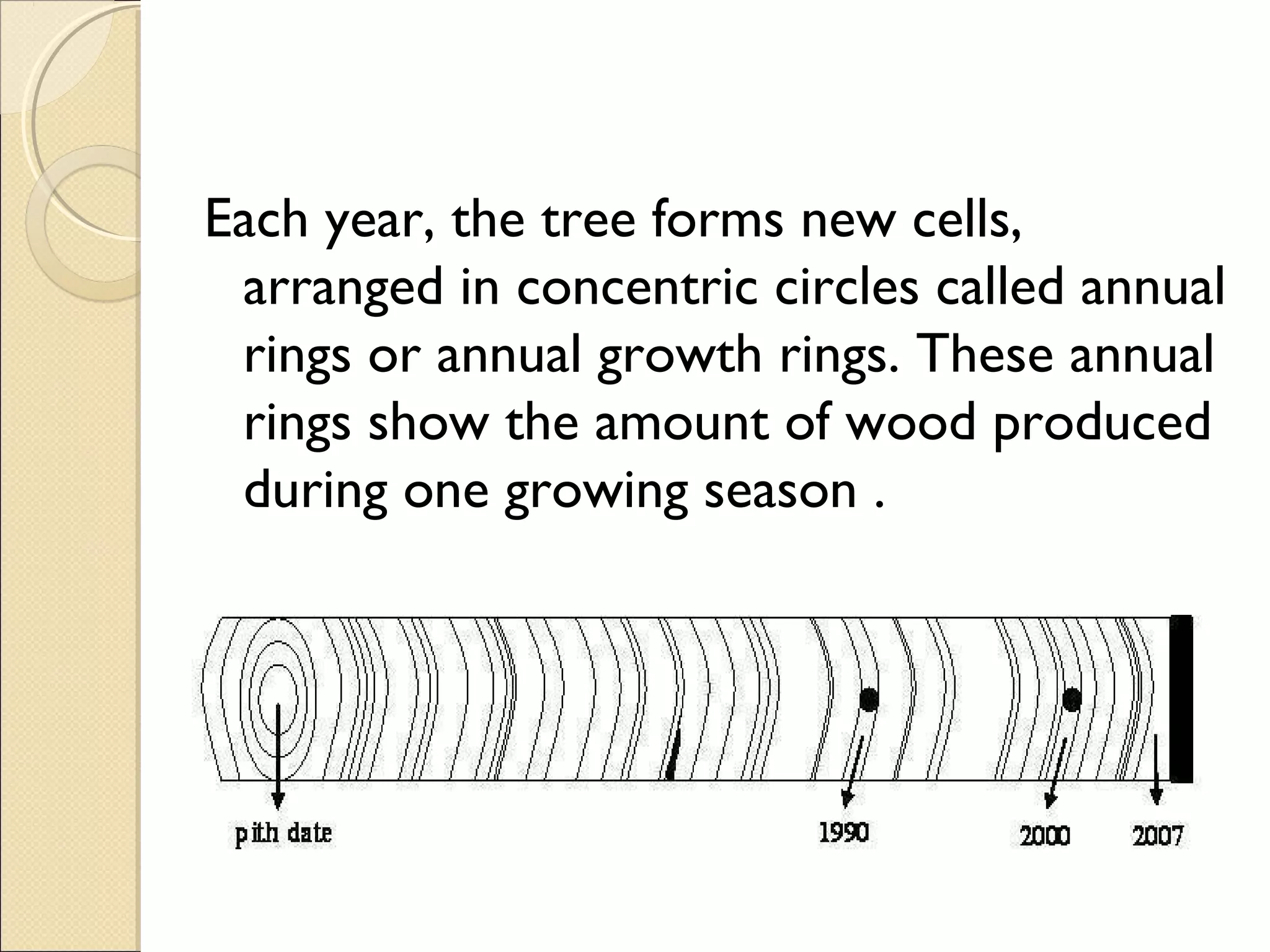
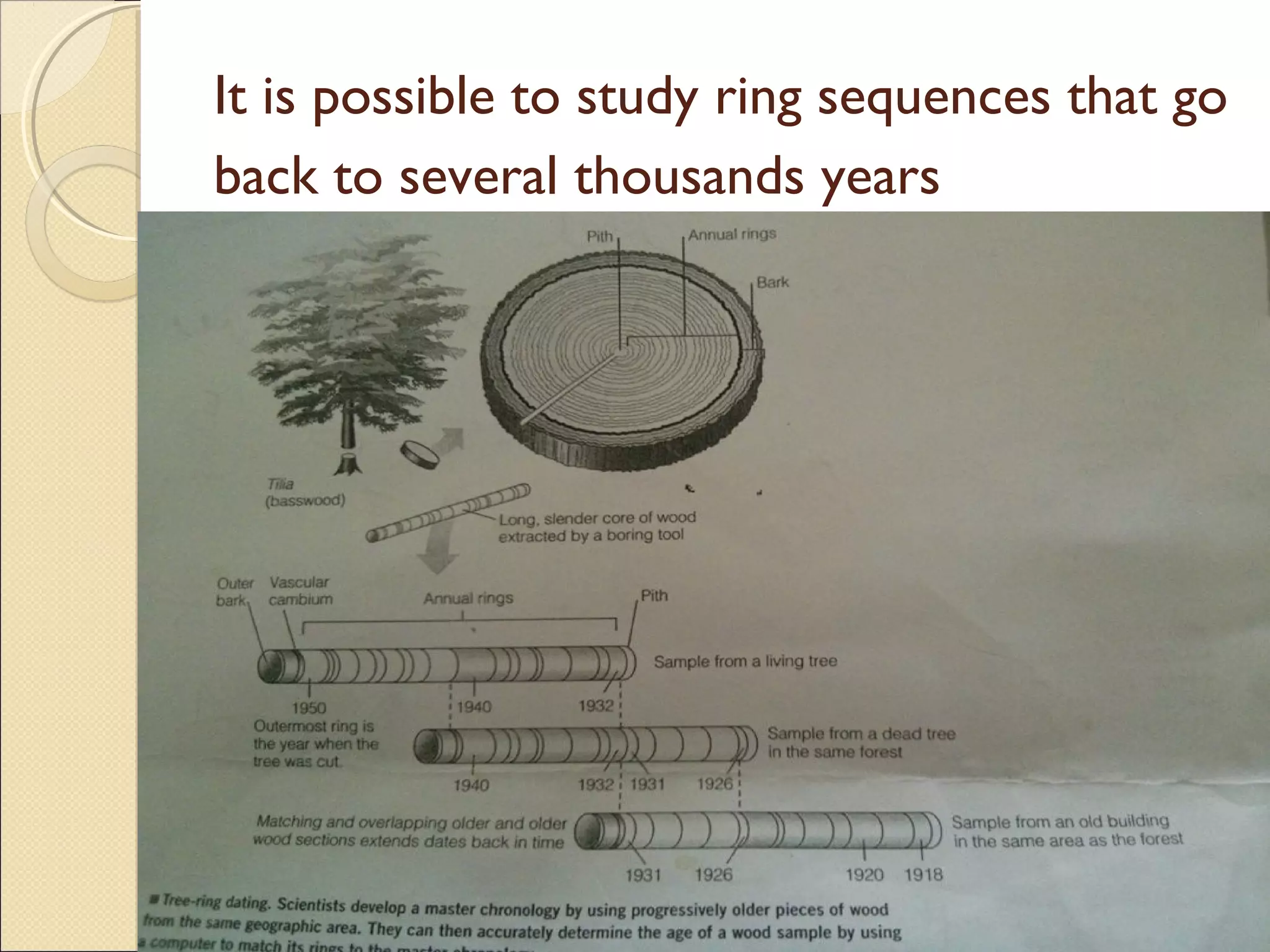
Tree ring analysis involves examining the growth rings of trees. Each year a tree forms a new growth ring, with wider rings indicating better growing conditions and narrower rings indicating drought or other environmental stressors. Scientists can use patterns in tree ring widths to date samples very precisely by year. Dendrochronology, the scientific study of tree ring patterns, helps researchers understand past climates and date archaeological sites by matching ring patterns among trees.