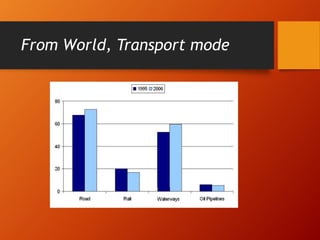
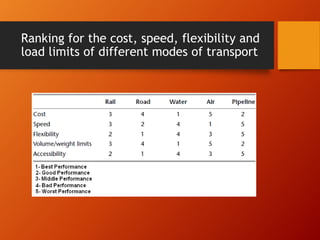
This document discusses different modes of transport and factors to consider when choosing a mode. The five main modes of transport are rail, road, air, water, and pipeline. Each has advantages and disadvantages related to cost, speed, flexibility, and load capacity. Choosing the optimal mode depends on characteristics of the goods like nature, volume, and distance as well as other factors like value, timeliness, reliability, and security.