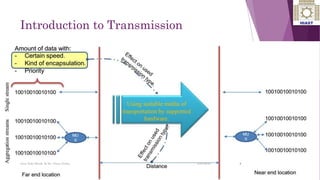
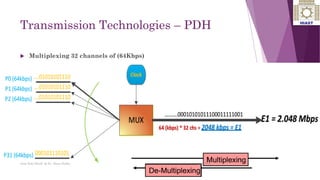
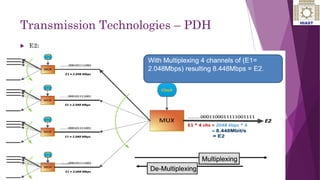
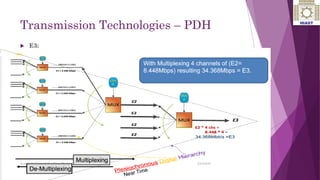
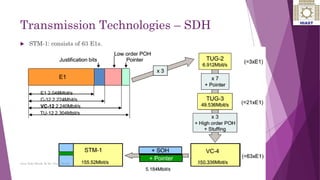
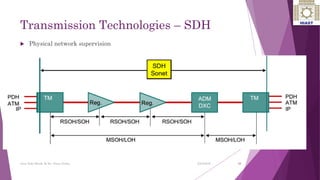
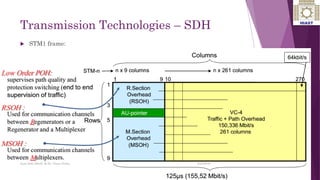
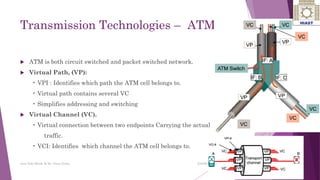
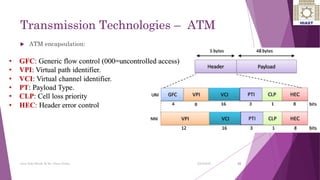
The document discusses various digital transmission technologies including PDH, SDH, and ATM. PDH uses time division multiplexing to transmit multiple digital signals over the same channel. It utilizes standards like E1, E2, E3. SDH was developed to replace PDH and allows synchronous transmission of multiple digital signals. It uses standards like STM-1, STM-4, STM-16. ATM encodes data into fixed size cells and can provide both circuit switched and packet switched networks using virtual paths and channels. Each technology has advantages like being connection oriented but also limitations like the entire path being reserved.