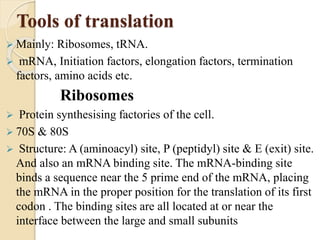
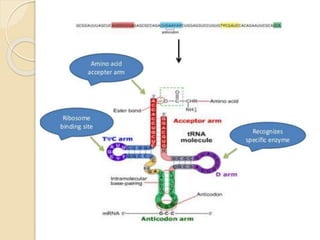
Translation in prokaryotes involves three main stages - initiation, elongation, and termination. During initiation, the small ribosomal subunit binds to mRNA and forms initiation complexes. In elongation, amino acids are linked together into a polypeptide chain as tRNAs bring successive amino acids to the ribosome. Termination occurs when a stop codon binds, causing release of the complete polypeptide. Prokaryotes regulate translation through ribosome dimerization and other factors that block initiation when nutrients are limited.