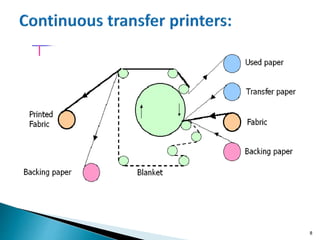
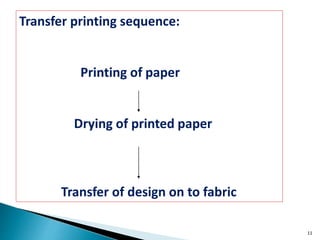
Transfer printing provides a 3-4% share of fabric printing but over 25% of garment printing. It involves printing designs onto paper using inkjet or other printing methods, then transferring the design to fabrics like polyester using heat presses. The key advantages are its ability to provide sharp images at a lower cost than embroidery, with short setup times compared to screen printing. Common applications include garment labels, banners, and home furnishings. The document outlines the history and development of transfer printing, factors that influence the process, types of machines used, and advantages and limitations.