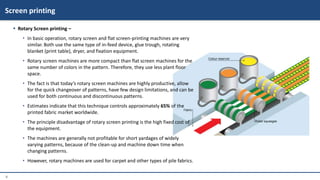
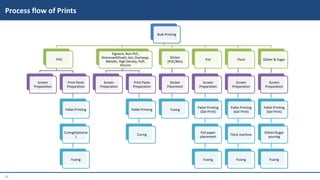
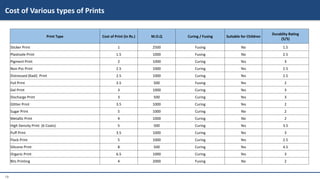
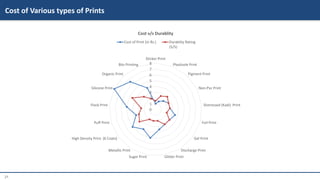
This document provides information on various garment printing methods and their costs. It discusses traditional methods like block printing and screen printing as well as digital methods like direct-to-garment (DTG) printing and sublimation printing. Specific printing techniques are outlined, such as plastisol, discharge, and foil printing. Production processes, suitable fabrics, costs per print, and minimum order quantities are compared for each method. In conclusion, the document serves as a guide for selecting printing styles based on needs and budgets.