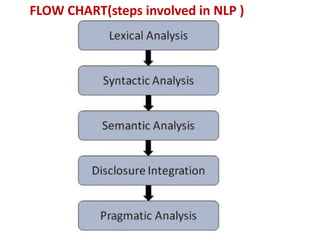
This document provides an overview of natural language processing (NLP). It discusses the key components of NLP, which are natural language understanding (NLU) and natural language generation (NLG). It also outlines the main steps involved in NLP, including lexical analysis, syntactical analysis, semantic analysis, disclosure integration, and pragmatic analysis. Finally, it lists some common applications of NLP such as natural language generation, question answering, speech recognition, and sentiment analysis.