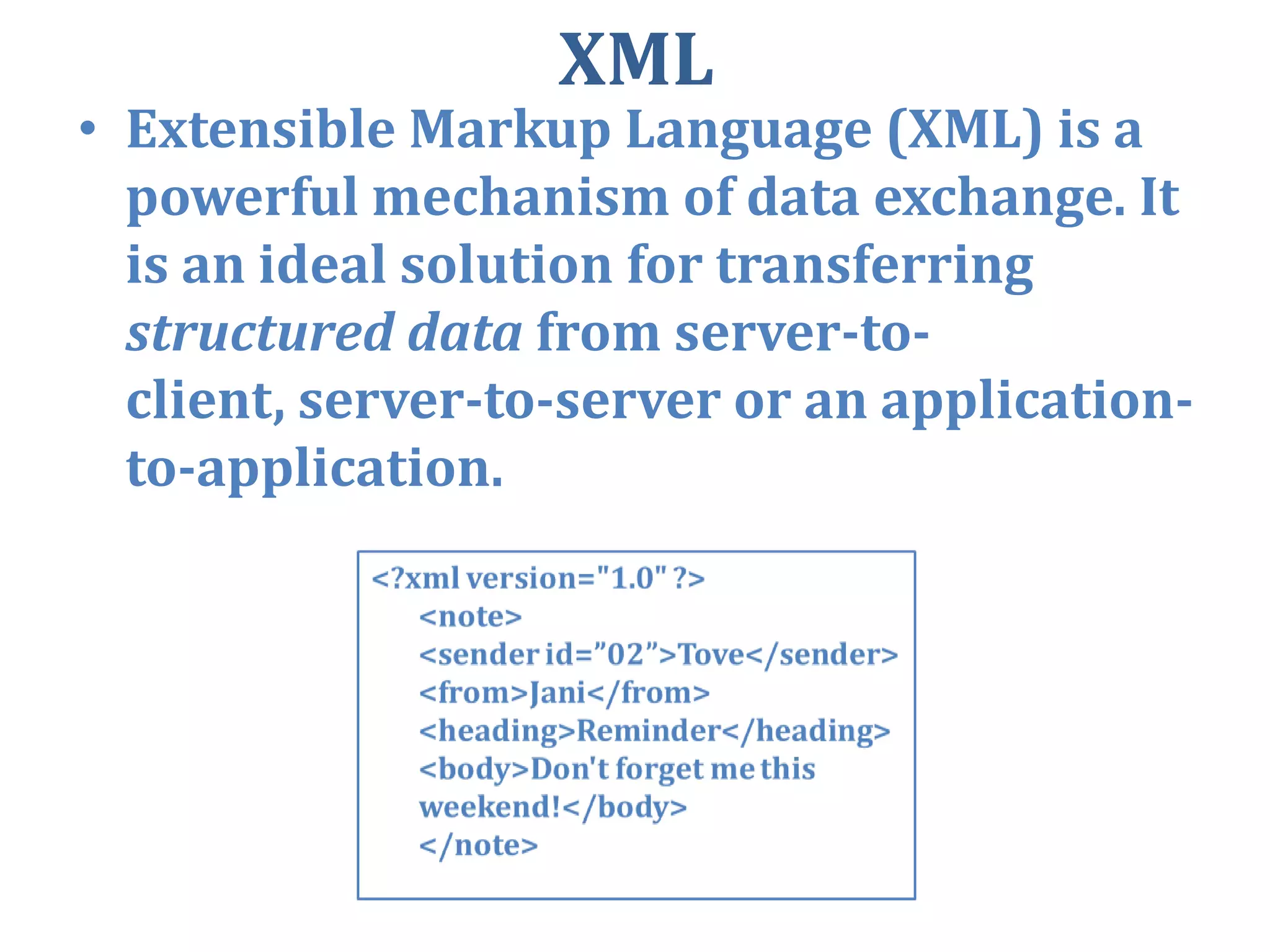
XML is a meta-markup language that specifies rules for creating markup languages. It is designed to carry data, not display data. XML uses tags to structure data, but does not have predefined tags - authors can define their own tags. XML documents must be "well-formed", following syntax rules like having one root element with matched opening and closing tags.